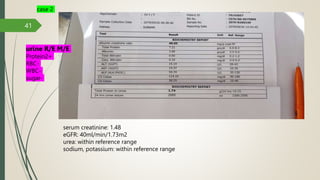
This document provides an overview of renal function tests and approaches to abnormal renal findings. It discusses the physiology of the kidney, methods to estimate glomerular filtration rate including serum creatinine and BUN, urinalysis, urine microscopy, imaging studies such as ultrasound and radionuclide scans, and when a renal biopsy may be indicated. Approaches to abnormalities such as hematuria, pyuria, and proteinuria are also reviewed. The document uses case examples to demonstrate approaches to acute kidney injury and abnormal urinalysis results.