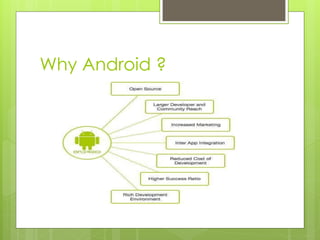
Android is an open-source, Linux-based operating system designed for mobile devices, developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance. It offers a unified approach to application development, supports a wide range of features, and has a continually evolving version history with significant updates enhancing performance, user interface, and security. As of October 2023, the latest version is Android 14, which emphasizes customization and efficiency improvements.