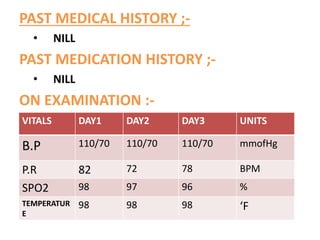
The patient presented with stomach pain, vomiting and loss of appetite for 1 day. Ultrasound showed a dilated and tender appendix. The patient was diagnosed with appendicitis and underwent an appendectomy. Post-surgery, the patient was prescribed medications including pantoprazole to decrease acid, ondansetron for nausea, cefaperazone/sulbactam and metronidazole for infection treatment, and diclofenac for pain. The patient's vital signs and lab tests were monitored daily and found to be stable and within normal ranges.






![DRUG CHART :-
DRUG
NAME
CATEG
ORY
MOA USE
ROA
FRE
QUE
NCY
DAYS
D1 D2 D3
Inj.pantop
[pantaprazol
e]
H+/k+
inhibotor
It inhibit final
step in gastric
acid production
Decrease
acid
secretion
IV OD + + +
Inj.zofer
[ondansetro
n]
5HT3
antagonist
It inhibits
seratonin
To treat
nausea
vomitings
IV BD + + +
Inj.xylocain
e[lidocaine]
Local
anesthetic
It blocks
VGSCs
Used to
numb an
area
IV OD + - -
Inj.sulcef
[cefaperazo
ne
salbactum
Cephalos
porin
&beta
lactamase
inhibitors
Inhibits cell
wall synthesis
To treat
bacterial
infections
IV BD + + +
Inj.metrogyl
[metronidaz
ole]
nitroimid
azole
It inhibits
protein
synthesis
Bacterial&
parasitic
infections
IV BD + + +](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitis-1-231230095534-1a0de11e/85/APPENDICITIS-2-pptx-8-320.jpg)


![Pathophysiology;-
Due to etiologic factors
Obstruction of appendix
[due to fecalith ,tumor]
Increased intraluminal pressure
Results in severe pain[appendicitis]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitis-1-231230095534-1a0de11e/85/APPENDICITIS-2-pptx-11-320.jpg)







