This document is a comprehensive guide to learning Python, highlighting its features, versatility, and usage in various fields. It provides instructions for setting up Python, covers essential programming concepts such as control structures, functions, and data structures, and includes programming examples. Ultimately, it emphasizes Python's importance in modern computing and encourages further exploration through projects.






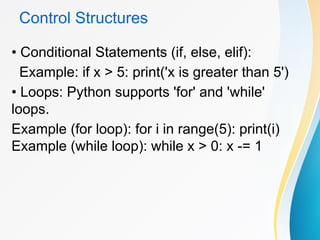

![Data Structures in Python
• Lists: Ordered and mutable collection of
elements.
Example: my_list = [1, 2, 3]
• Tuples: Ordered but immutable collection of
elements.
Example: my_tuple = (1, 2, 3)
• Dictionaries: Key-value pairs for storing
related data.
Example: my_dict = {'name': 'John', 'age':
25}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allaboutpythongrade8cambridge-241027133450-9bd7657d/85/All_About_Python_and_more-Cambridge-pptx-9-320.jpg)


