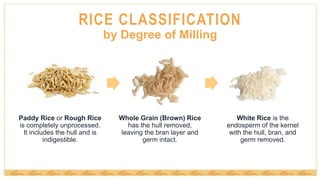
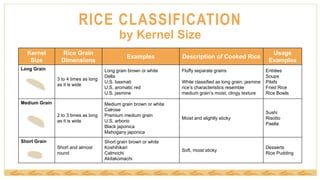
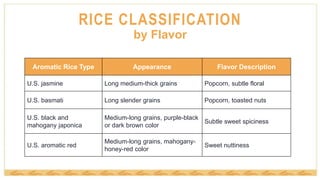
This document provides an overview of rice classification and nutrition. It discusses how rice is categorized by degree of milling, kernel size, starch content, and flavor. Long, medium, and short grain varieties are described. The nutrition content and benefits of rice are highlighted, including its versatility, low cost, and status as a gluten-free staple ingredient in many cuisines. Whole grain brown rice is noted as a source of fiber, phytonutrients, and antioxidants.