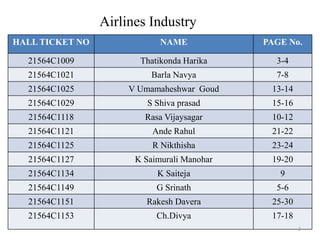
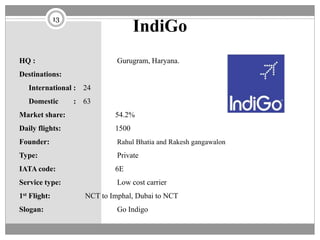
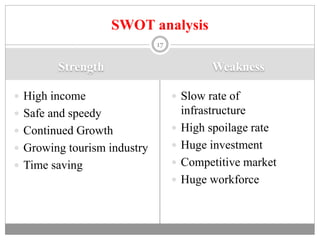
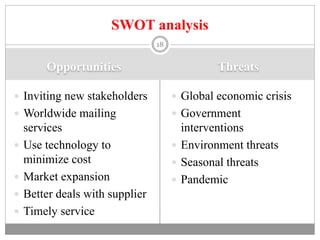
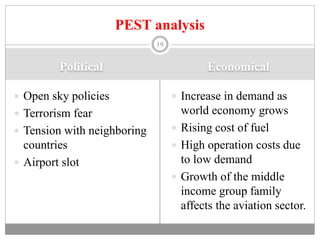
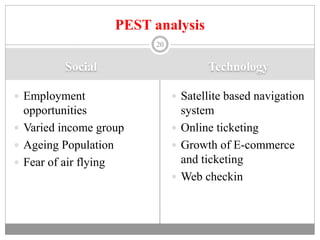
The document discusses the airline industry in India, detailing its historical development, current operations, and significant contributions to the economy. It highlights key players like Air India and Indigo, outlines the industry’s impact on GDP, and addresses recent challenges and policies, including responses to the COVID-19 pandemic. Additionally, it outlines the government's vision for future growth, emphasizing regional connectivity and affordability in air travel.