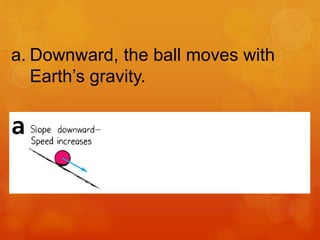
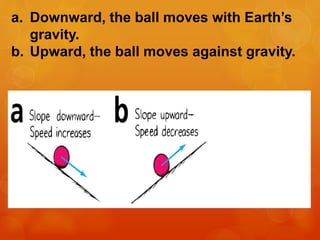
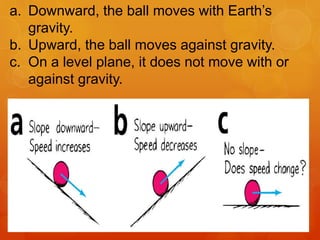
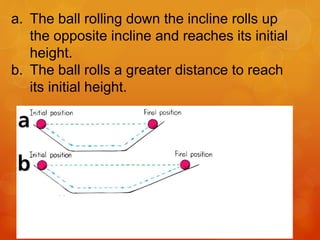
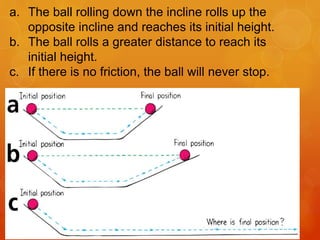
1) Galileo conducted experiments rolling balls down inclined planes and argued that without friction, an object in motion would continue moving indefinitely, challenging Aristotle's view that motion requires a continuous force.
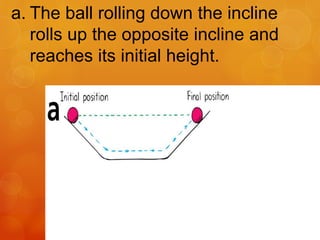
2) Galileo showed that a ball rolling down one plane would roll up an opposite plane to the same height, demonstrating that the ball's motion is conserved regardless of the plane's angle or length.
3) Galileo concluded that objects have a natural tendency to resist changes to their state of motion, which we now call inertia, rather than having a natural tendency towards rest as Aristotle claimed.