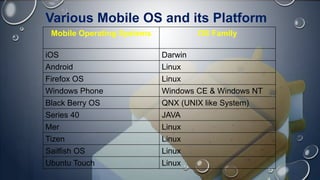
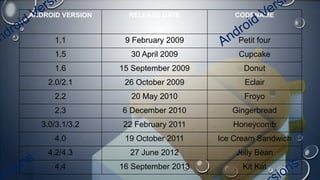
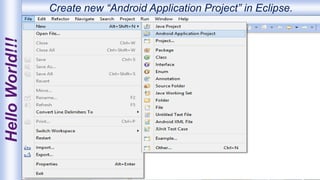
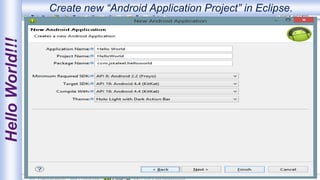
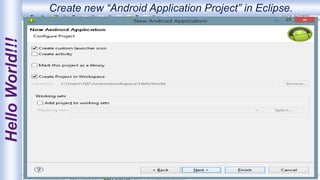
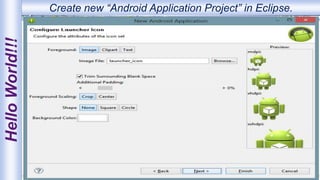
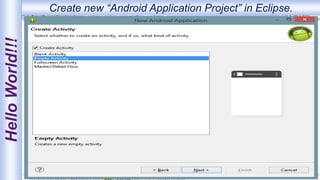
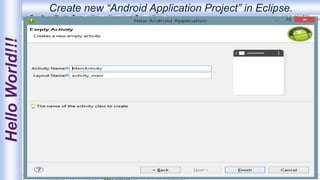
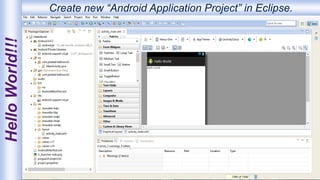
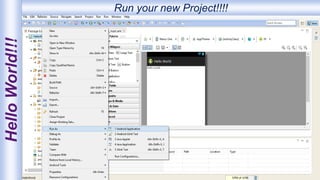
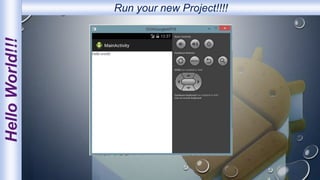
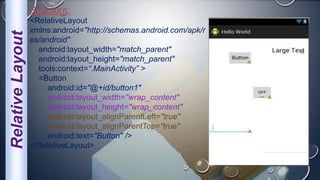
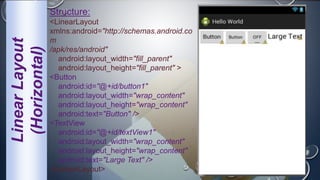
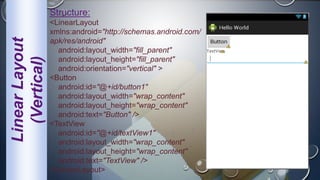
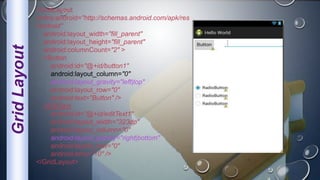
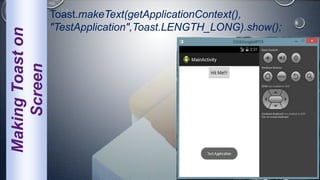
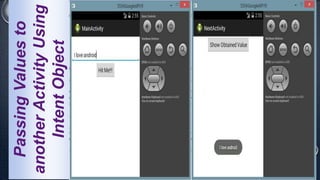
Android is an open-source, Linux-based operating system that was originally developed by Android Inc. and is now maintained by Google. It uses SQLite for data storage, supports connectivity through cellular networks and WiFi, and includes features like messaging, web browsing, media playback, and multi-touch input. The Android architecture includes components like activities, services, content providers and broadcast receivers that apps can use to perform tasks and interact with the system.