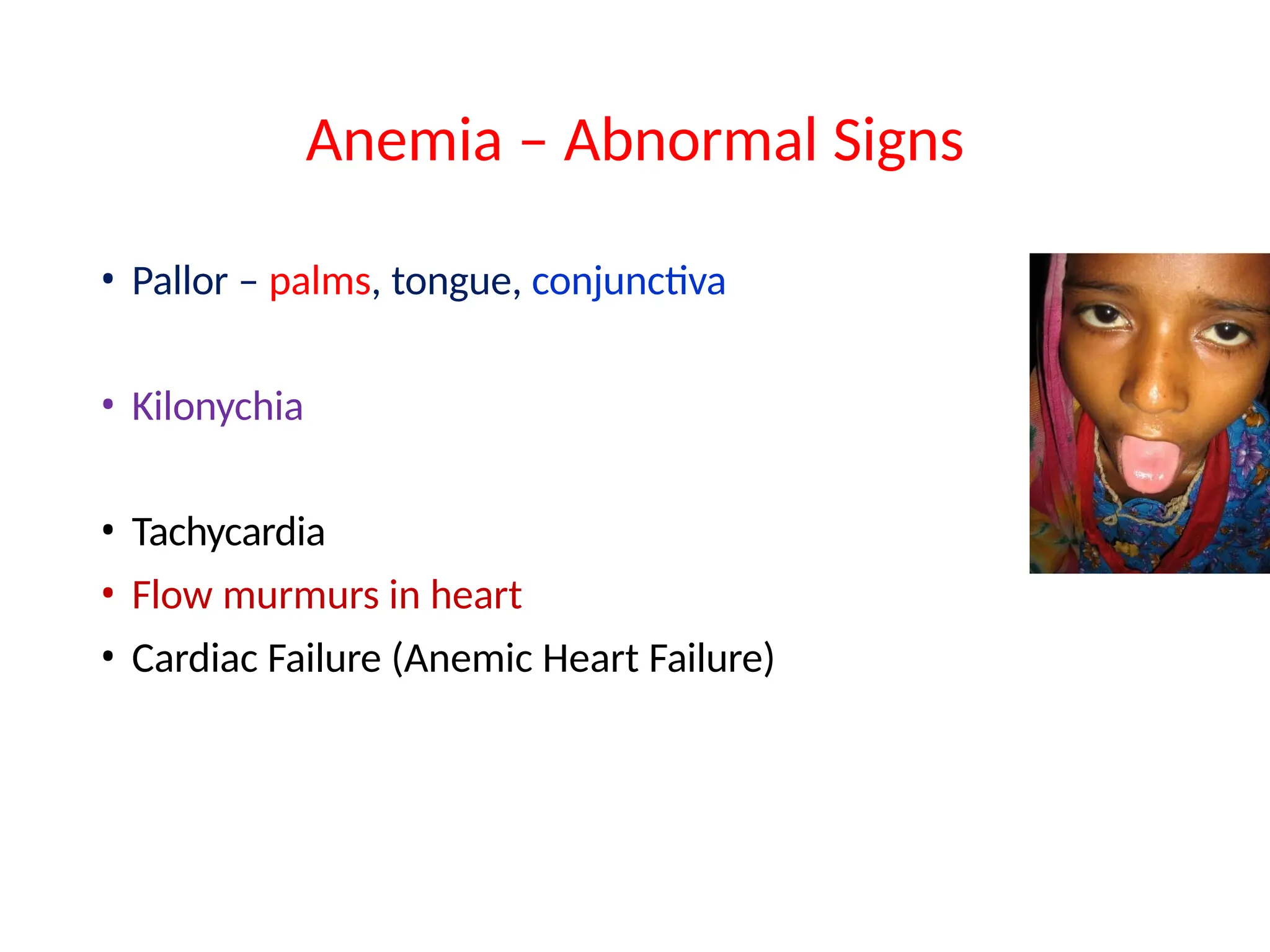
The document provides a comprehensive overview of anemia in children, including its epidemiology, clinical features, and classification. Anemia is prevalent among children, especially in Pakistan, with symptoms ranging from pallor and fatigue to irritability. It discusses various etiologies such as nutritional deficiencies, chronic diseases, and genetic conditions, along with diagnostic approaches and types of anemia.