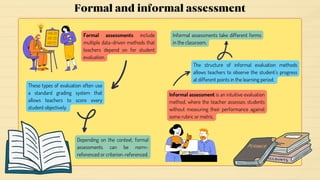
The document discusses various topics related to assessment and evaluation in language teaching. It defines assessment as a series of measures to determine attributes of individuals or groups. It also discusses different types of assessments like tests, measurements, and evaluations. Specifically, it describes formative and summative assessments, informal and formal assessments, achievement tests, diagnostic tests, placement tests, proficiency tests, and aptitude tests. It discusses principles of language assessment like reliability, practicality, validity, authenticity, and washback effect. Finally, it provides details on content-related validity, criterion-related validity, and construct-related validity.