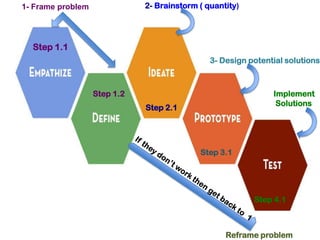
The document outlines the design thinking process for redesigning lockers at a public high school. It discusses:
1) The process of design thinking includes steps like empathizing, defining problems, ideating, prototyping, and testing solutions.
2) For the locker redesign, the ideation and prototyping steps, as well as testing, should be modified. Ideation should generate at least 50 ideas, and prototyping should closely follow the empathy findings.
3) Testing involves getting feedback, surveying users, and redesigning if needed to address problems identified through empathy and ensure quality, safety, and meeting user needs.