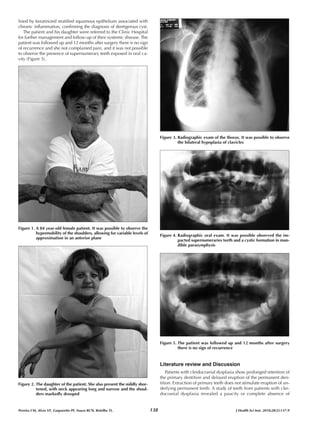
This case report describes an 84-year-old female patient with cleidocranial dysplasia who presented with a dentigerous cyst. Cleidocranial dysplasia is a skeletal and dental developmental disorder. On examination, the patient exhibited features of cleidocranial dysplasia including short stature, maxillary hypoplasia, impacted supernumerary teeth, and bilateral clavicle hypoplasia, which was confirmed on radiographs. The patient underwent surgery to remove the supernumerary teeth and excise the dentigerous cyst. Follow-up after 12 months found no recurrence. This case highlights the association between cleidocranial dysplasia and dentigerous cyst