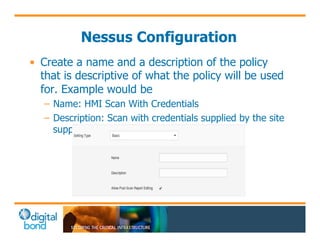
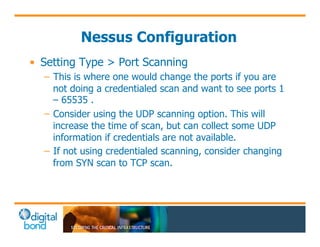
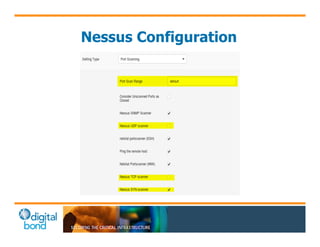
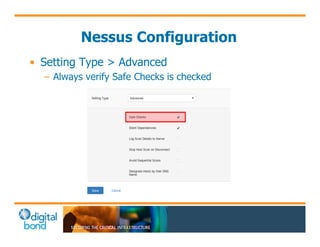
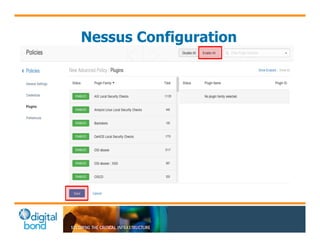
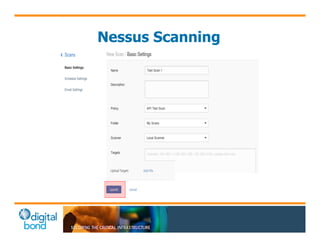
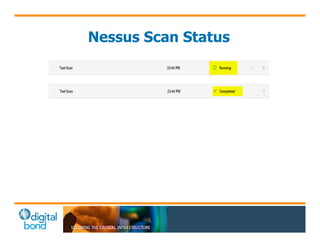
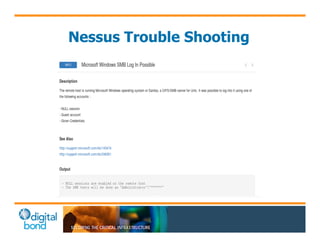
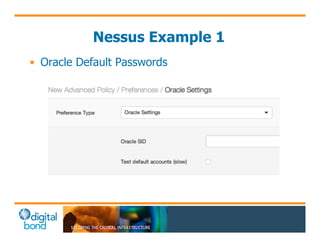
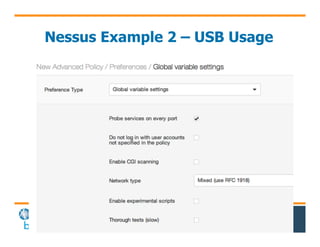
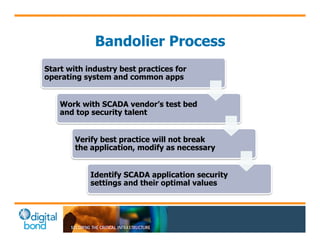
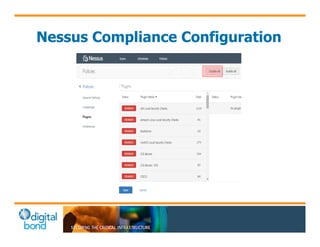
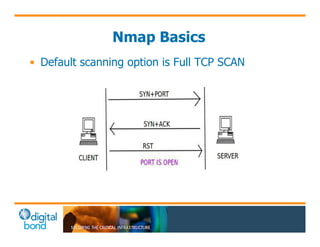
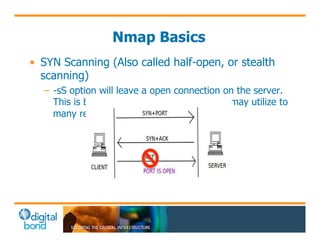
The document discusses the use of cybersecurity assessment tools on Industrial Control Systems (ICS), emphasizing Digital Bond's expertise in performing thorough security assessments since 2000. It outlines various assessment types, the importance of secure configuration, and risk reduction strategies while highlighting issues with ICS protocols that are insecure by design. Additionally, it provides detailed guidance on scanning methodologies, specific tools like Nessus, and effective patch management practices tailored for ICS environments.




















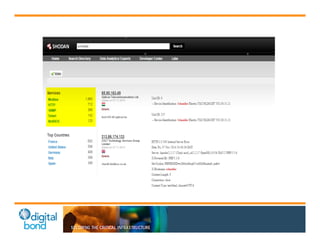
![Nessus Basics
• Nessus is a proprietary comprehensive
vulnerability scanner which is developed by
Tenable Network Security. Nessus is the world's
most popular vulnerability scanner, taking first
place in the 2000, 2003, and 2006 security tools
survey.[2] Tenable Network Security estimates
that it is used by over 75,000 organizations
worldwide.
– http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nessus_(software)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/api-141110235709-conversion-gate02/85/API-Training-10-Nov-2014-21-320.jpg)