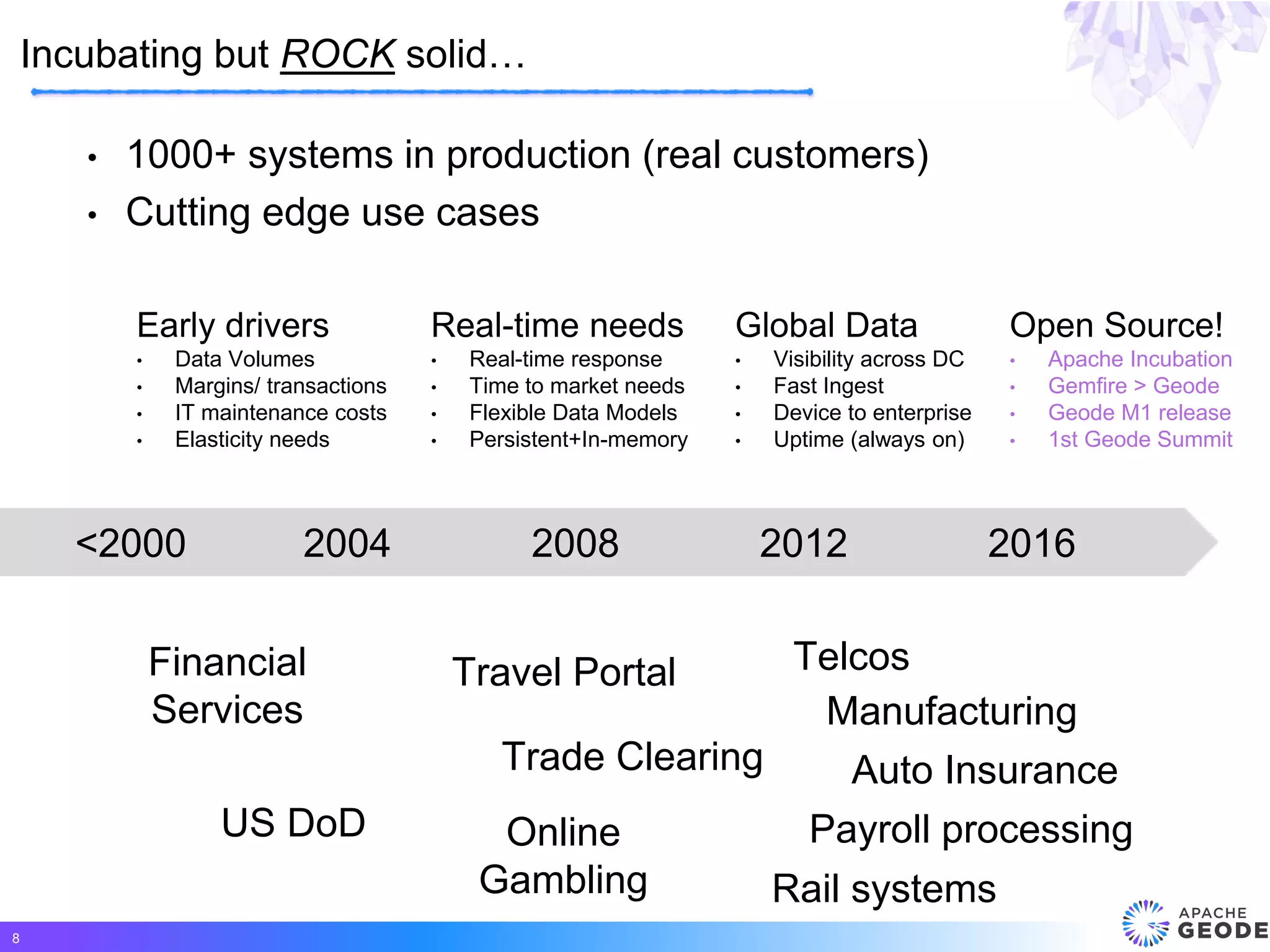
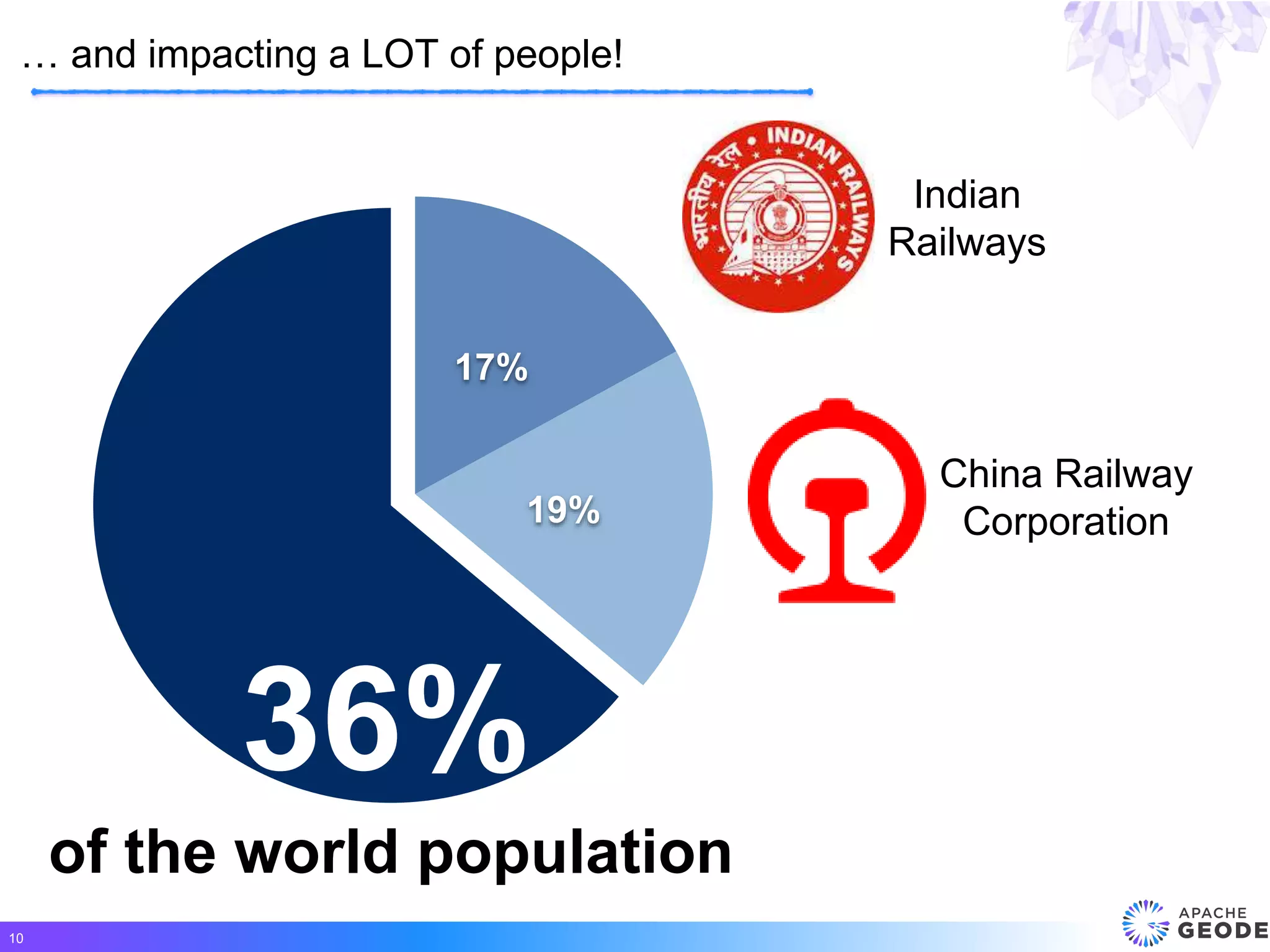
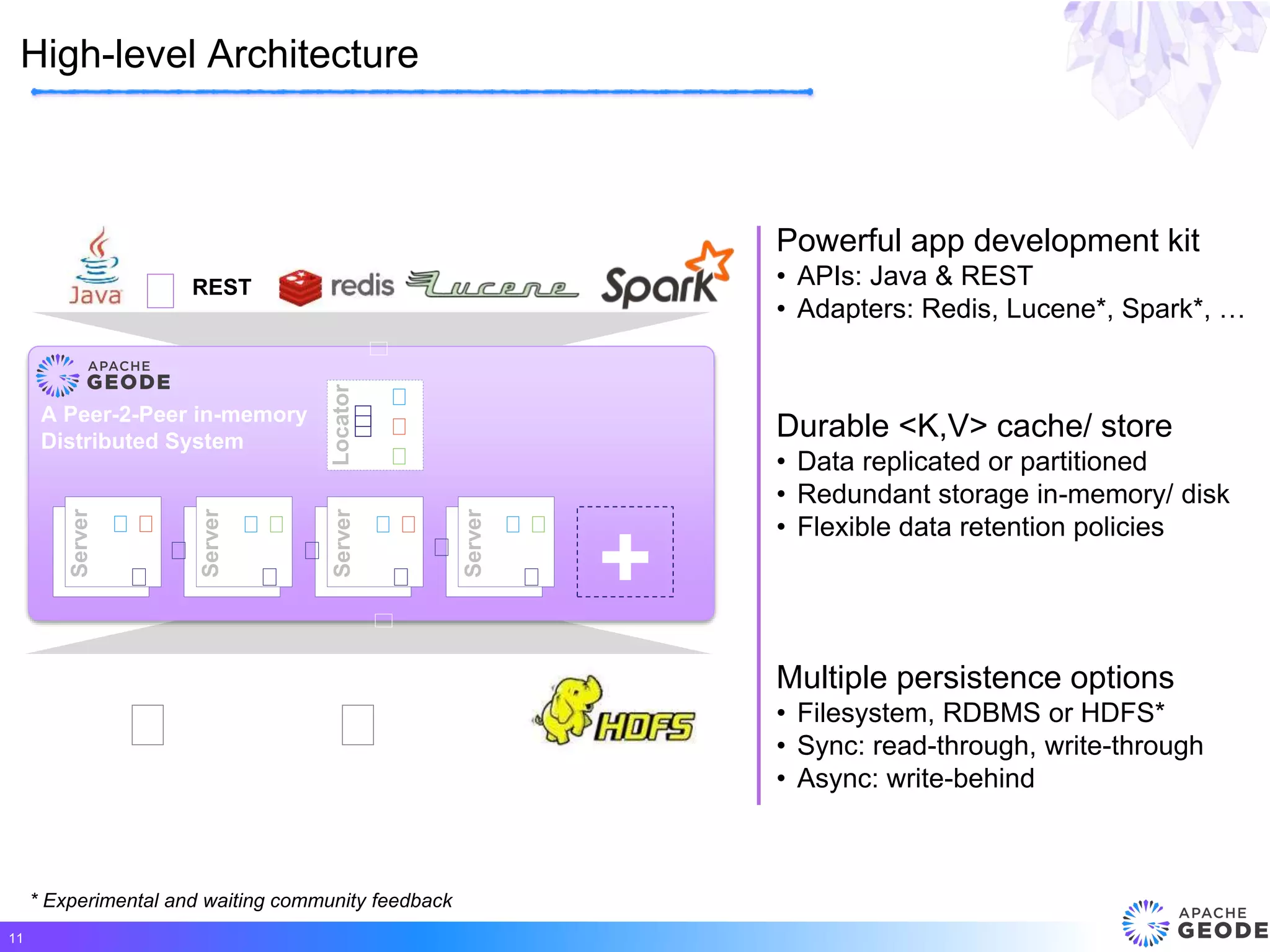
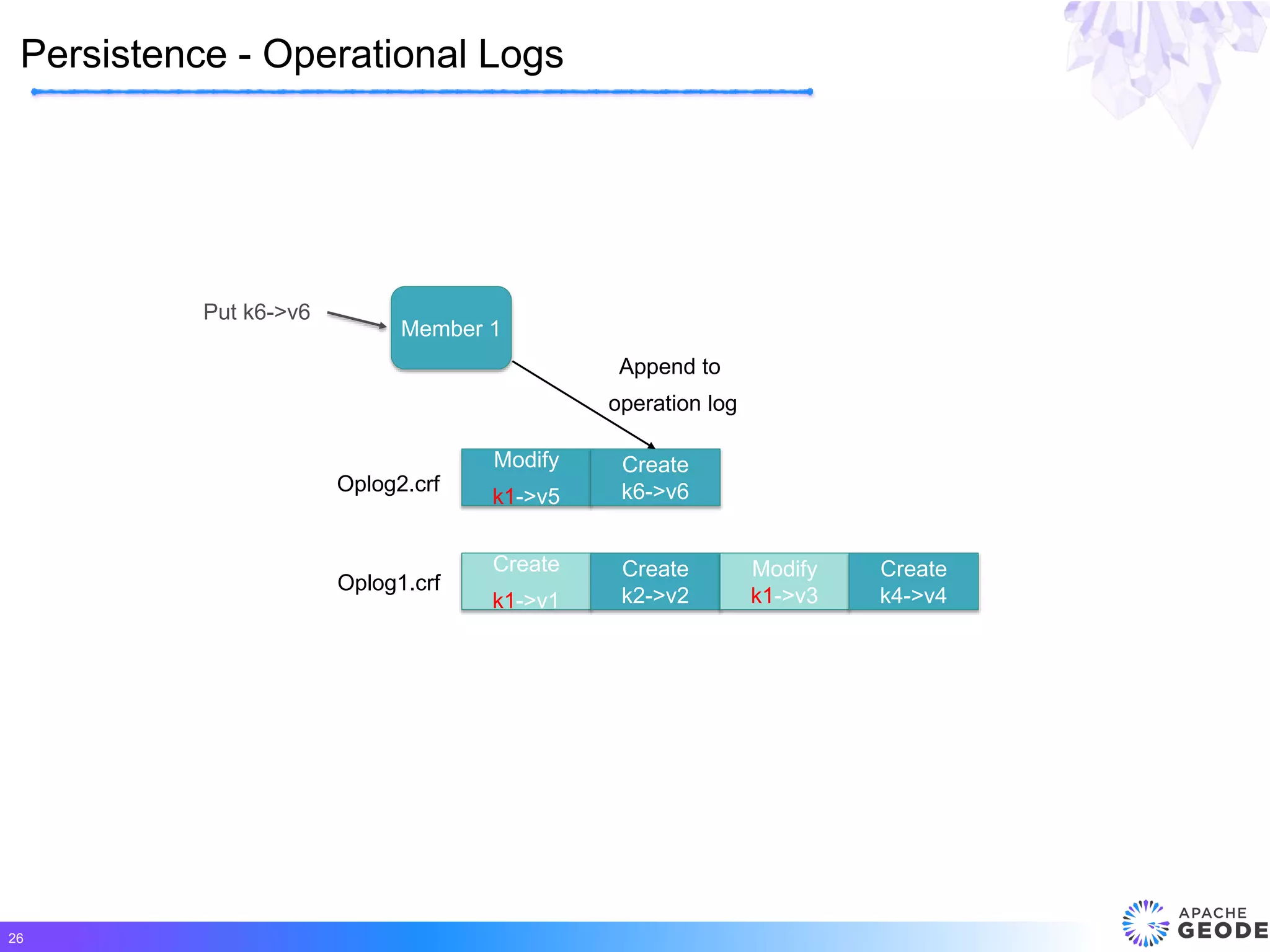
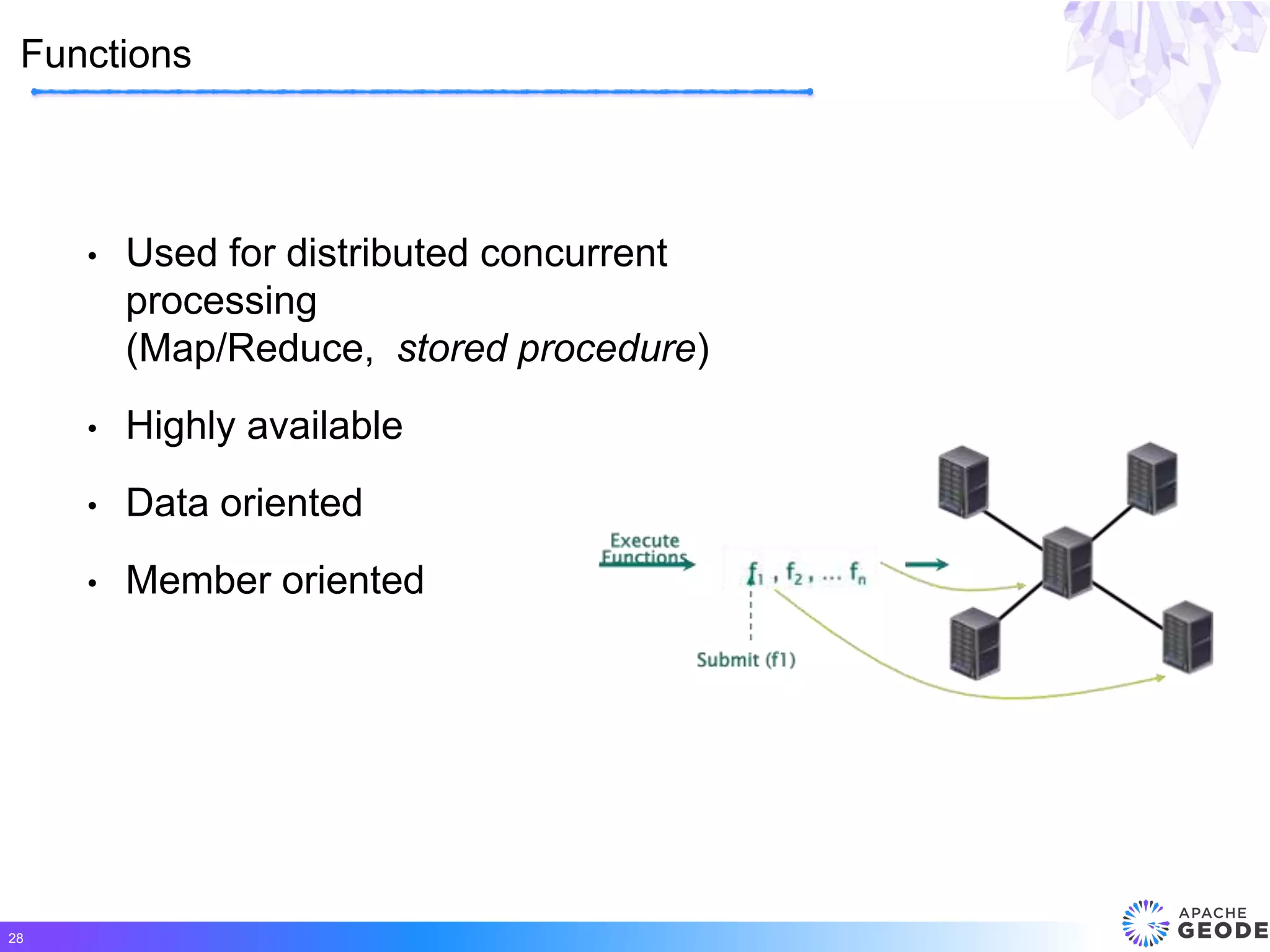
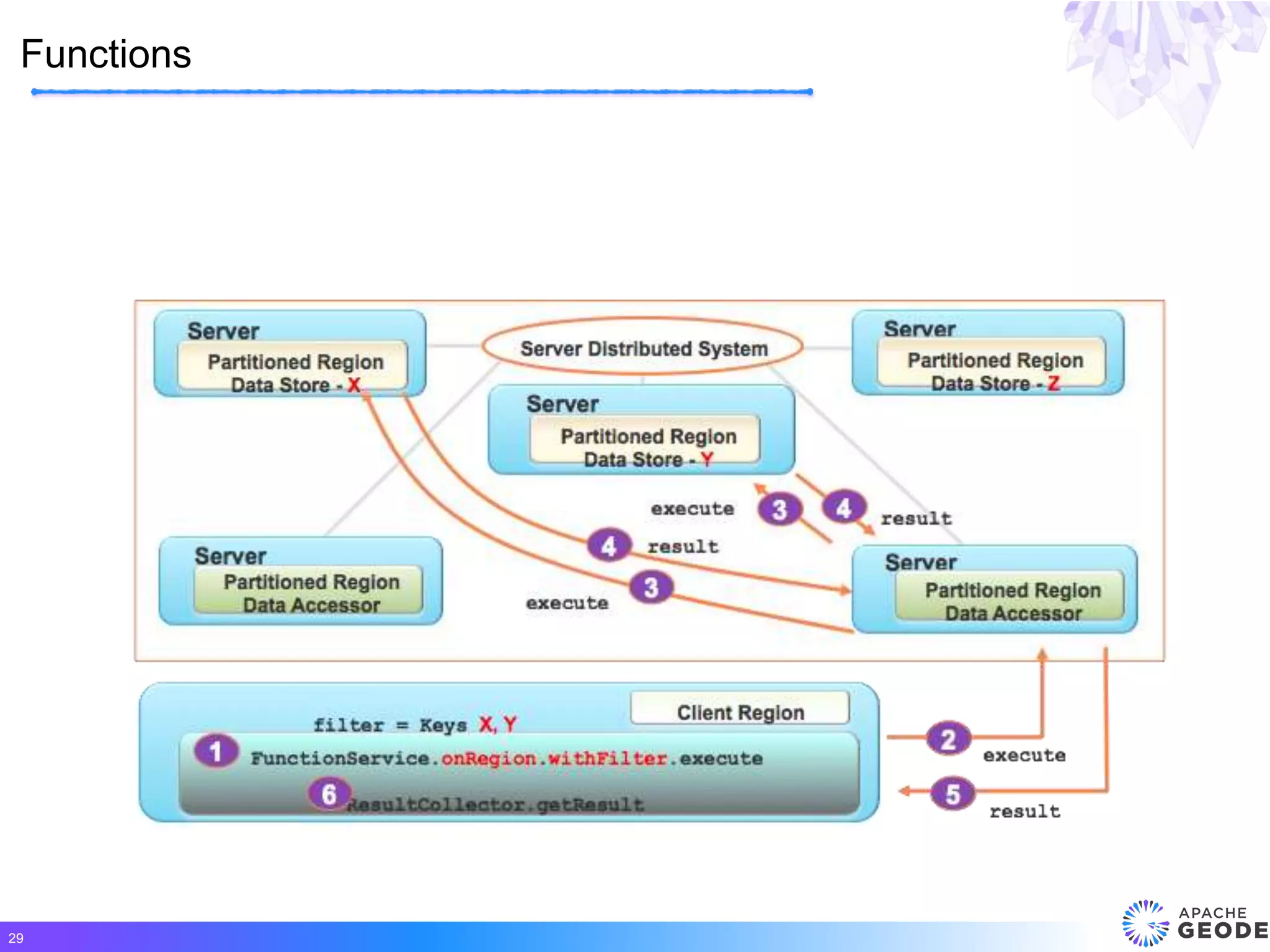
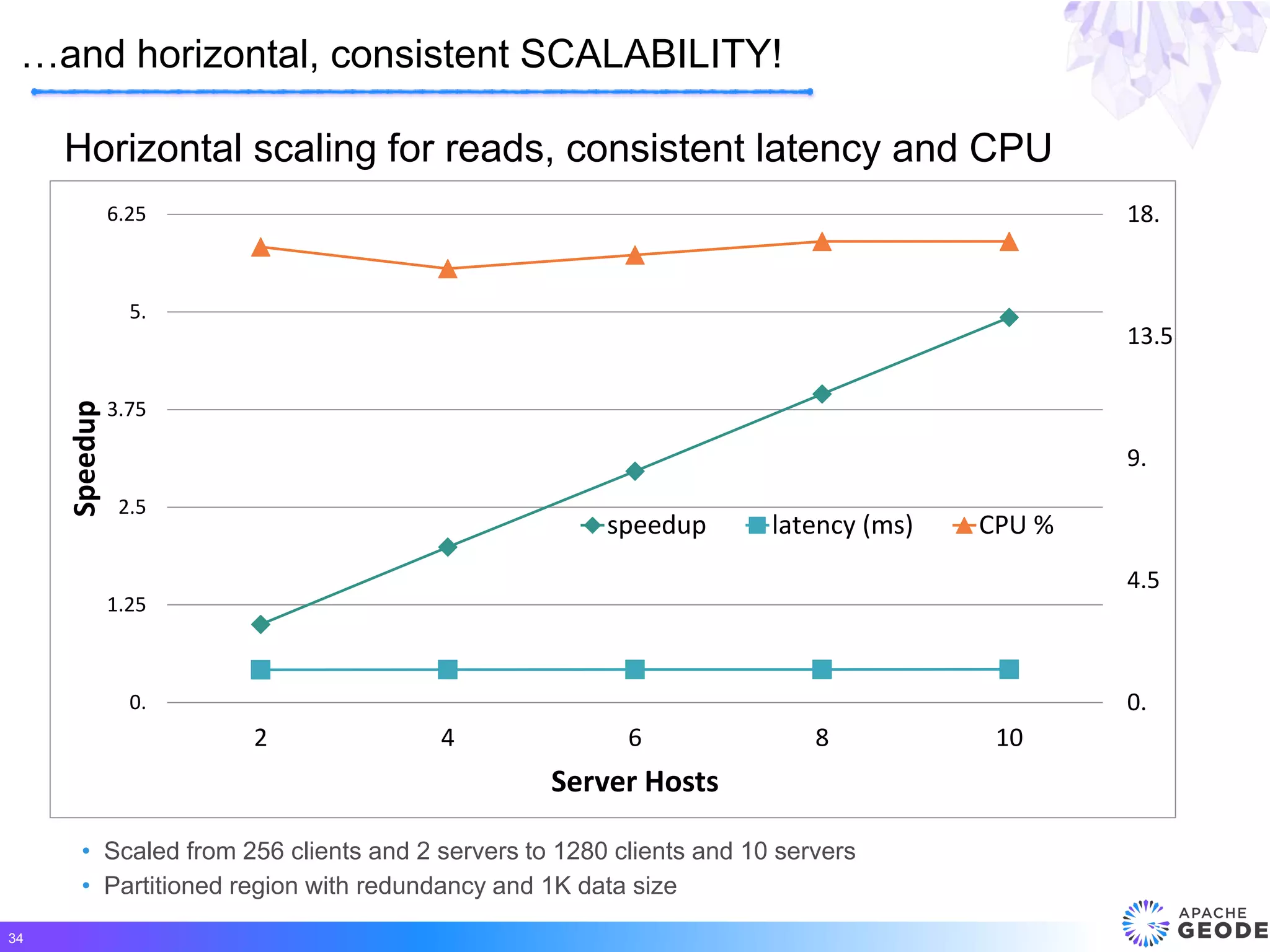
Apache Geode is a distributed, memory-based data management platform that provides high performance, scalability, resiliency and continuous availability for data-oriented applications. It originated from Pivotal's open sourcing of Gemfire in 2015. Some key features of Geode include fast access to critical datasets, location-aware distributed data processing, and an event-driven data architecture. It has been used in many large-scale production systems and sees adoption rates increasing.