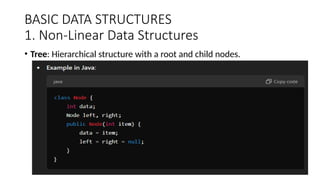
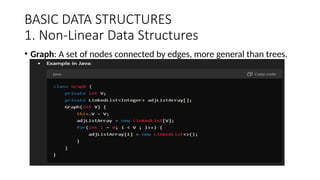
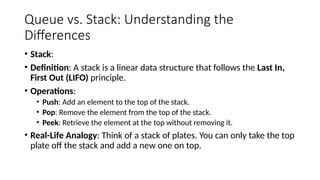
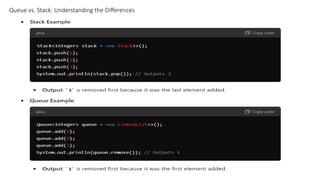
This document provides an overview of data structures and algorithms, defining key concepts such as data structure, algorithm, and their types. It discusses the importance of understanding data structures for efficient searching, improved performance, and managing concurrent data requests. Key characteristics, execution cases, and examples of various data structures like arrays, linked lists, stacks, and queues are also detailed.