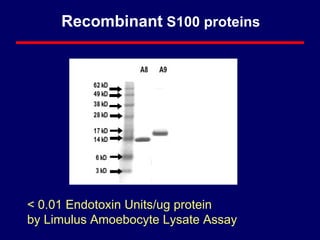
1) S100A8 and S100A9 are proteins expressed by neutrophils and macrophages that are secreted during inflammation and recruit lymphocytes.
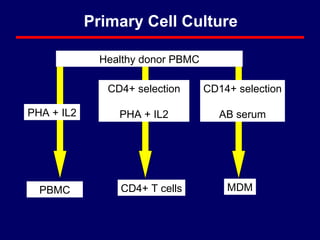
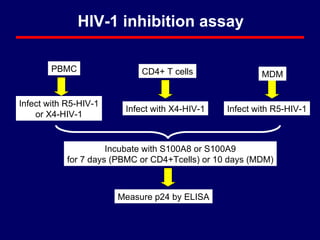
2) The study evaluated the effect of S100A8 and S100A9 on HIV-1 replication in primary CD4+ T cells and monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs).
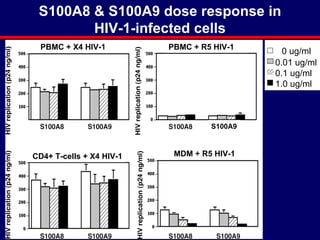
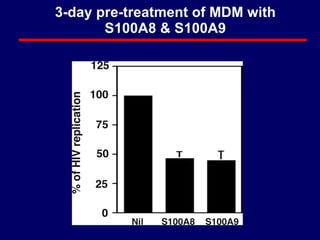
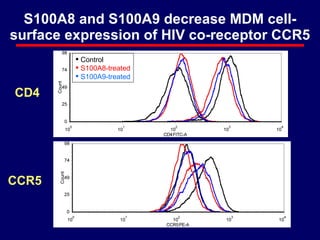
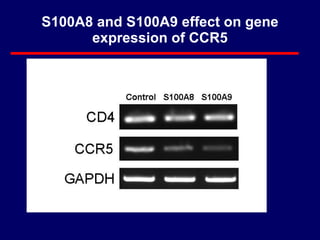
3) The results showed that S100A8 and S100A9 reduced HIV production in MDMs by decreasing expression of the HIV co-receptor CCR5, but did not inhibit HIV replication in CD4+ T cells or peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs).