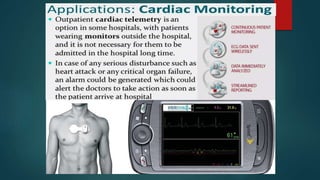
The document discusses industrial control engineering and automation, highlighting the importance of control systems in improving productivity across various industries. It emphasizes design considerations for industrial control systems, including control timing, geographic distribution, hierarchy, complexity, availability, safety, and the impact of failures. Additionally, it covers telemetry technology, its applications in monitoring unsafe environments, and its benefits in various fields, including healthcare.