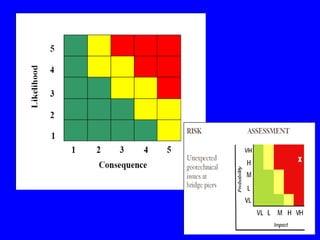
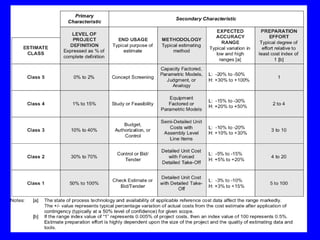
The document discusses various aspects of estimating and pricing construction contract risk. It provides examples of risk drivers in construction contracts related to scope, performance standards, changes, loss shifting, and schedule. It also discusses different approaches to pricing risk such as using risk premiums between 8-20% depending on market conditions. Effective risk management requires understanding different risk types and their impacts, and well prepared estimates can help document scope and risks to aid the project team.