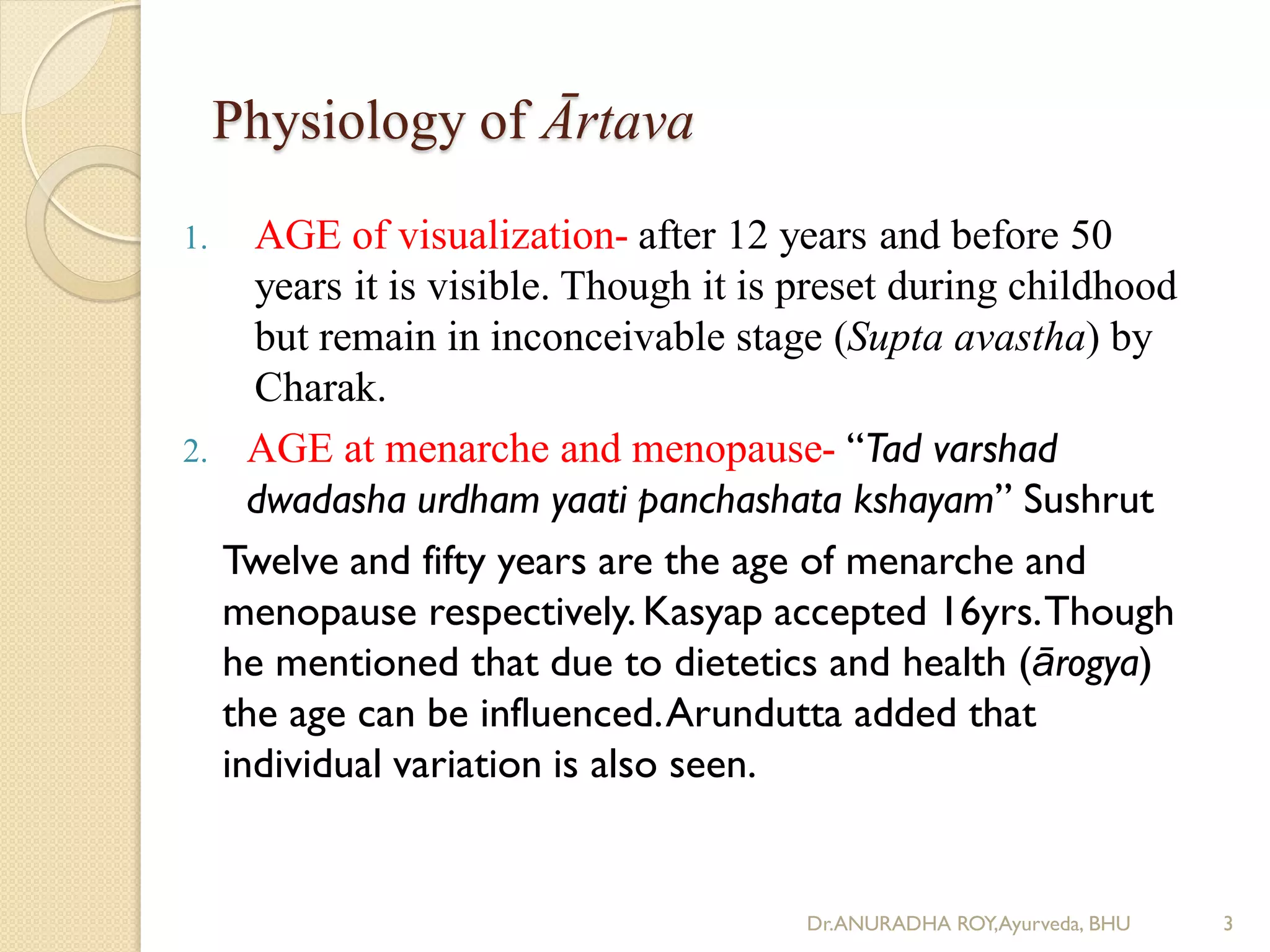
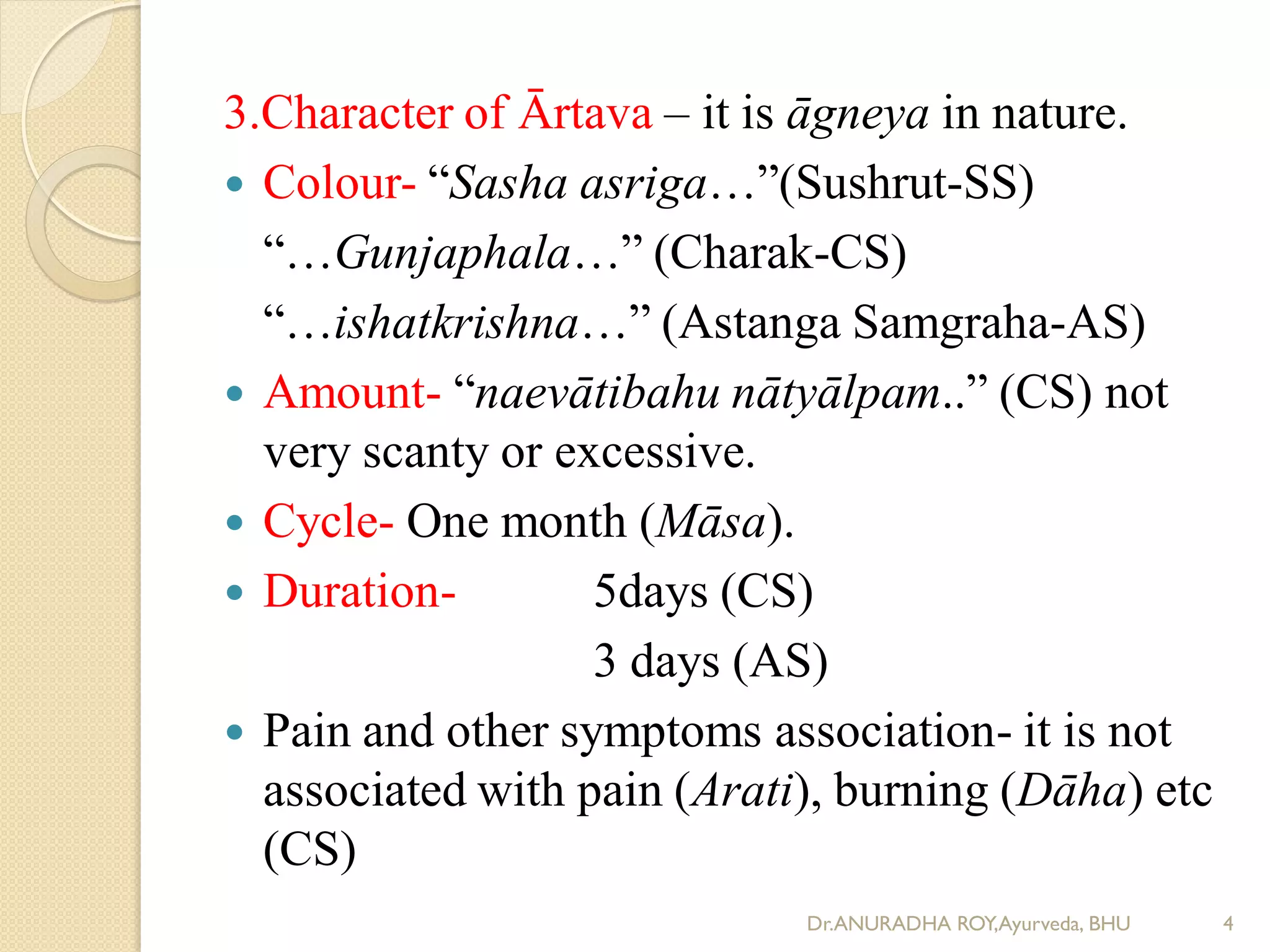
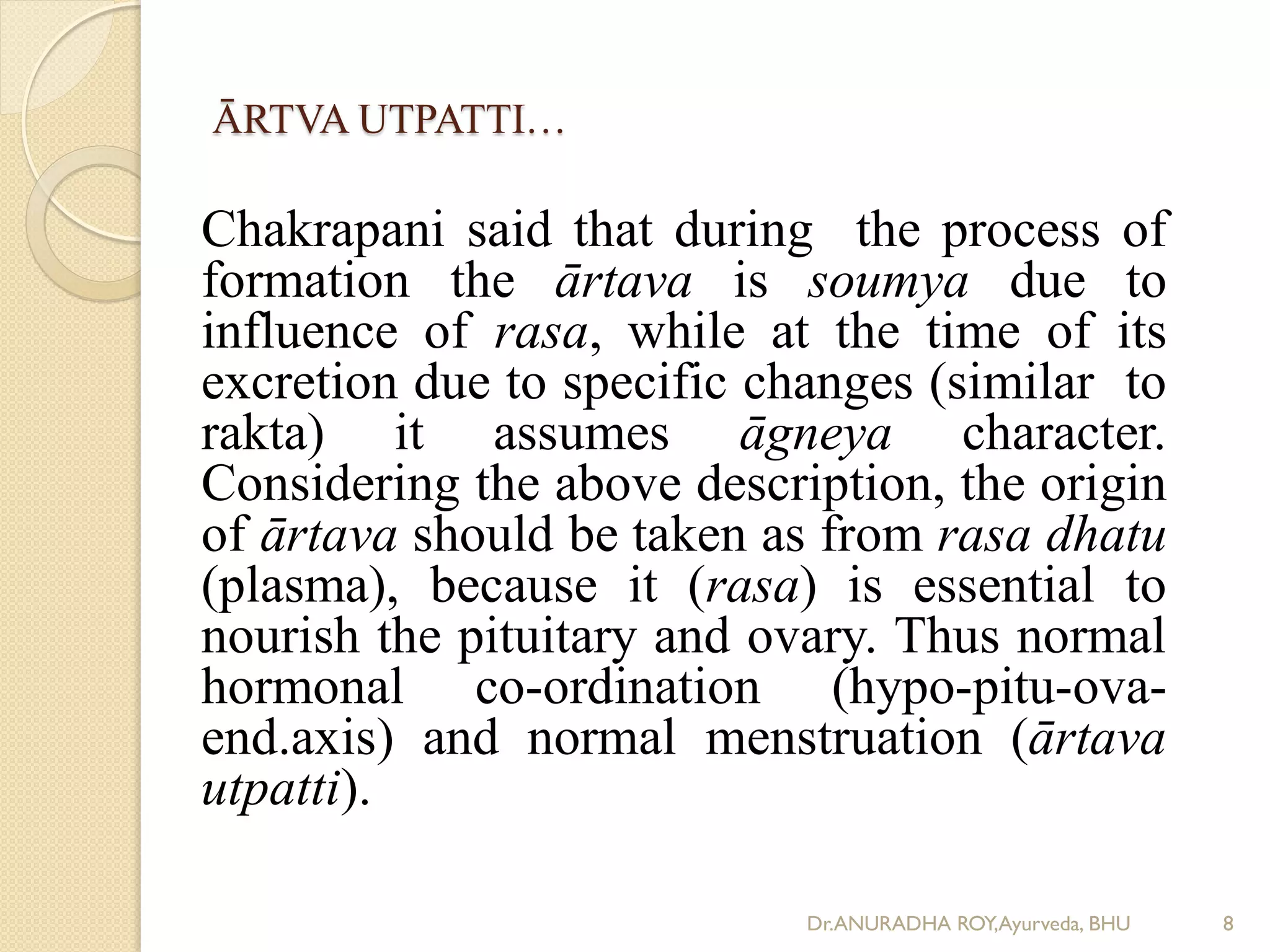
1) The document discusses the physiology of ārtava (menstruation) according to Ayurveda, including its meaning, age of onset and cessation, characteristics, function, and origin from rasa dhatu.
2) It describes the modern understanding of the hormonal menstrual cycle, including the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis and the three phases of the uterine cycle.
3) Menstrual blood is summarized as consisting mainly of arterial blood and endometrial tissue, with an unpleasant odor due to decomposing elements, and microscopically containing various cells, mucus, hormones, and other components.