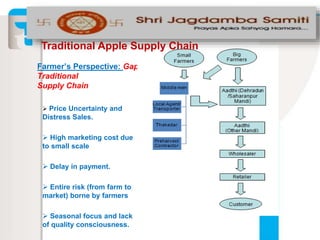
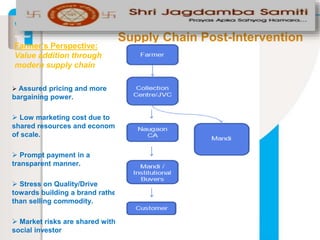
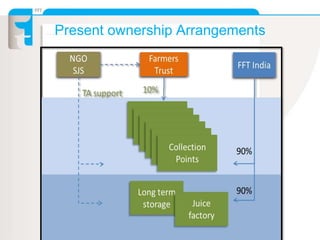
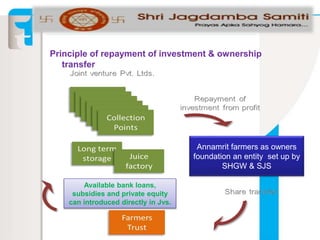
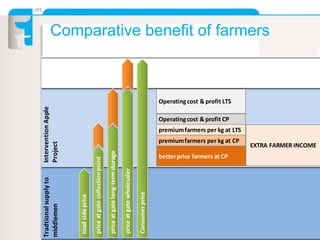
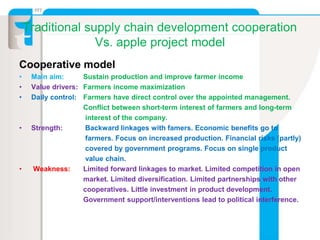
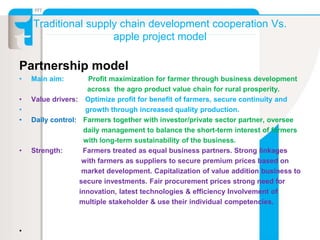
The document summarizes an apple project in Uttarakhand, India that was initiated in 2007. The project aims to improve the situation of small apple farmers by providing opportunities to move up the value chain through partnerships between farmers collectives, a social organization, and social investors. The project establishes farmer-owned joint venture companies to handle quality production, collection, grading, storage, distribution and marketing of apples. This is intended to create a self-perpetuating model that gives farmers more bargaining power, assured pricing, prompt payment, and shares the risks and market access benefits with investors. The document compares this partnership model to traditional cooperative and private sector models, noting the strengths of linking farmers as business partners while balancing short and