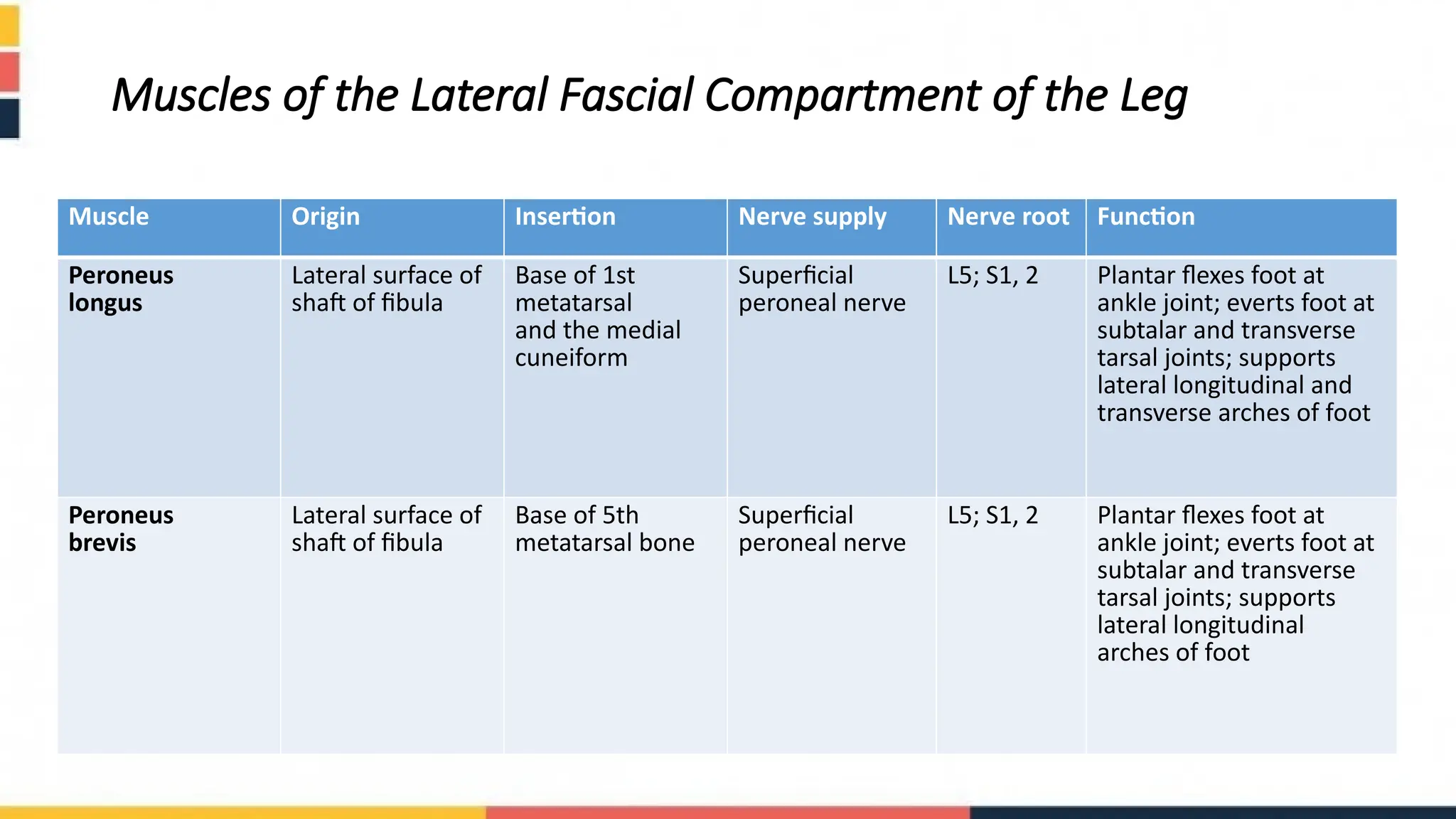
The document details the anatomy of the fascial compartments of the leg, including descriptions of the fascia, muscles, nerves, and blood supply for the anterior, lateral, and posterior compartments. It outlines the specific muscles within each compartment, their origins, insertions, nerve supplies, and functions. Key structures such as retinacula and cutaneous nerves are also discussed, along with their roles in support and mobility of the leg.