Embed presentation
Download to read offline


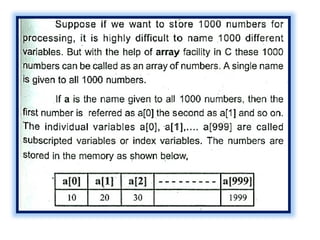


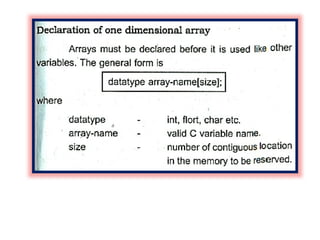

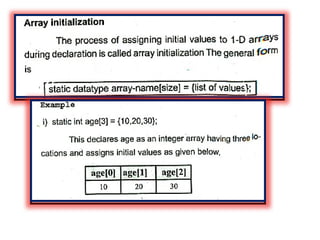
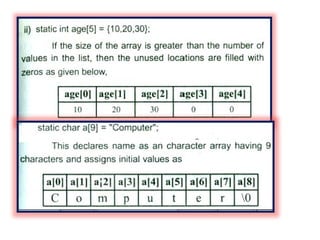
































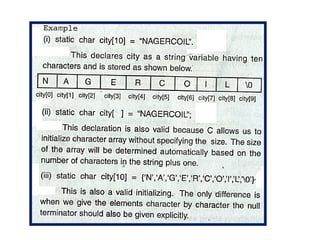


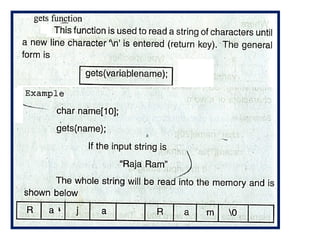


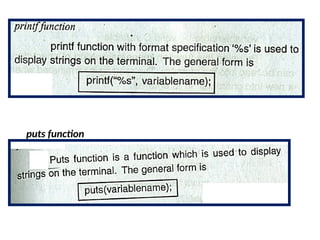













![Program to copy a string into another
without string function
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
char s1[10],s2[10];
Int i=0;
printf(“enter the string to be copiedn”);
scanf(“%s”,s1);
while(s1[i]!=‘0’)
{
s2[i]=s1[i];
i++;
}
s2[++i]=‘0’;
puts(s2);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayunit1andstrings-250709061134-8a770a42/85/array-unit-1-and-strings-fffff-pptx-66-320.jpg)
![Program to reverse a string without string
function
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
char s1[10],s2[10];
int L=0;
printf(“enter the string to be reversedn”);
scanf(“%s”,s1);
while(s1(L) != ‘0’)
L++;
j=L;
for(i=0;i<L;i++)
{
j--;
s2[j]=s1[i];
}
s2[L]=‘0’;
puts(s2);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayunit1andstrings-250709061134-8a770a42/85/array-unit-1-and-strings-fffff-pptx-67-320.jpg)
![Program to concatenate two string without
string function
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
char s1[10],s2[10];
int L,I,j;
printf(“enter two strings to be concatenatedn”);
scanf(“%s%s”,s1,s2);
while(s1(L) != ‘0’)
L++;
i=L;
i=0;
while(s2[i]!=‘0’)
{
s1[j]=s2[i];
j++;
i++;
}
s1[++j]=‘0’;
puts(s2);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayunit1andstrings-250709061134-8a770a42/85/array-unit-1-and-strings-fffff-pptx-68-320.jpg)


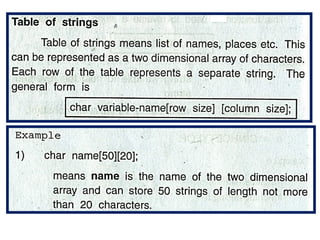
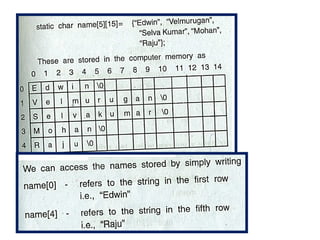







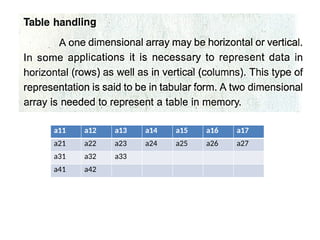
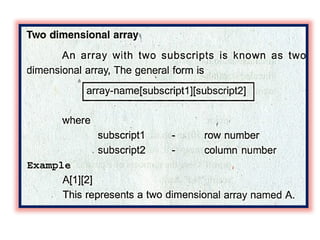
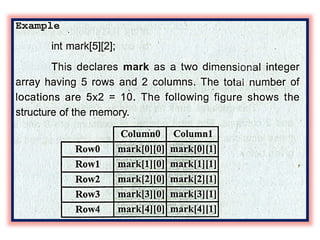
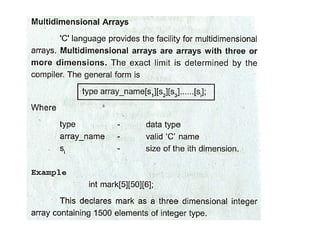
array unit 1 and strings Array: A collection of similar data elements stored in consecutive memory locations. Arrays can be one-dimensional (1D) or multi-dimensional (2D/3D) and support operations like traversal, insertion, deletion, searching, and sorting. String: A sequence of characters ending with a null character (\0), stored as a character array. Common string functions include strlen(), strcpy(), strcat(), and strcmp() from <string.h>. Arrays store numbers or characters, while strings specifically handle text data using character arrays. Array: A collection of similar data elements stored in consecutive memory locations. Arrays can be one-dimensional (1D) or multi-dimensional (2D/3D) and support operations like traversal, insertion, deletion, searching, and sorting. String: A sequence of characters ending with a null character (\0), stored as a character array. Common string functions include strlen(), strcpy(), strcat(), and strcmp() from <string.h>. Arrays store numbers or characters, while strings specifically handle text data using character arrays. Array: A collection of similar data elements stored in consecutive memory locations. Arrays can be one-dimensional (1D) or multi-dimensional (2D/3D) and support operations like traversal, insertion, deletion, searching, and sorting. String: A sequence of characters ending with a null character (\0), stored as a character array. Common string functions include strlen(), strcpy(), strcat(), and strcmp() from <string.h>. Arrays store numbers or characters, while strings specifically handle text data using character arrays.Array: A collection of similar data elements stored in consecutive memory locations. Arrays can be one-dimensional (1D) or multi-dimensional (2D/3D) and support operations like traversal, insertion, deletion, searching, and sorting. String: A sequence of characters ending with a null character (\0), stored as a character array. Common string functions include strlen(), strcpy(), strcat(), and strcmp() from <string.h>. Arrays store numbers or characters, while strings specifically handle text data using character arrays. Array: A collection of similar data elements stored in consecutive memory locations. Arrays can be one-dimensional (1D) or multi-dimensional (2D/3D) and support operations like traversal, insertion, deletion, searching, and sorting. String: A sequence of characters ending with a null character (\0), stored as a character array. Common string functions include strlen(), strcpy(), strcat(), and strcmp() from <string.h>. Arrays store numbers or characters, while strings specifically handle text data using character arrays.Array: A collection of similar data elements stored in consecutive memory locations. Arrays can be one-dimensional (1D) or multi-dimensional (2D/3D) and support operations like traversal, insertion, deletion, searching, and sorting. String: A sequence of characters ending with a null character (\0), stored

































































![Program to copy a string into another
without string function
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
char s1[10],s2[10];
Int i=0;
printf(“enter the string to be copiedn”);
scanf(“%s”,s1);
while(s1[i]!=‘0’)
{
s2[i]=s1[i];
i++;
}
s2[++i]=‘0’;
puts(s2);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayunit1andstrings-250709061134-8a770a42/85/array-unit-1-and-strings-fffff-pptx-66-320.jpg)
![Program to reverse a string without string
function
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
char s1[10],s2[10];
int L=0;
printf(“enter the string to be reversedn”);
scanf(“%s”,s1);
while(s1(L) != ‘0’)
L++;
j=L;
for(i=0;i<L;i++)
{
j--;
s2[j]=s1[i];
}
s2[L]=‘0’;
puts(s2);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayunit1andstrings-250709061134-8a770a42/85/array-unit-1-and-strings-fffff-pptx-67-320.jpg)
![Program to concatenate two string without
string function
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
char s1[10],s2[10];
int L,I,j;
printf(“enter two strings to be concatenatedn”);
scanf(“%s%s”,s1,s2);
while(s1(L) != ‘0’)
L++;
i=L;
i=0;
while(s2[i]!=‘0’)
{
s1[j]=s2[i];
j++;
i++;
}
s1[++j]=‘0’;
puts(s2);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayunit1andstrings-250709061134-8a770a42/85/array-unit-1-and-strings-fffff-pptx-68-320.jpg)










