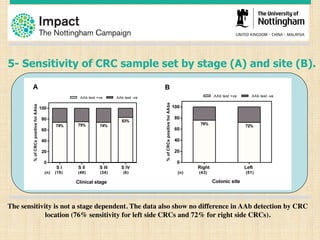
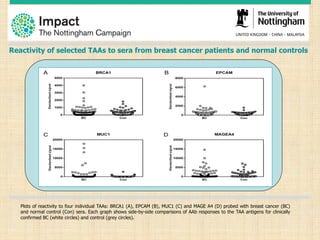
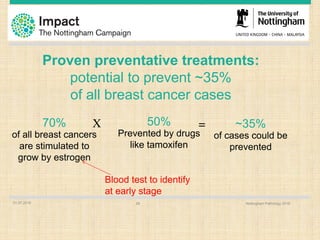
This document discusses the potential for a blood test to enable early cancer detection. It notes that cancer incidence is predicted to double worldwide by 2030 while survival rates for many cancers have changed little in recent decades. Early detection through screening has been shown to significantly reduce mortality for some cancers like breast, lung, and colon cancer. The document proposes a blood test that could detect autoantibodies produced in response to cancer cells, providing improved sensitivity and specificity over other screening methods. It summarizes pilot studies showing this approach can detect colorectal, lung, and breast cancers at early stages with promising sensitivity and specificity. The goal is to make early cancer detection more accessible and improve clinical outcomes through increased survival rates and reduced treatment costs.



![Early detection and treatment has been shown to
significantly reduce mortality:
Randomised trials (‘Level 1’ evidence)
• Breast Cancer - Mammography (50-74yrs)
– 23% reduction in deaths from breast cancer
– [NB: only ~1/3rd of BCs occur between 50-74]
• Lung Cancer – CT scans (55-74yrs, >30 pys)
– 20% reduction in deaths from lung cancer
– [NB: Only ~1/3rd LCs occur in NLST trial]
• Colon Cancer – faecal occult blood test + colonoscopy (>50yrs)
– 16% reduction in deaths from colon cancer
– [NB: Only ~1/3rd individuals accept colon screening]
01.07.2016 Nottingham Pathology 20164](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c1df2bed-de9a-4203-89d1-35f5e997f907-170107171428/85/Antigen-Microarray-Technology-for-Early-detection-of-Solid-Cancers-4-320.jpg)