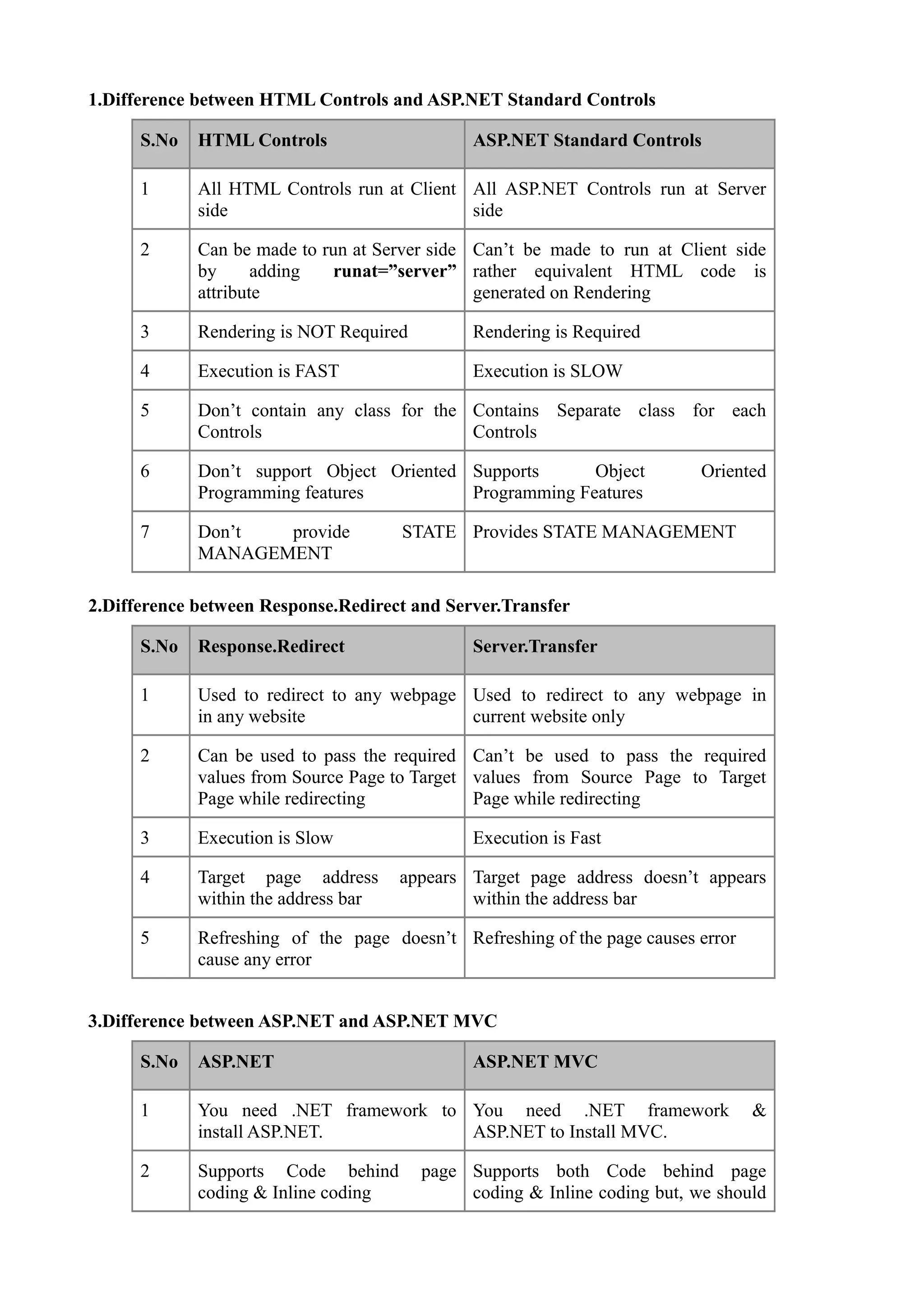
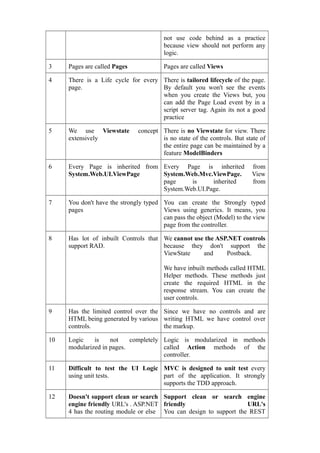
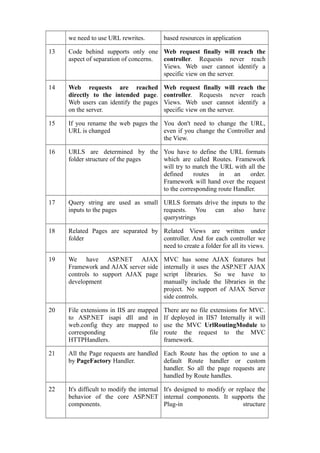
The document compares HTML controls and ASP.NET standard controls, Response.Redirect and Server.Transfer, and ASP.NET and ASP.NET MVC. For HTML vs ASP.NET controls, it notes that HTML controls run on the client side while ASP.NET controls run on the server side. For Response.Redirect vs Server.Transfer, it highlights that Response.Redirect can pass values between pages while Server.Transfer cannot. For ASP.NET vs ASP.NET MVC, key differences include MVC having a tailored page lifecycle, no viewstate, and stronger support for testing and clean URLs.