The document summarizes various Active Record query interface features in Ruby on Rails, including:
1) Eager loading associations to reduce N+1 queries problems by including associated records in fewer queries.
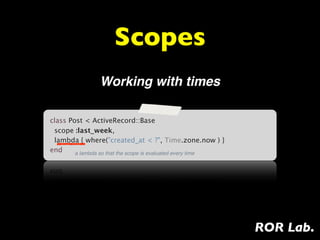
2) Using scopes to define reusable Active Record relation queries and chain them for complex queries.
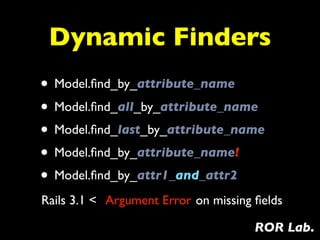
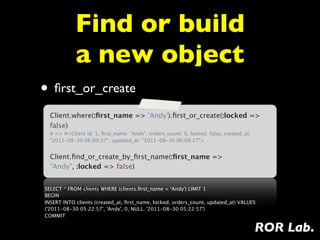
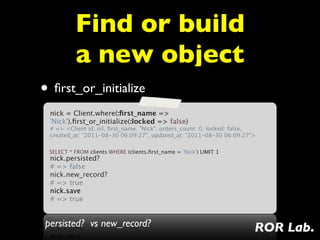
3) Finding records using dynamic finders like find_by and find_or_create to retrieve or initialize records matching attributes.












![Eager Loading
Associations
- Eager Loading Multiple Associations -
Array of Multiple Associations
Nested Associations Hash
Category.includes(
:posts => [{:comments => :guest}, :tags]).find(1)
ROR Lab.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ar-queryinterface2-120406072445-phpapp01/85/Active-Record-Query-Interface-2-Season-1-13-320.jpg)




![Scopes
chainable
class Post < ActiveRecord::Base
scope :published,
where(:published => true).joins(:category)
end
chainable within scopes
class Post < ActiveRecord::Base
scope :published, where(:published => true)
scope :published_and_commented,
published.and(self.arel_table[:comments_count].gt(0))
ROR Lab.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ar-queryinterface2-120406072445-phpapp01/85/Active-Record-Query-Interface-2-Season-1-18-320.jpg)
![Scopes
To call the scope
Post.published # => [published posts]
category = Category.first
category.posts.published
# => [published posts belonging to this category]
ROR Lab.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ar-queryinterface2-120406072445-phpapp01/85/Active-Record-Query-Interface-2-Season-1-19-320.jpg)











![Existence of
Objects
Client.exists?(1)
Client.exists?(1,2,3)
# or
Client.exists?([1,2,3])
Client.where(:first_name => 'Ryan').exists?
cf. find method
ROR Lab.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ar-queryinterface2-120406072445-phpapp01/85/Active-Record-Query-Interface-2-Season-1-35-320.jpg)








