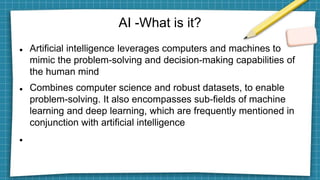
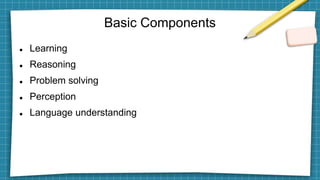
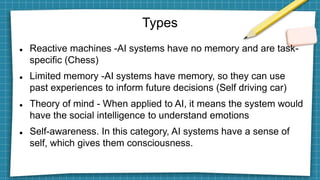
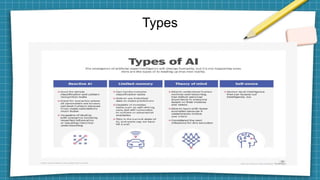
Artificial intelligence leverages computer science and large datasets to enable problem-solving capabilities similar to the human mind. There are two main types: weak AI which is designed for specific tasks, and strong AI which can solve unfamiliar problems autonomously. AI has many applications including speech recognition, automated trading, customer service chatbots, and computer vision. Key developments in AI include Alan Turing's 1950 paper, the coining of the term in 1956, and recent advances in neural networks that have led to systems that can beat humans at games like Go. Potential issues with AI include bias, privacy concerns, job loss, and lack of generalizability.