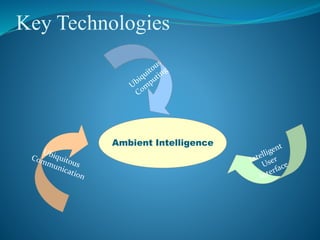
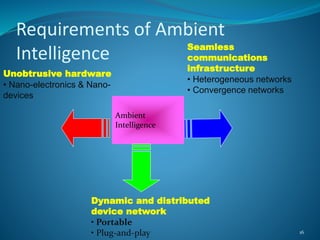
Ambient intelligence (AmI) refers to digital environments that are sensitive, adaptive, and responsive to human presence and needs. AmI aims to enhance safety and quality of life through networked sensors and devices that recognize users and adapt environments accordingly. Key technologies enabling AmI include ubiquitous computing, ubiquitous interfaces, and ubiquitous communications. Major applications of AmI include healthcare monitoring, public transportation, education, emergency services, and production monitoring through technologies like sensors, RFID, affective computing, and biometrics. While AmI promises benefits, challenges include high costs, ensuring user acceptance, and addressing security and privacy risks.