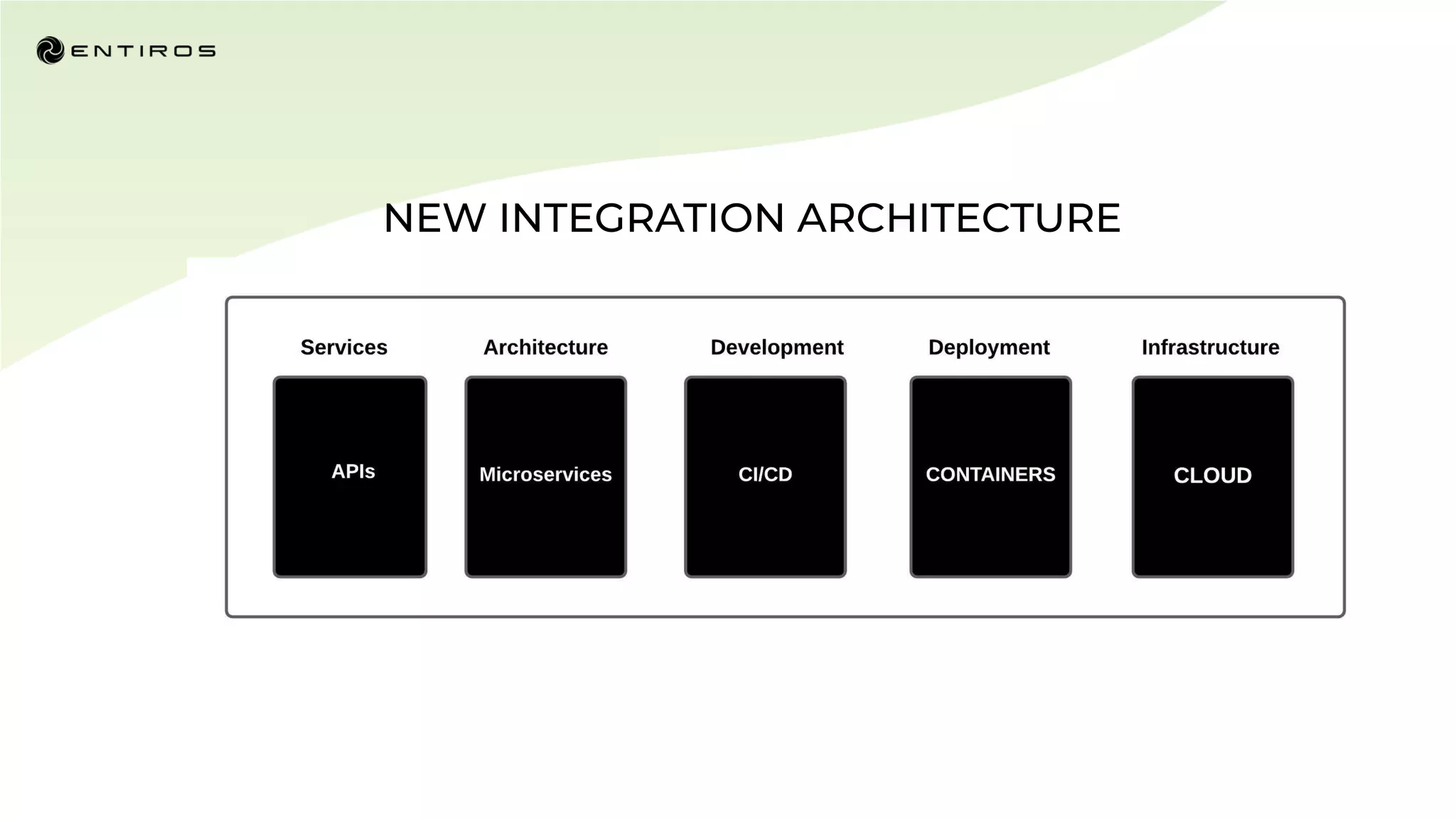
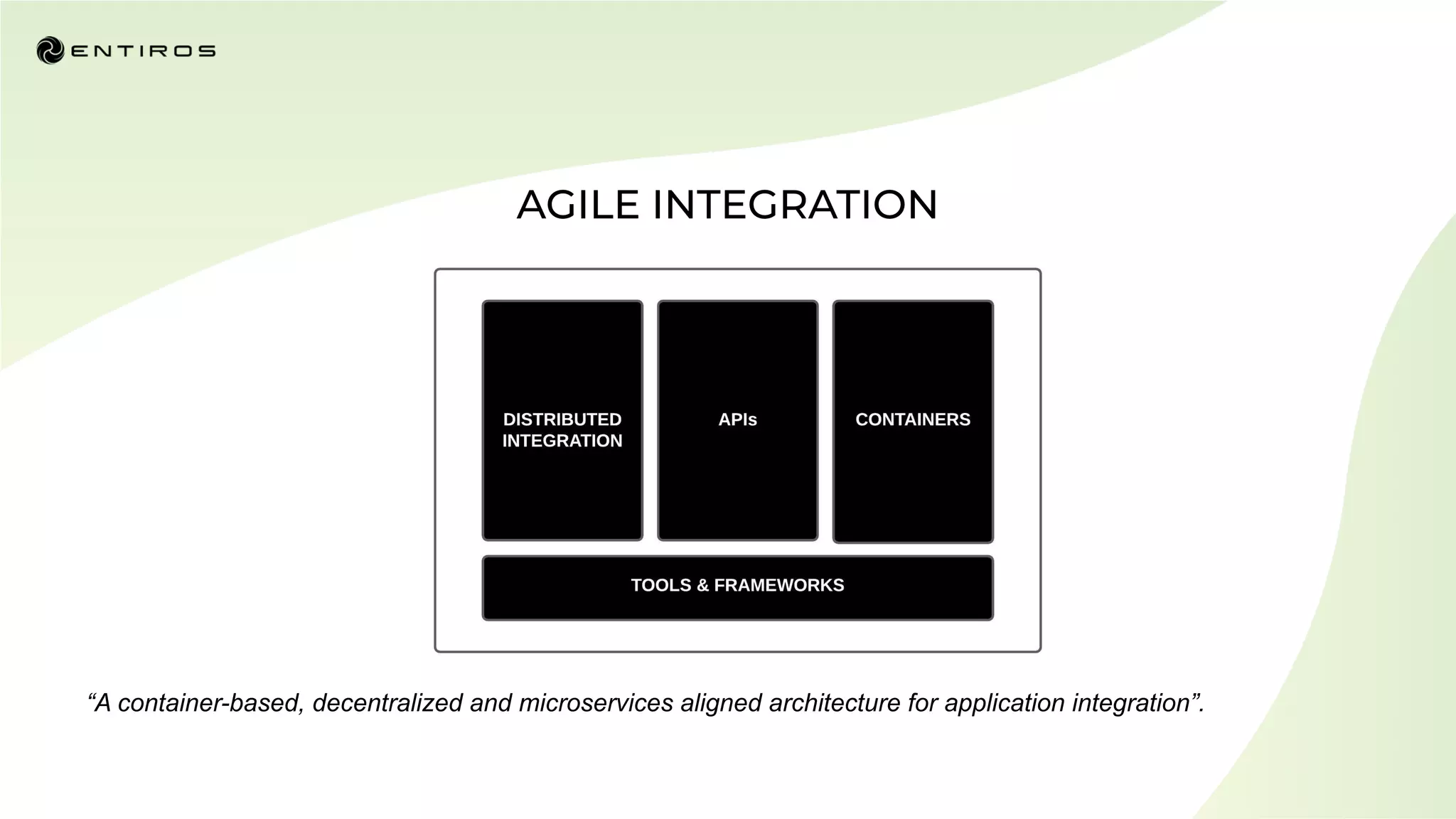
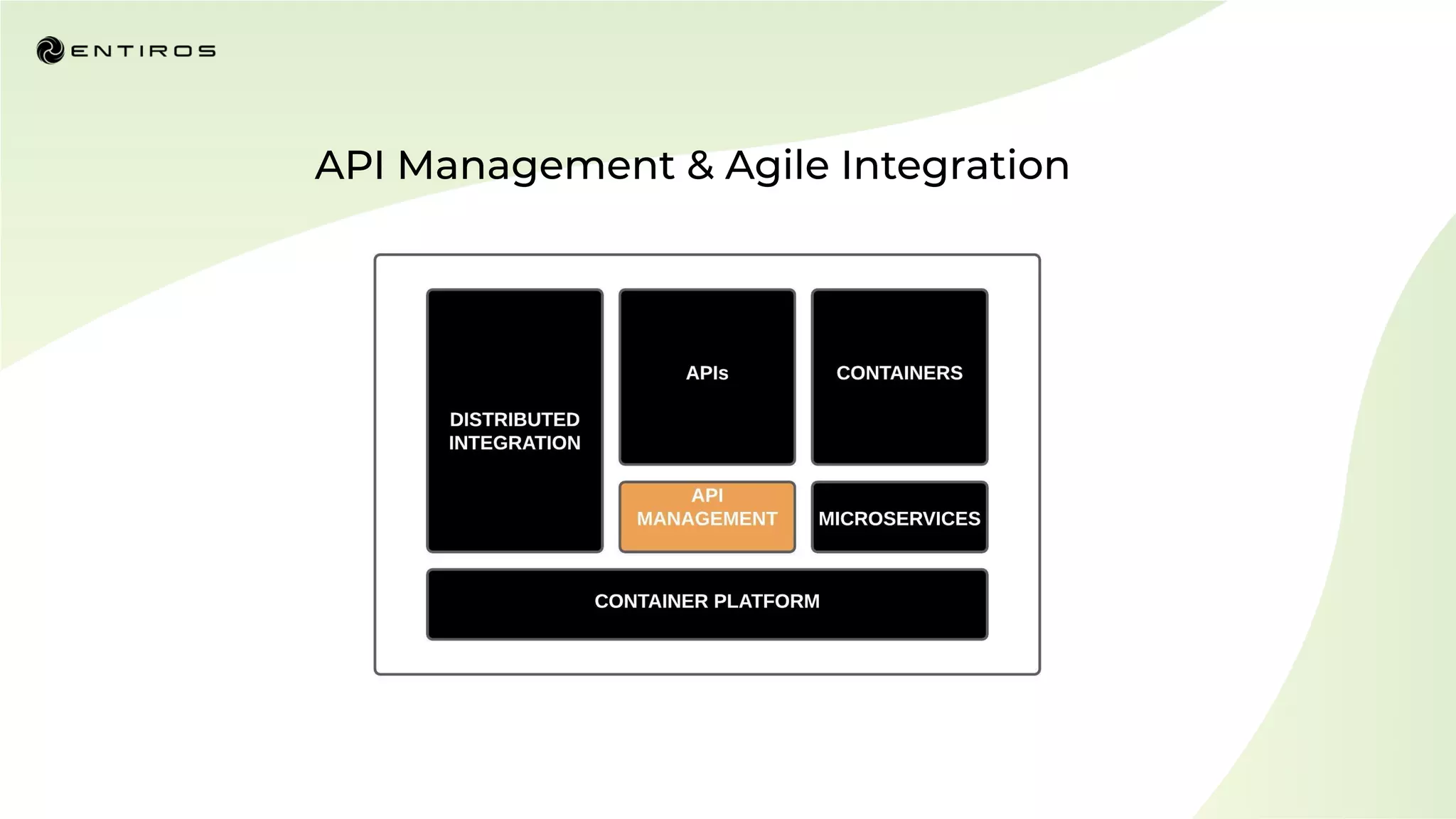
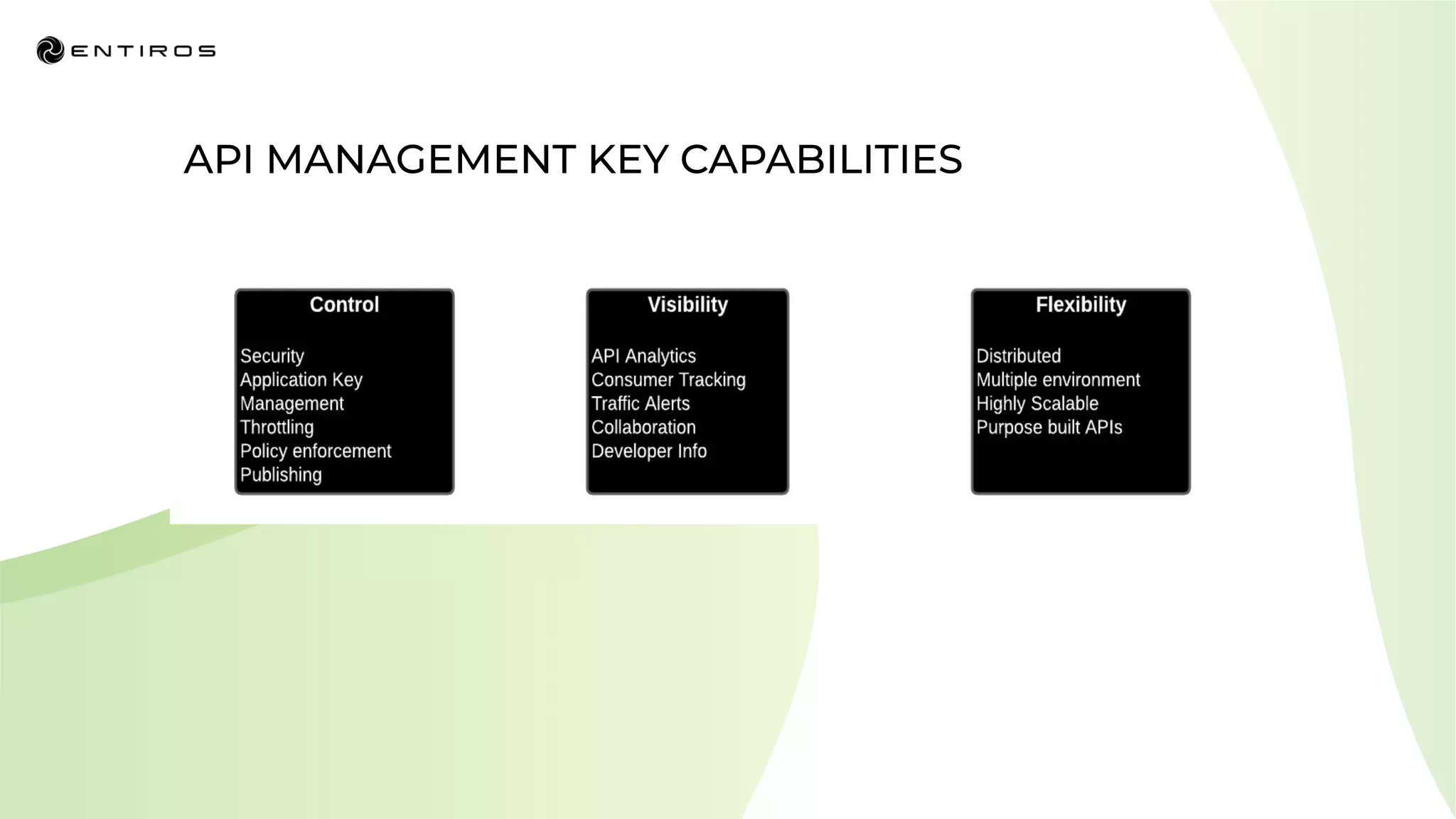
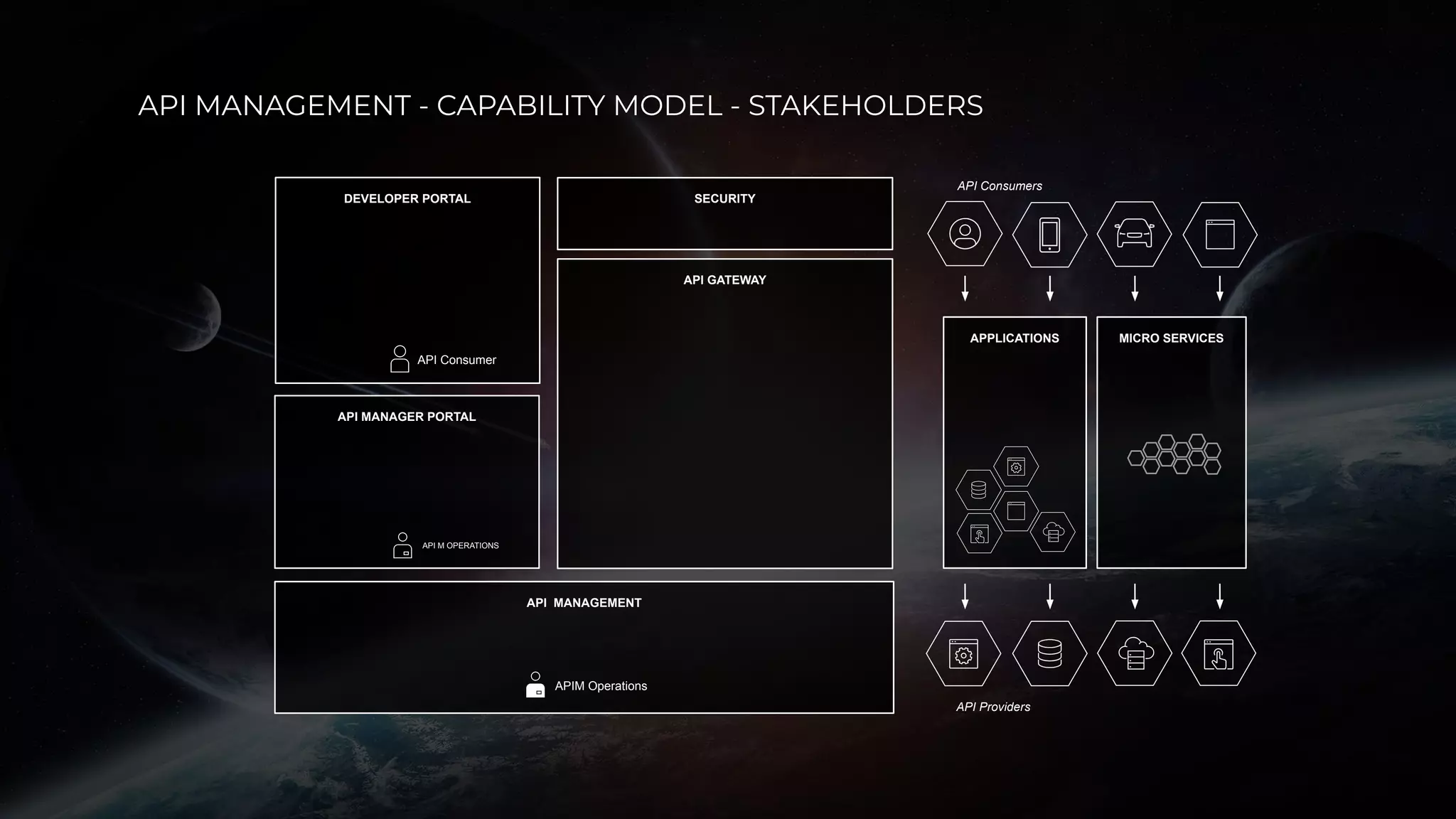
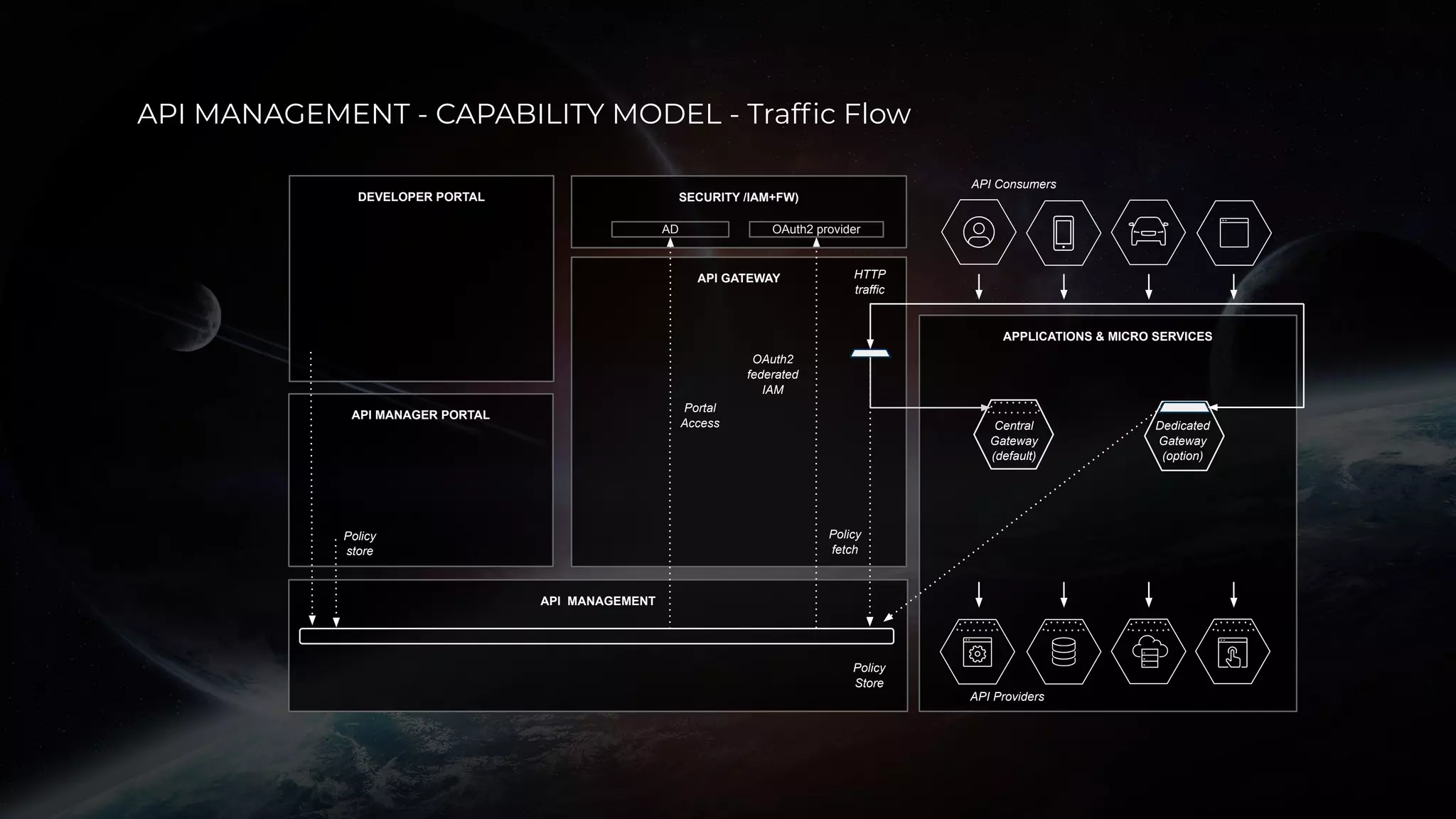
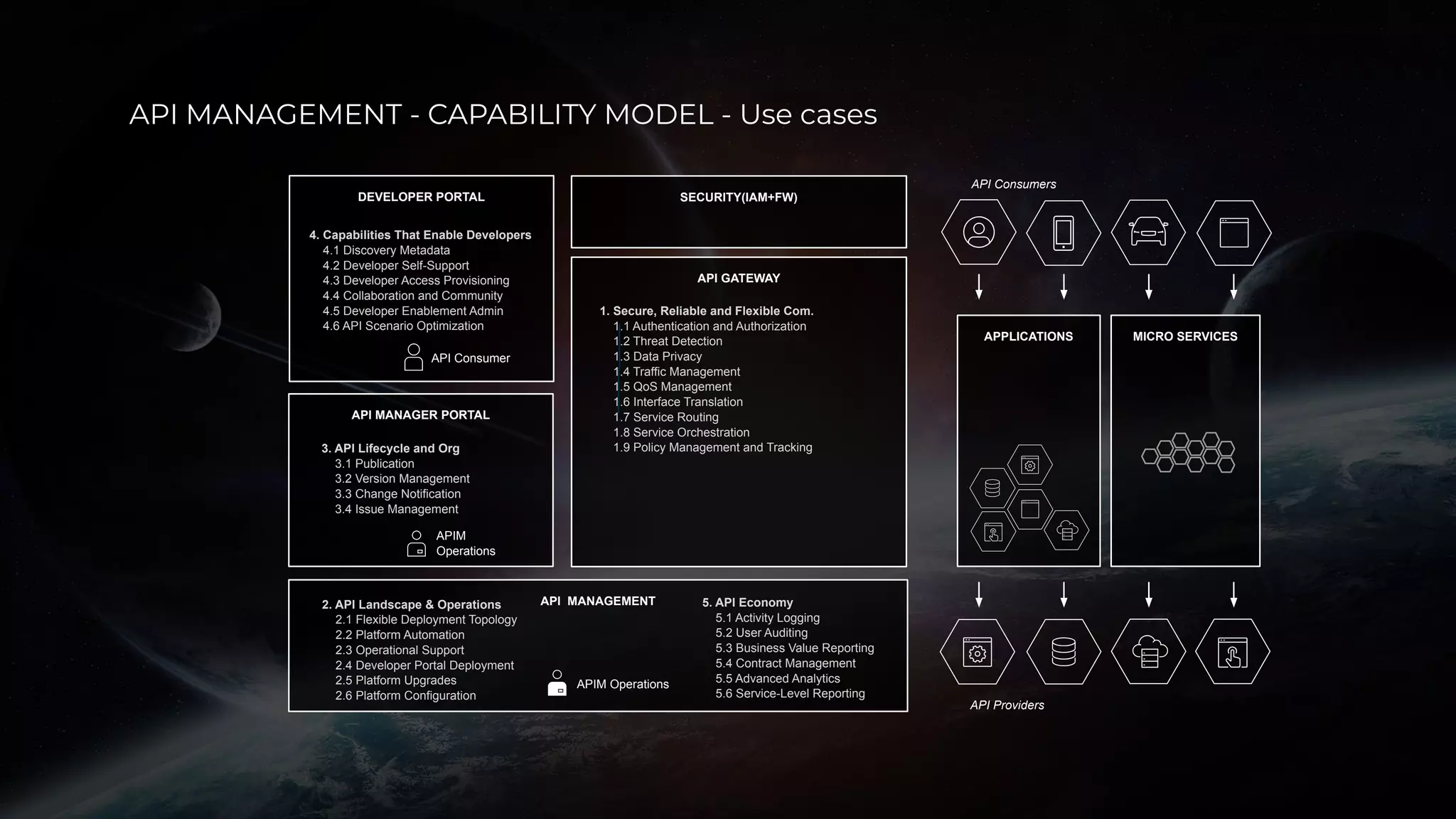
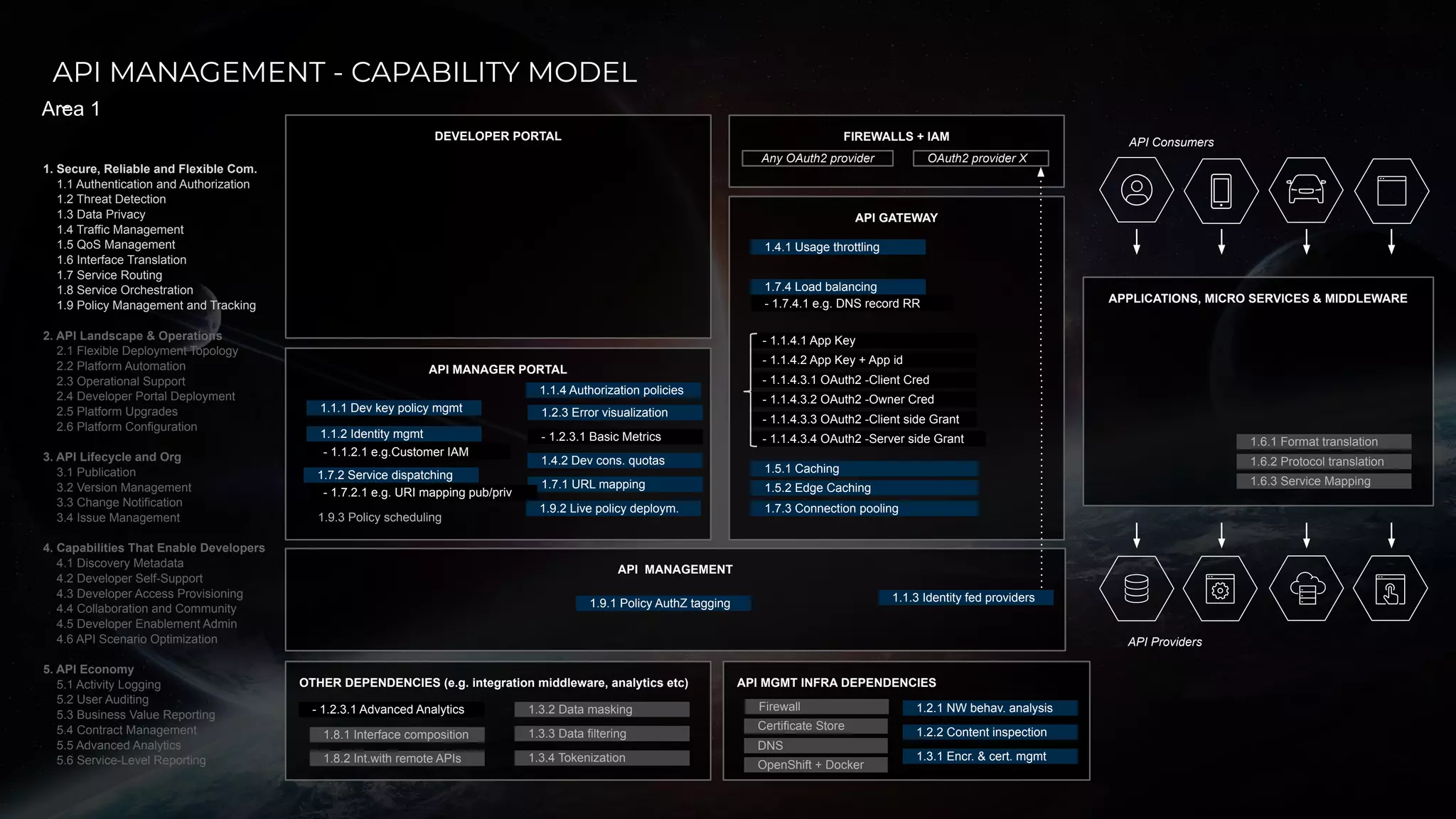
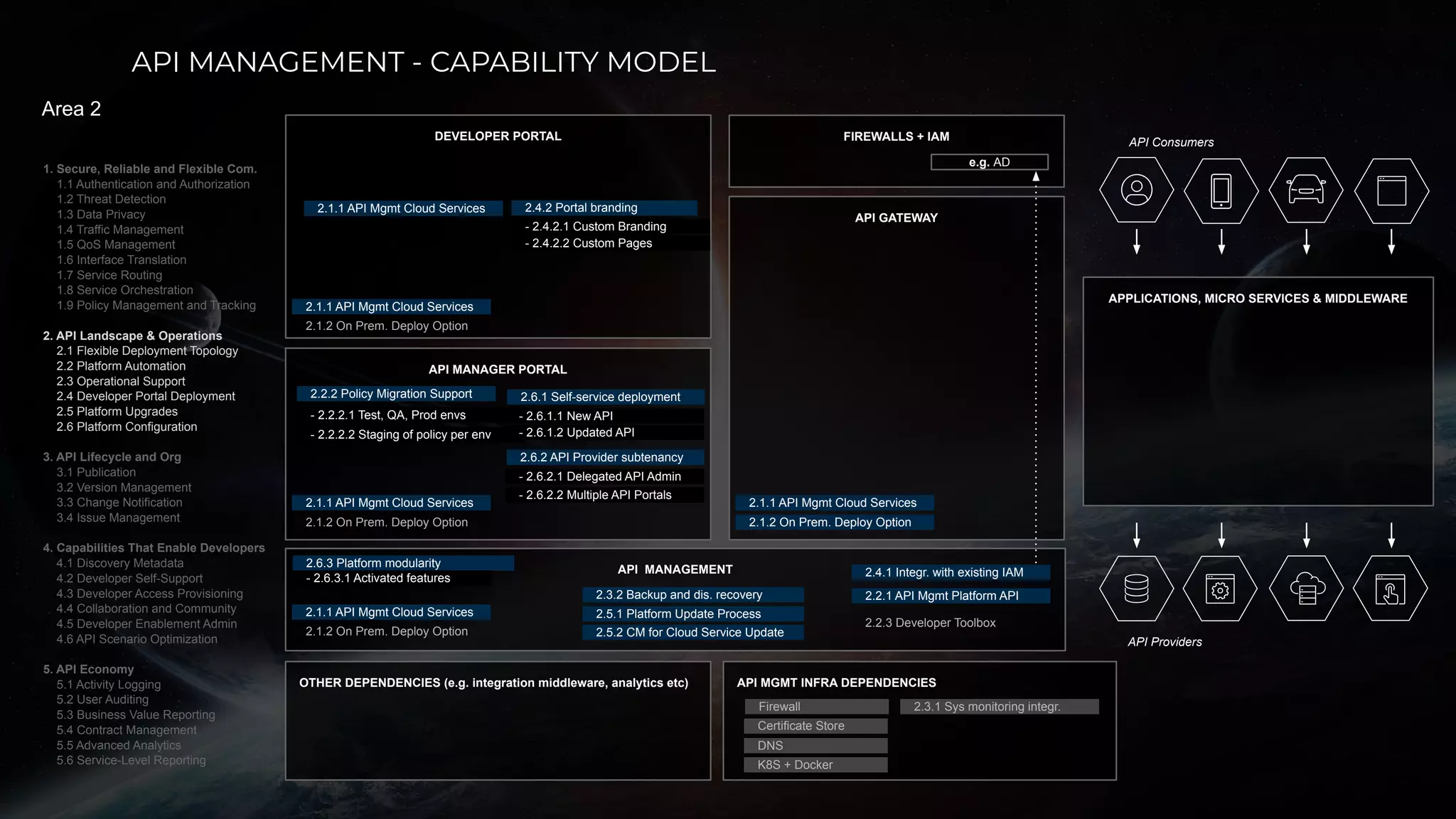
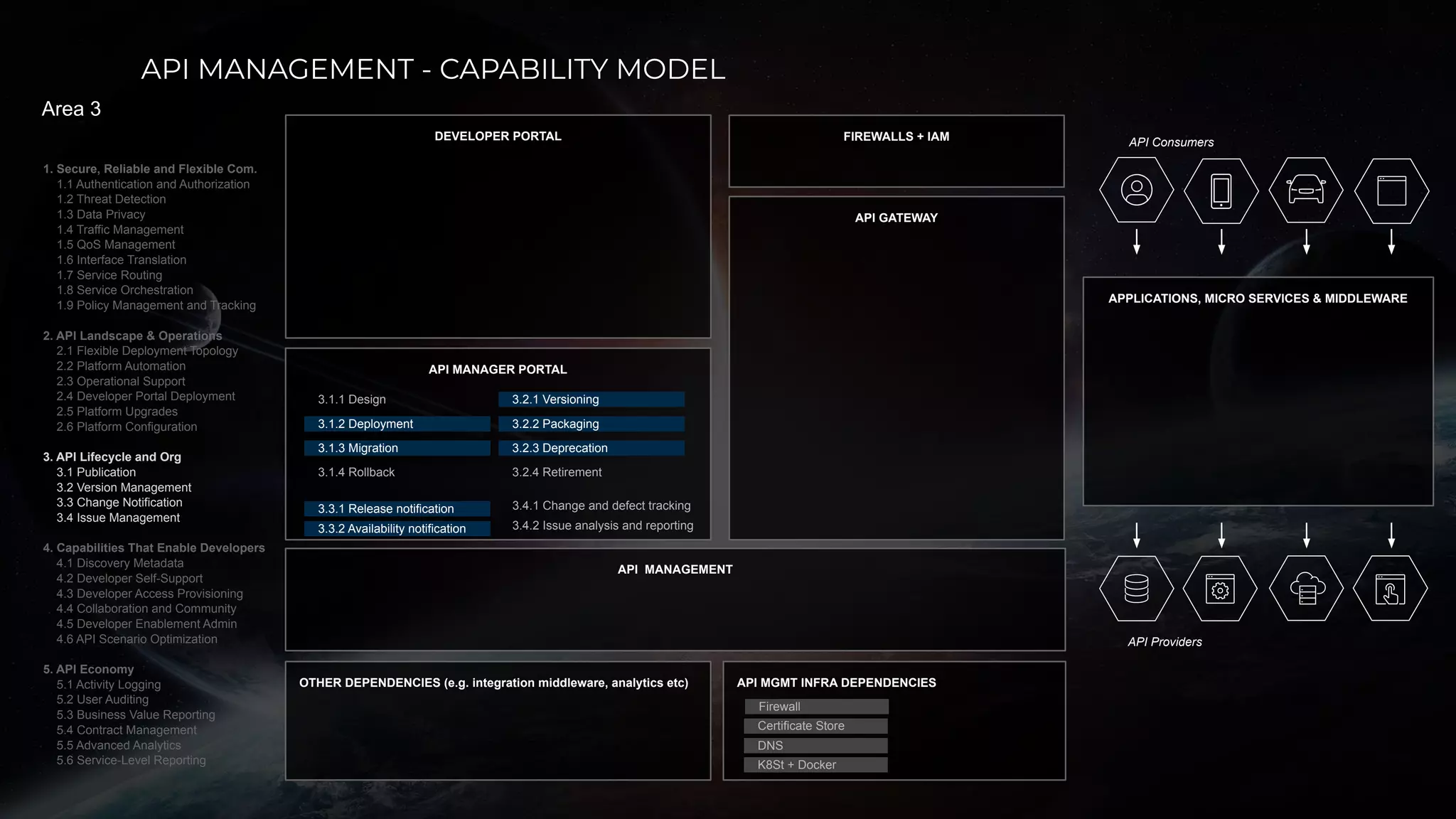
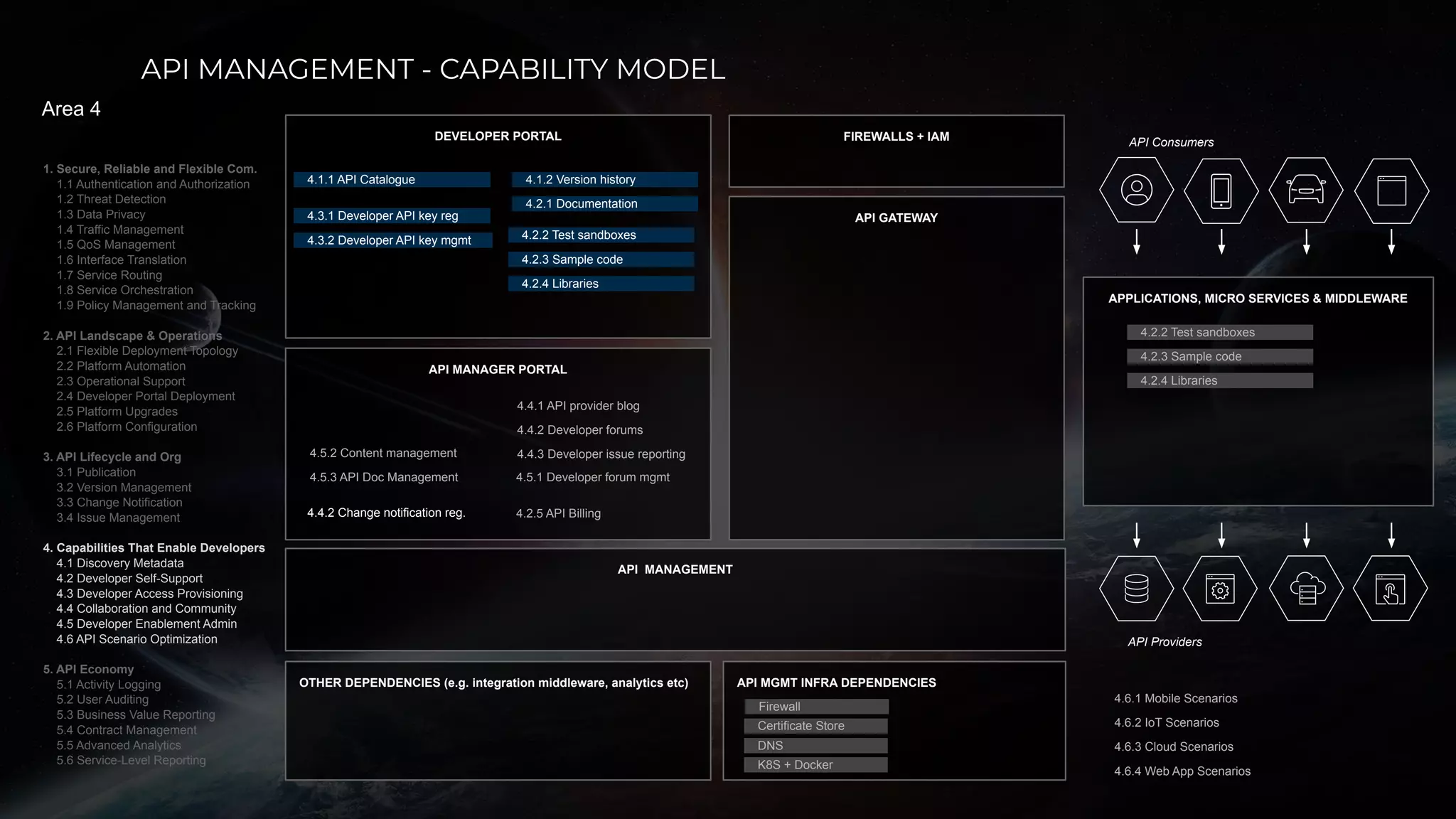
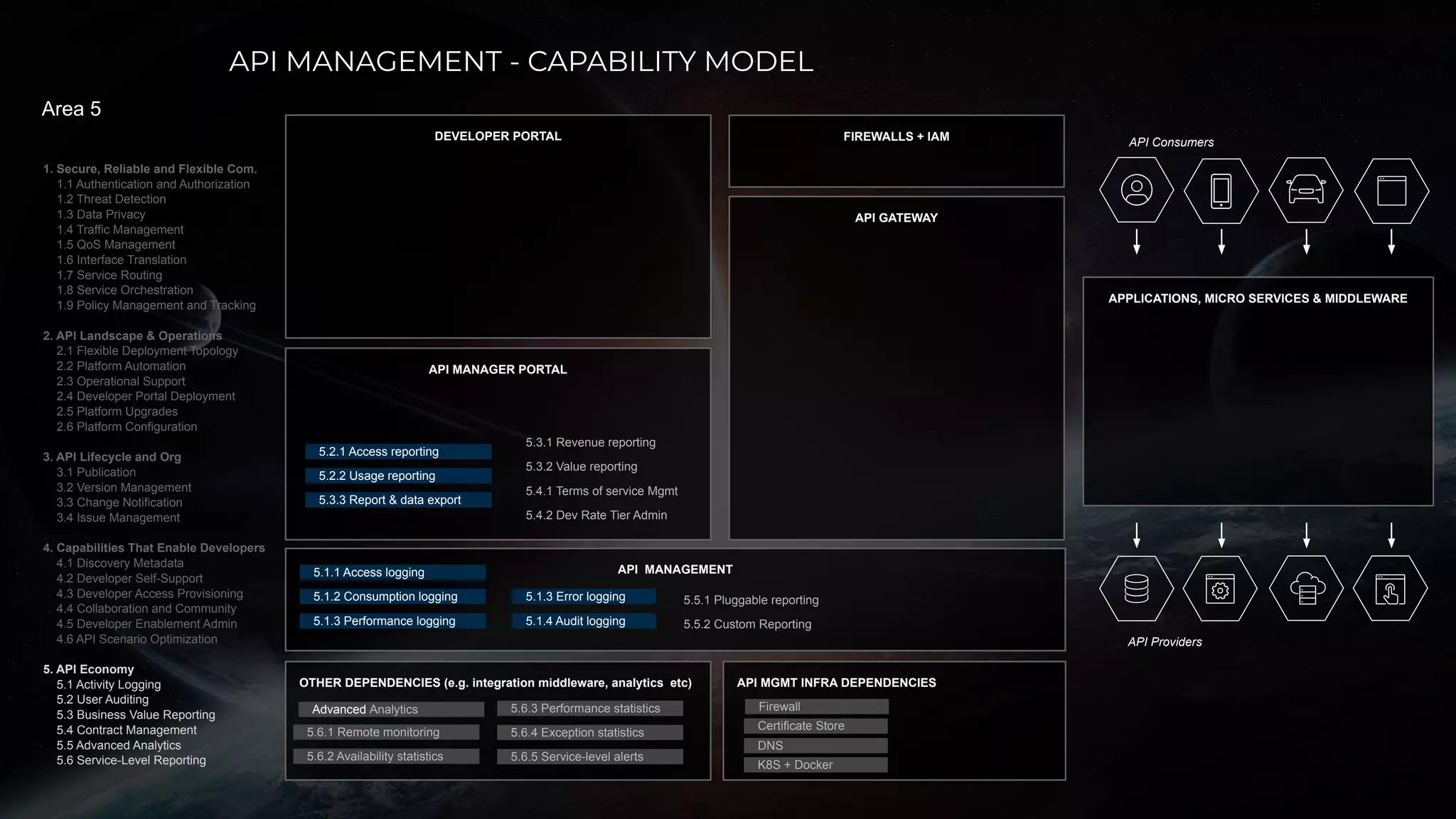
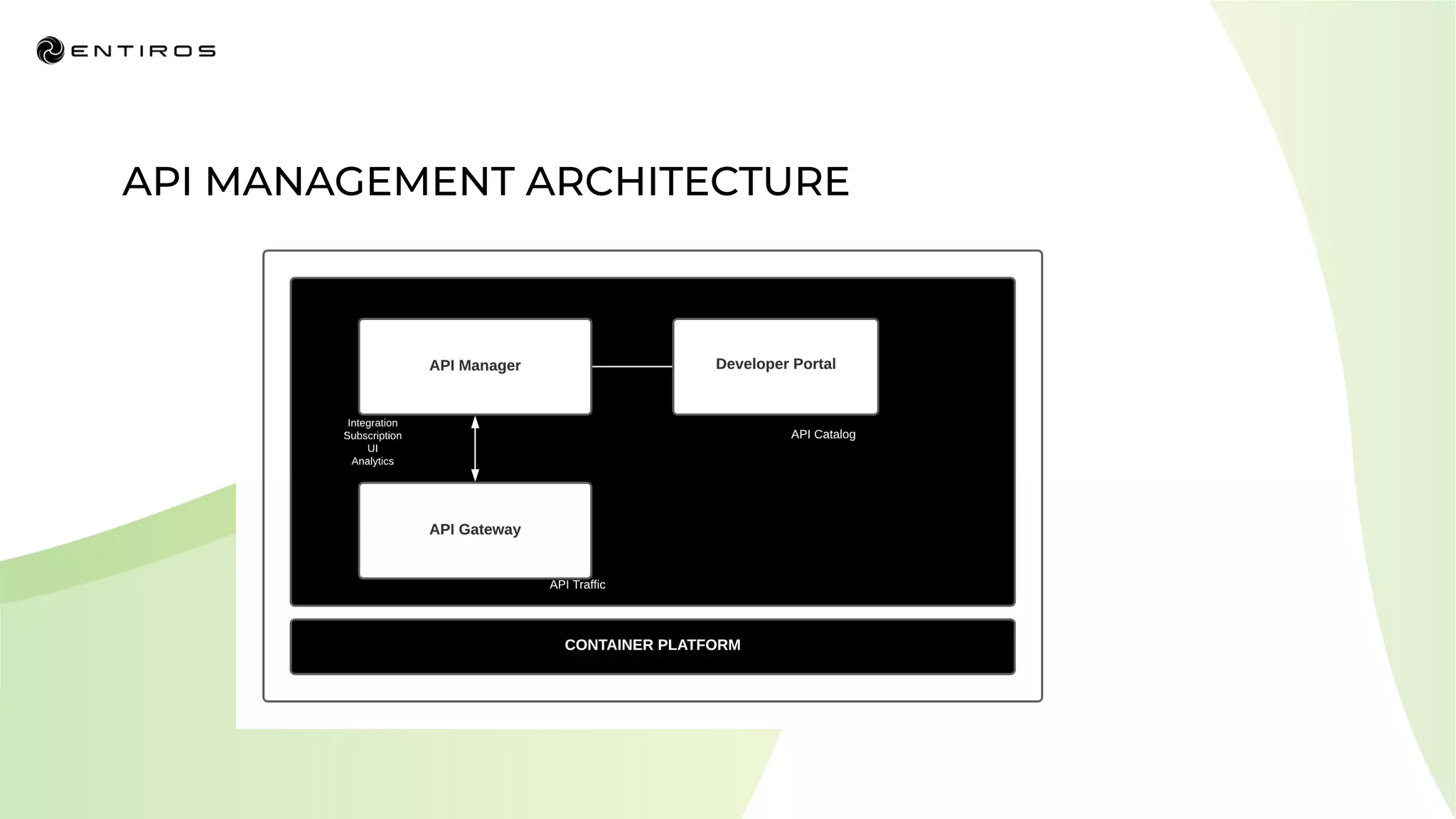
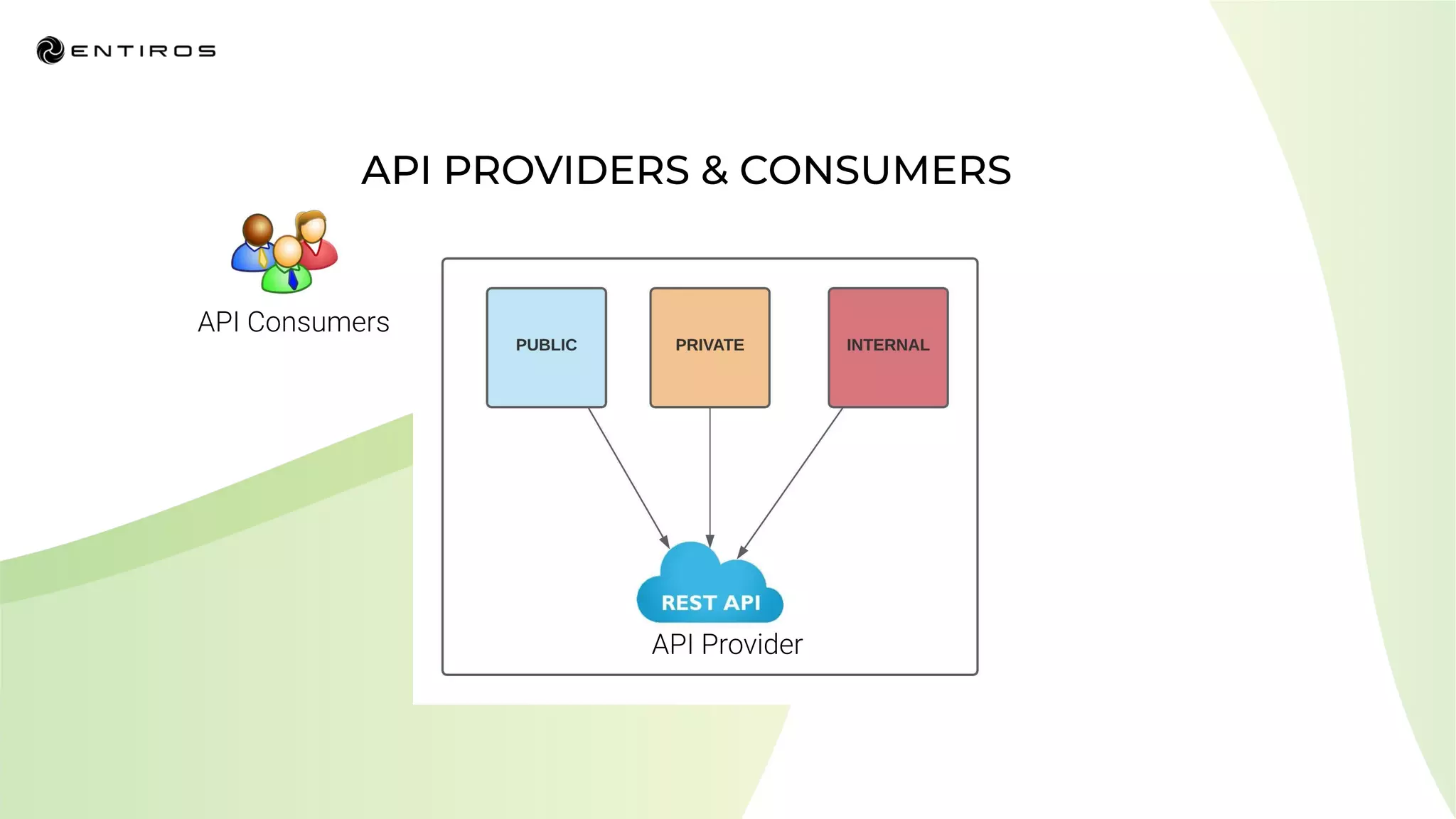
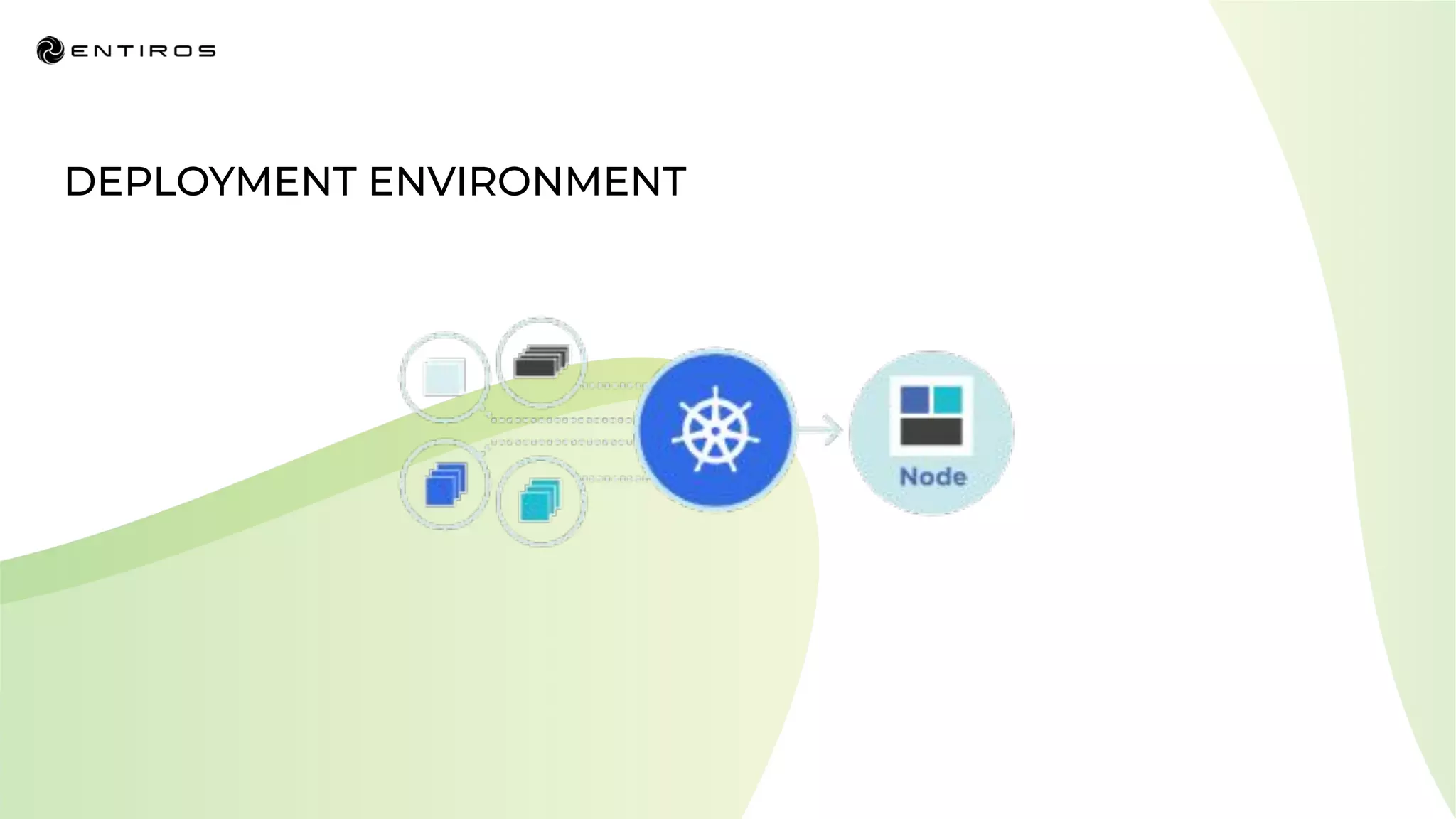
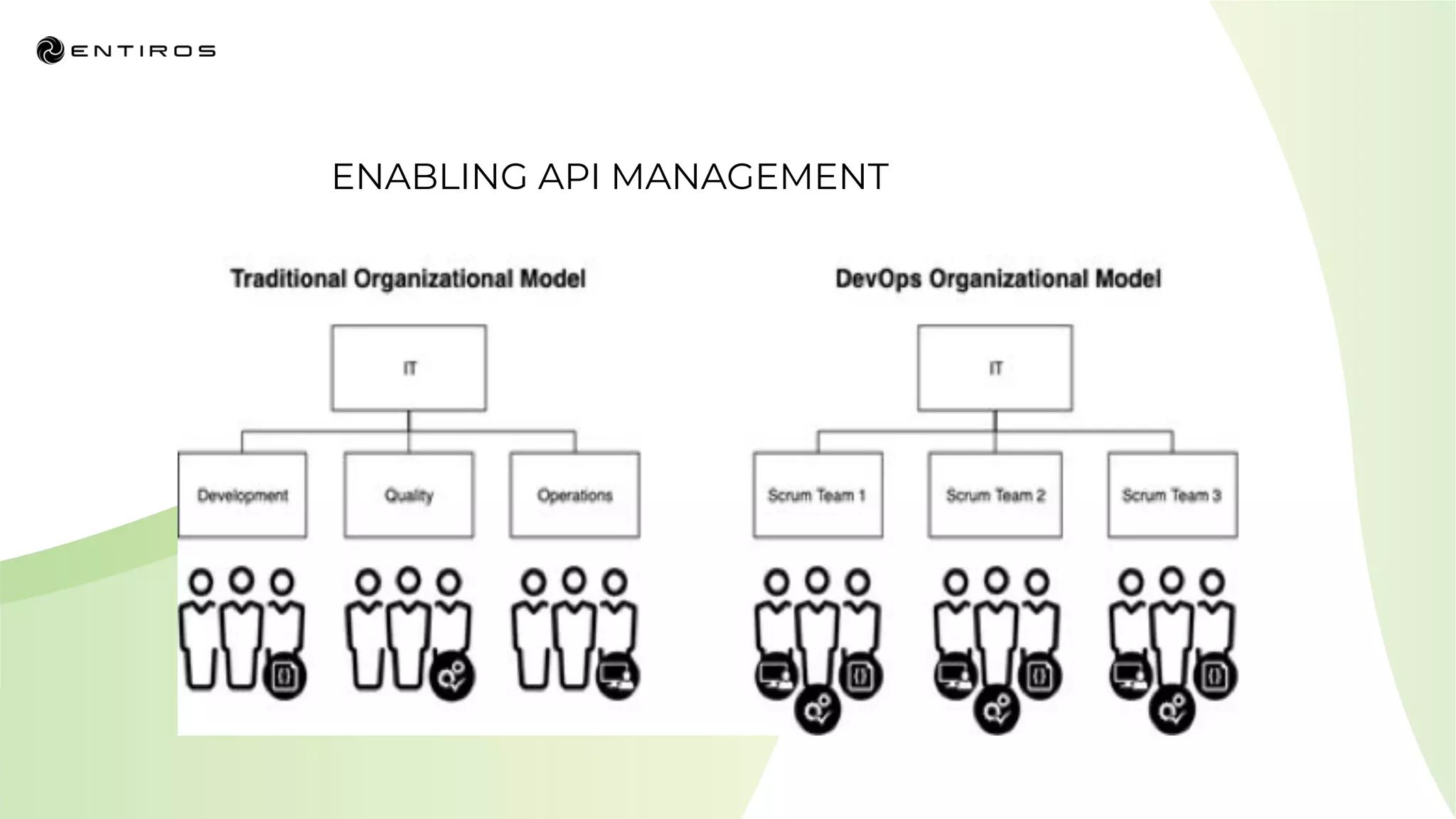
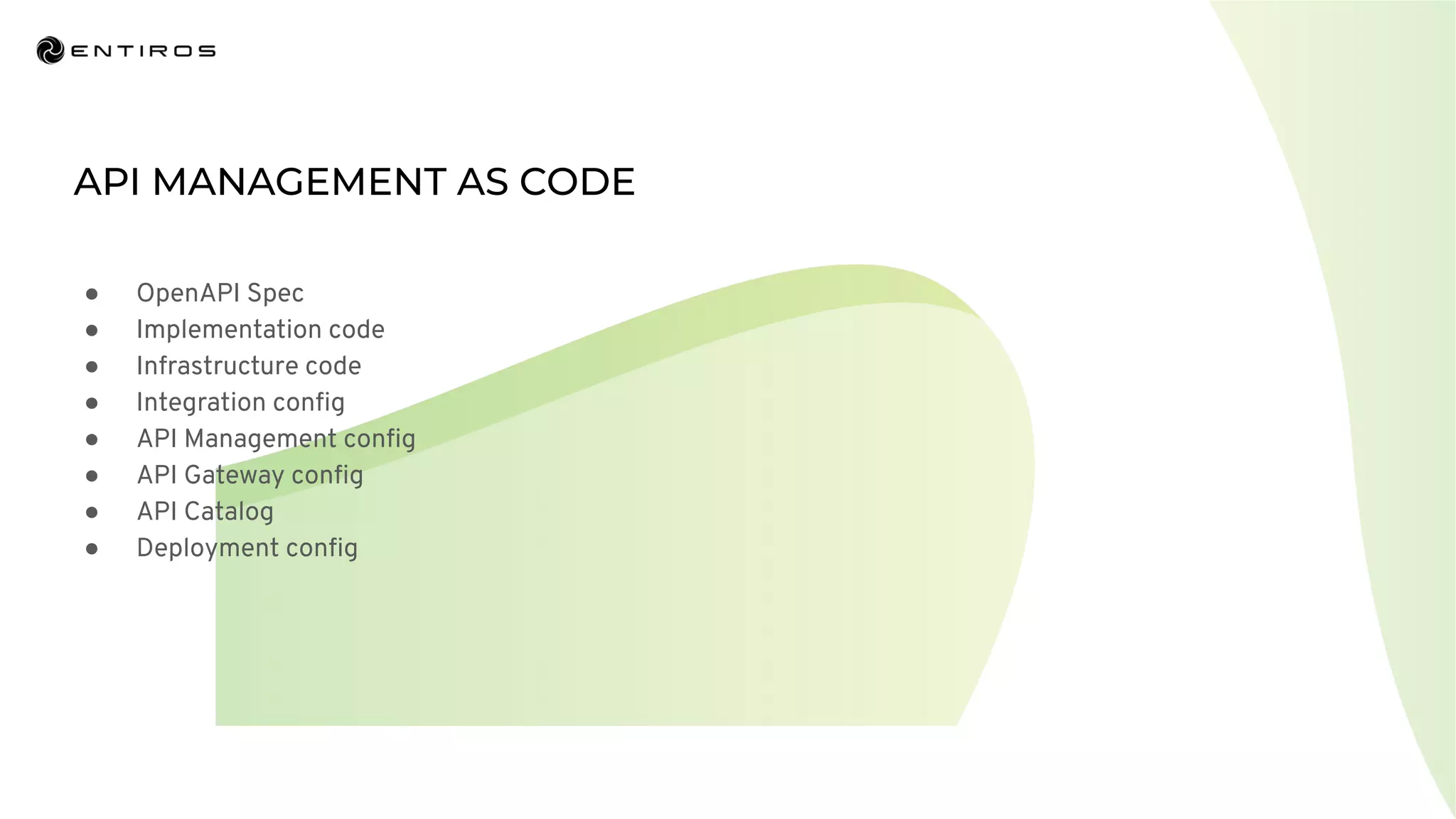
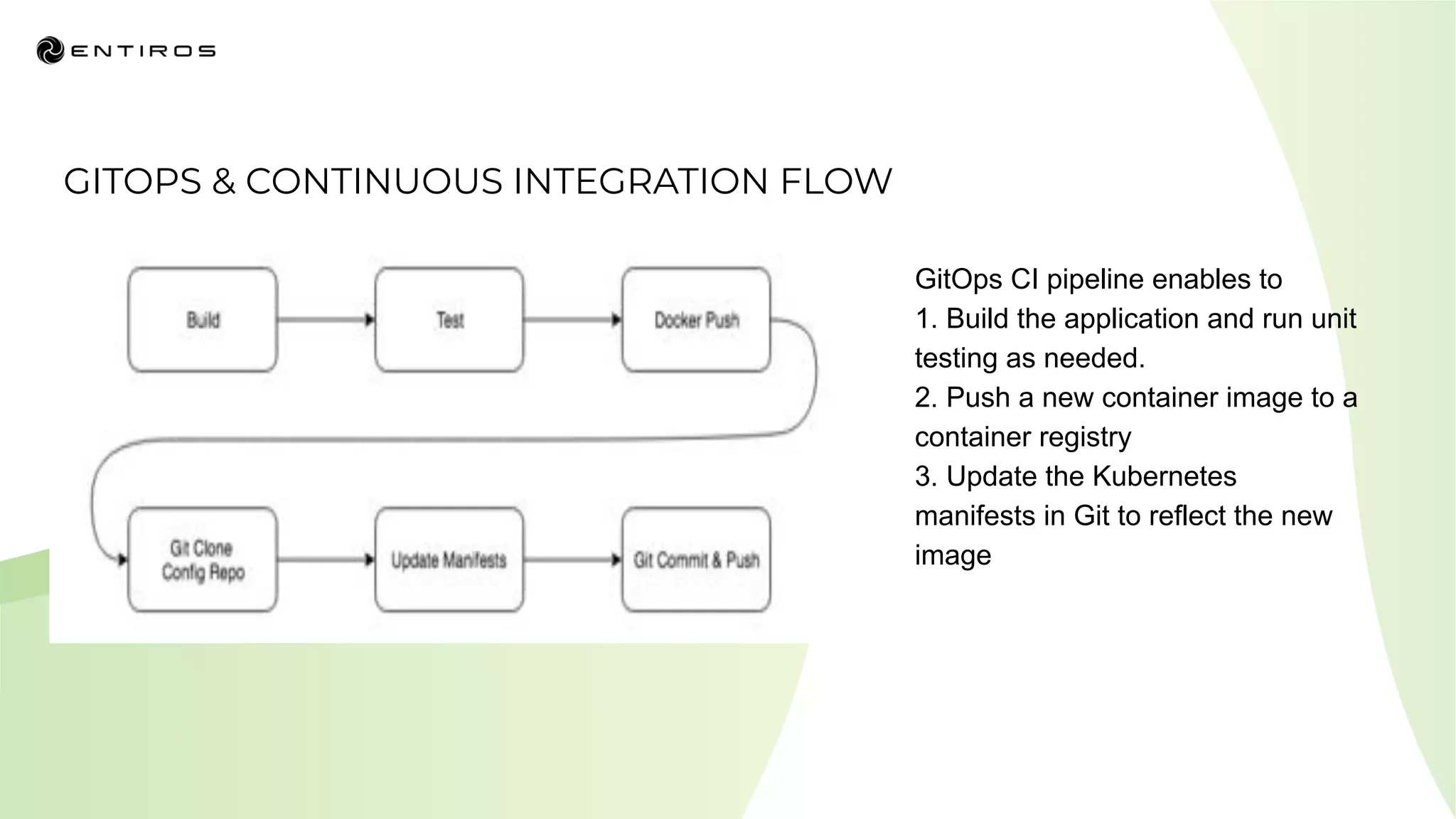
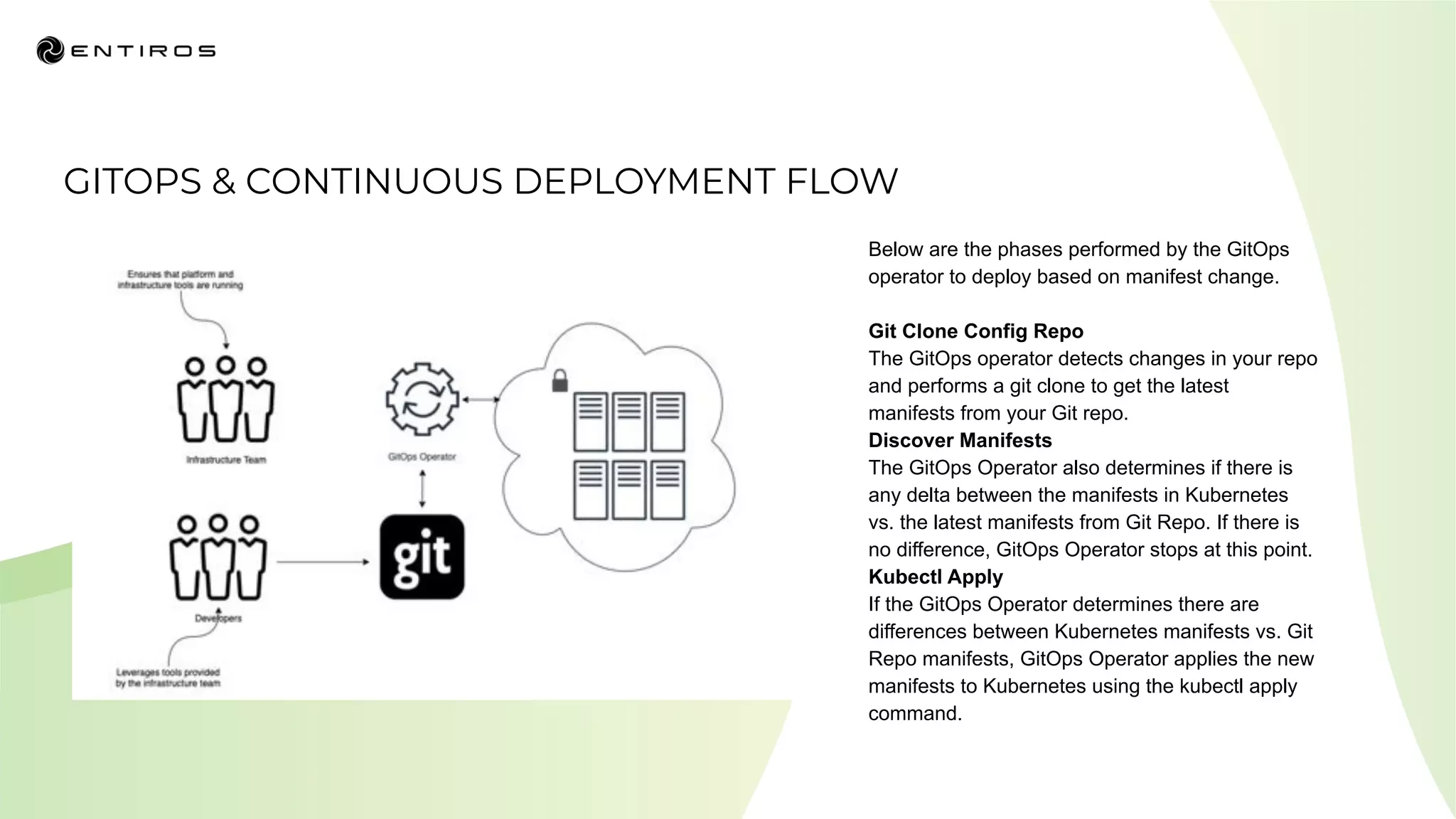
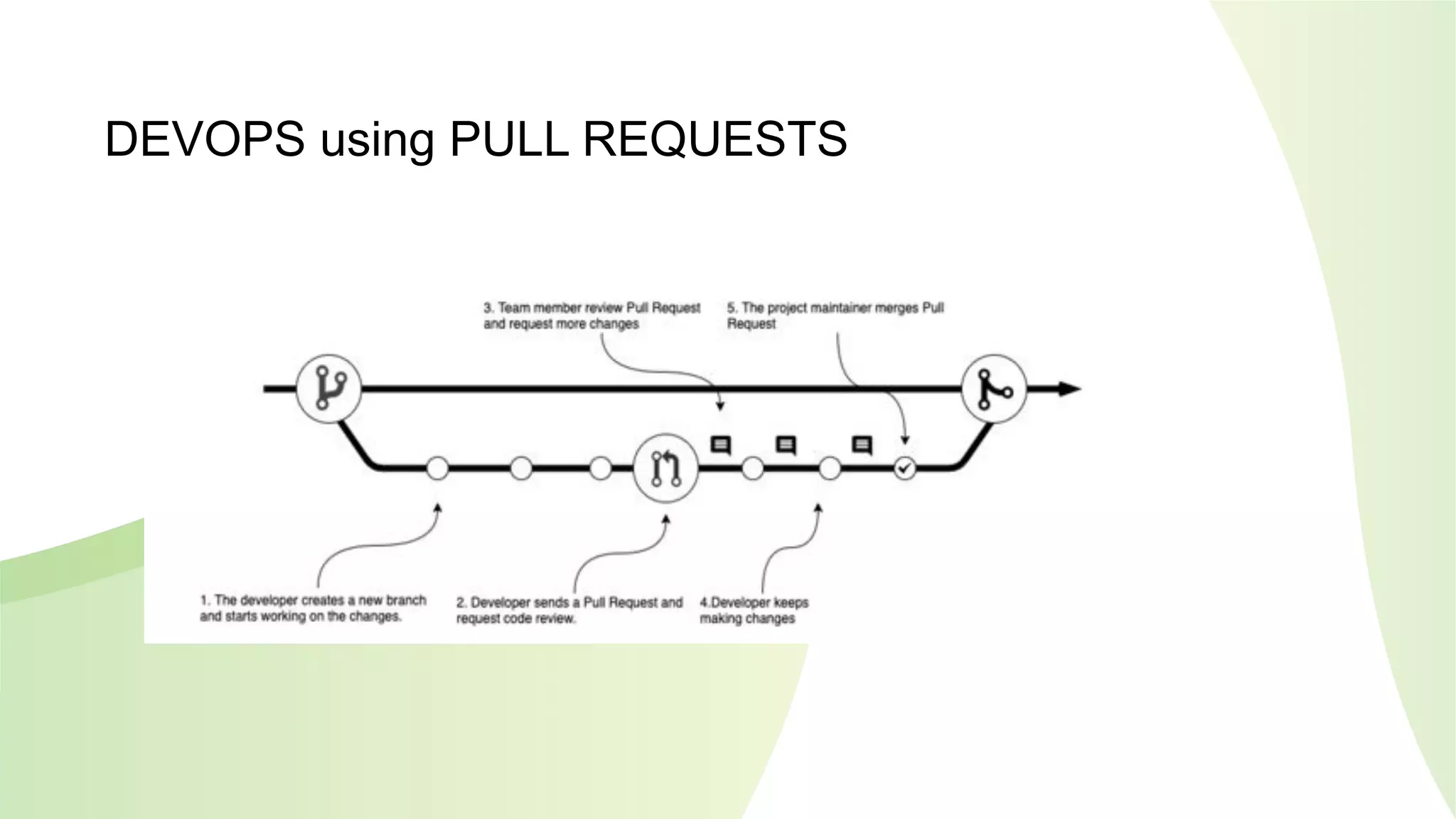
The document discusses enabling API management using a GitOps framework. It describes key components needed for API management like the OpenAPI spec, implementation code, infrastructure code, integration configuration, API management configuration, API gateway configuration, and API catalog. Using GitOps provides benefits like empowering developers to manage infrastructure configuration similarly to code using Git, keeping configurations declarative and version controlled, and enabling simple, automated, auditable deployments that detect deviations from the configuration.