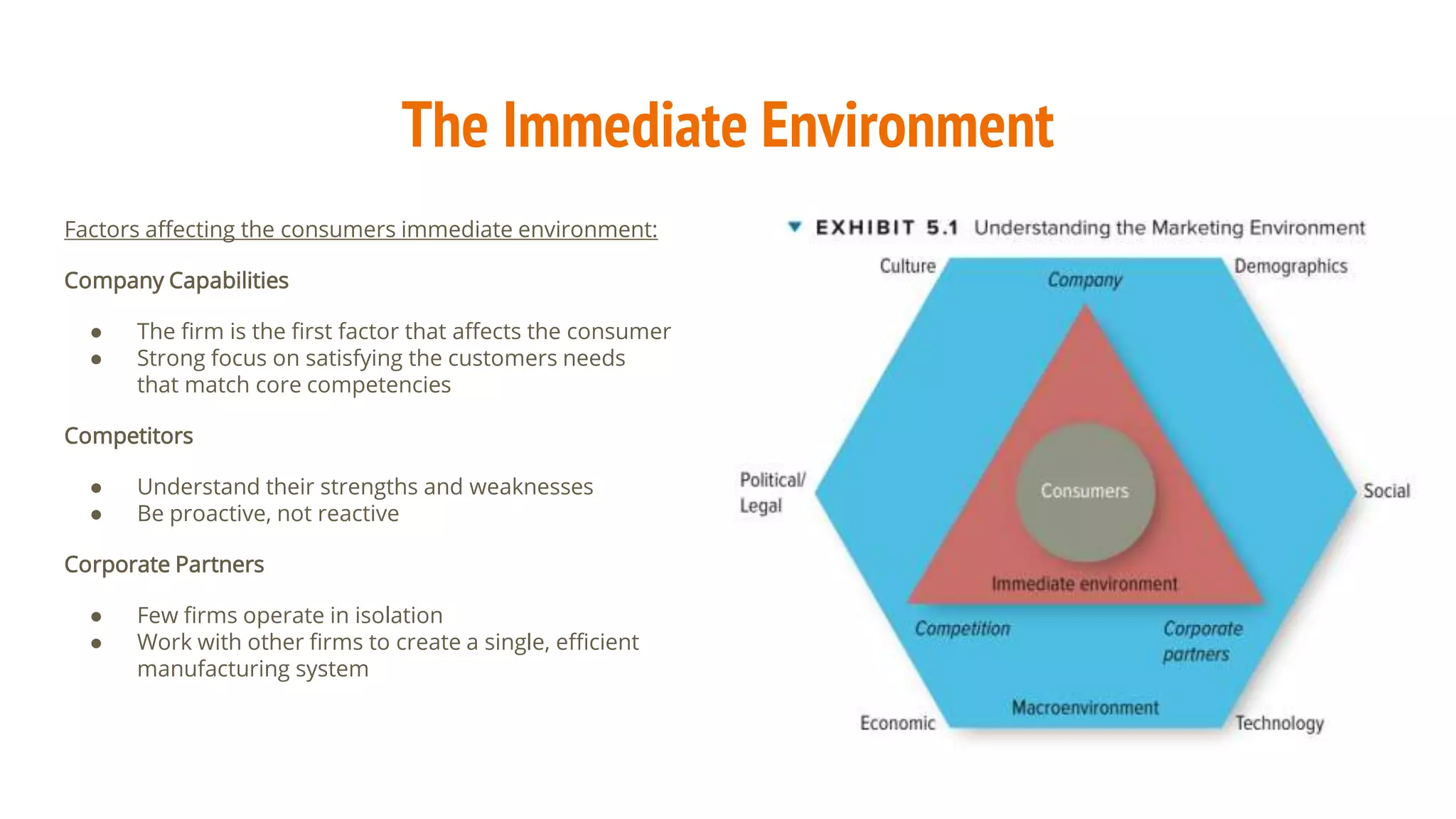
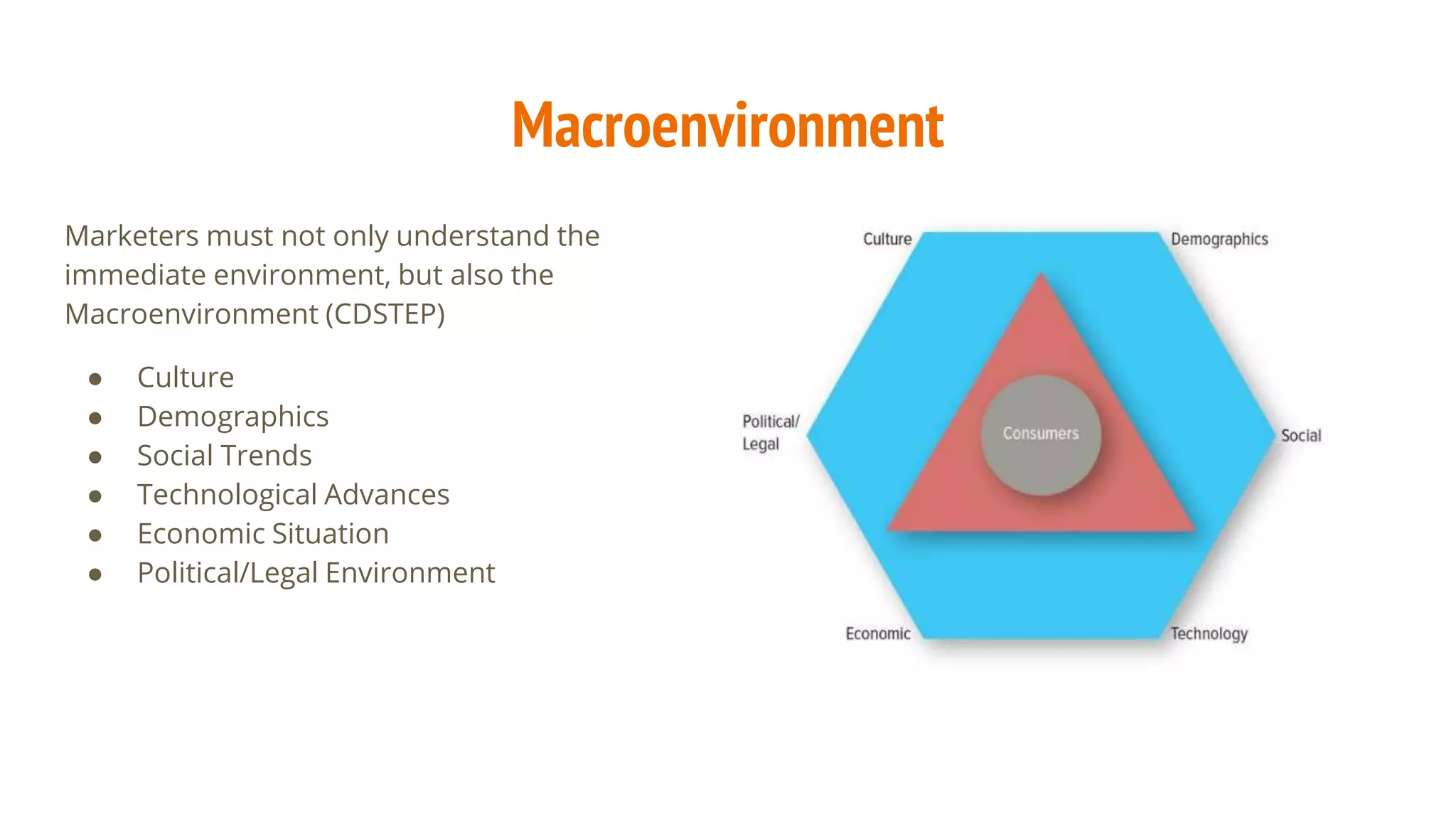
The document discusses the factors influencing the marketing environment, including immediate elements like company capabilities, competitors, and corporate partners, as well as broader macroenvironmental factors such as culture, demographics, social trends, technology, and economic conditions. It emphasizes the importance of sustainability in consumer preferences and the impact of technological advancements like AI and IoT on product value and efficiency. Additionally, it highlights regulatory concerns regarding consumer protection and fair competition in the marketplace.