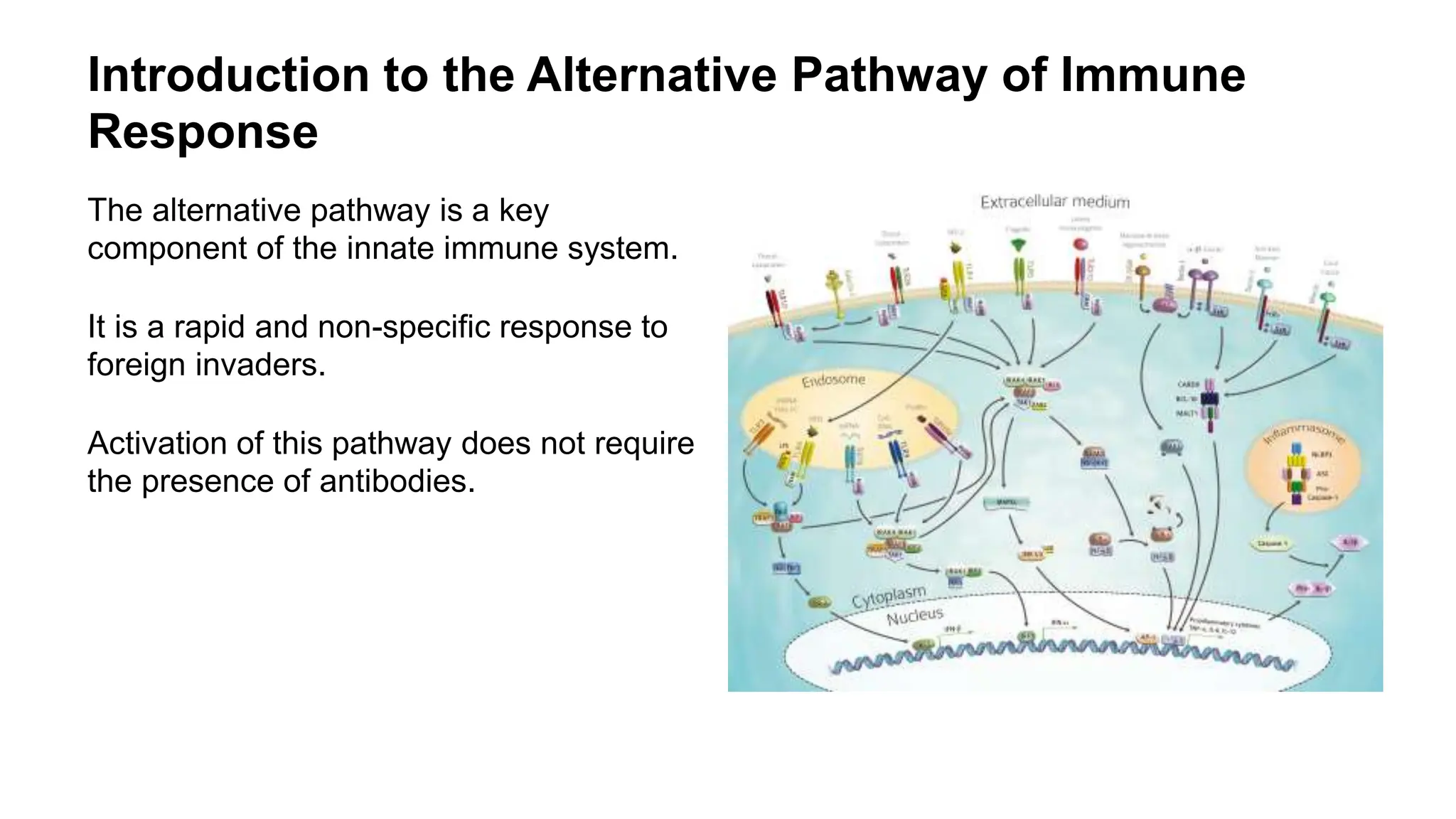
The alternative pathway of immune response is a crucial part of the innate immune system, offering rapid, non-specific defense against pathogens without the need for antibodies. Key components like factor B, factor D, and properdin are involved in activating the complement cascade, which enhances pathogen opsonization and lysis. Ongoing research aims to explore its mechanisms and therapeutic potentials for various diseases, particularly in the context of immune dysregulation and inflammation.