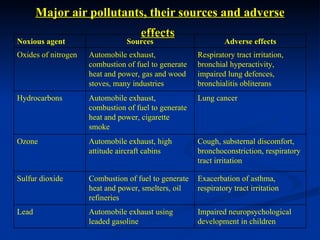
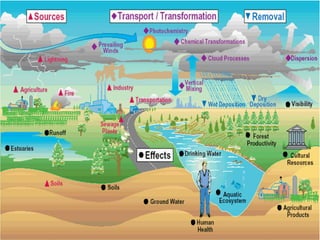
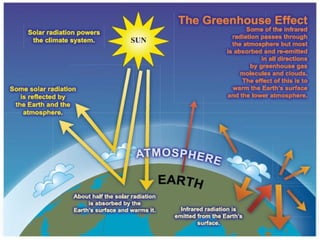
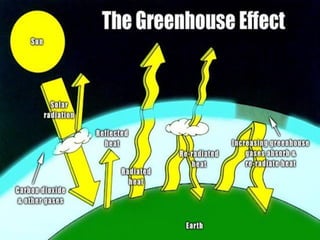
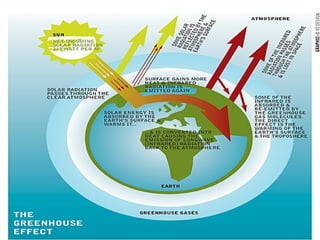
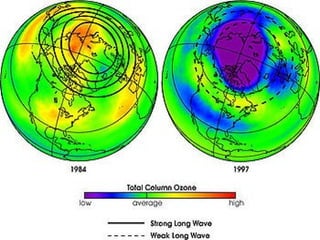
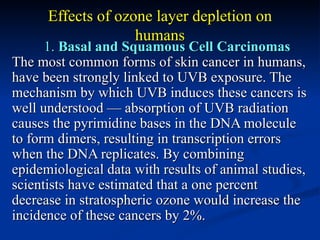
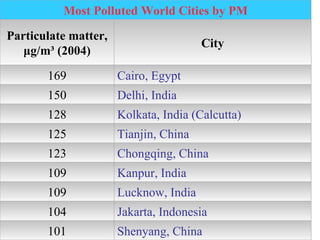
Air pollution is caused by both natural sources like dust storms and volcanic emissions, as well as human activities such as burning fossil fuels. The main primary pollutants from human activity are nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, carbon monoxide, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds emitted from vehicles, power plants, industry, and other sources. These primary pollutants can then form secondary pollutants in the atmosphere through complex chemical reactions. Air pollution poses risks to human health through respiratory and cardiovascular issues and can also damage ecosystems and contribute to global warming through increased greenhouse gases.