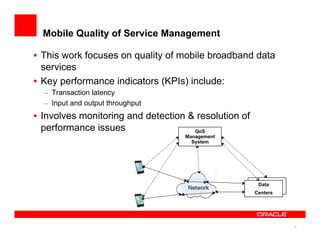
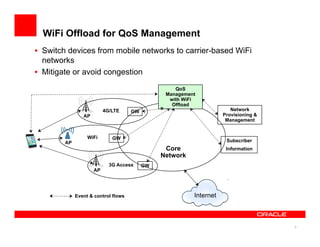
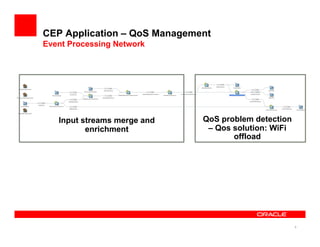
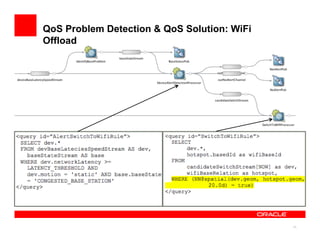
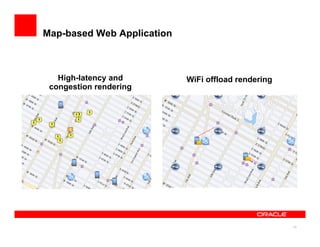
The document discusses a framework for managing mobile quality of service (QoS) using complex event processing, highlighting the importance of user experience and real-time monitoring in mobile broadband services. It details the implementation of QoS management through device-based measurements, network monitoring, and the potential for Wi-Fi offloading to alleviate congestion. Future work includes predicting congestion patterns and improving interactions with other infrastructure systems while ensuring data privacy.