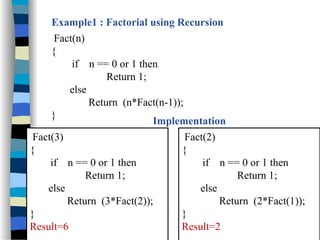
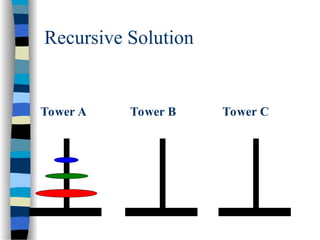
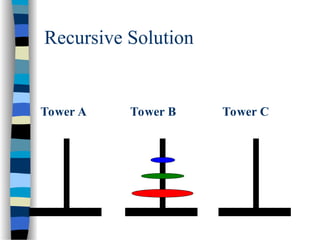
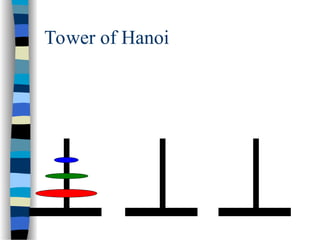
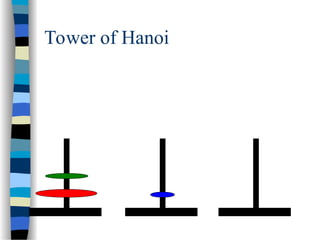
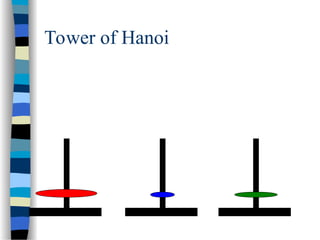
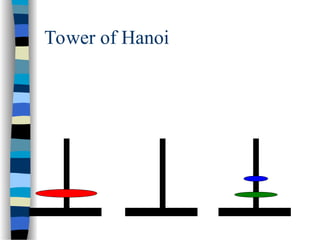
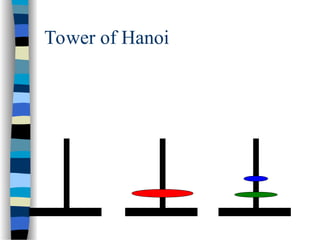
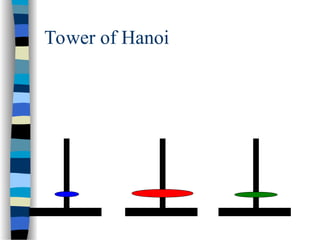
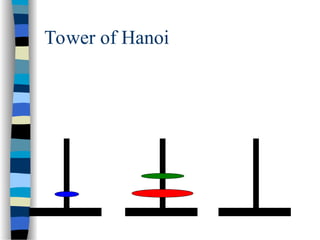
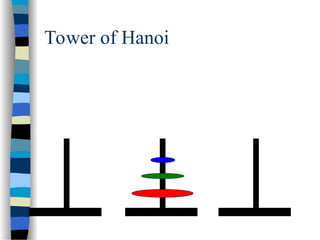
The document provides an introduction to algorithms, including their definitions, specifications, and complexities such as space and time complexity, along with a discussion on recursive algorithms. It features examples of recursion, specifically highlighting the calculation of factorials and the Towers of Hanoi problem. The examples illustrate the powerful nature of recursive functions and how they can be applied to solve complex problems.