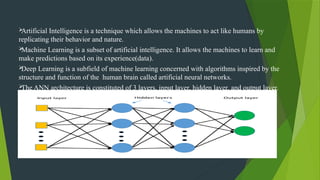
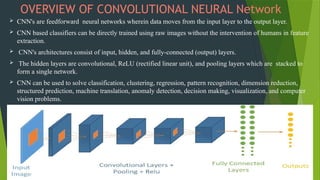
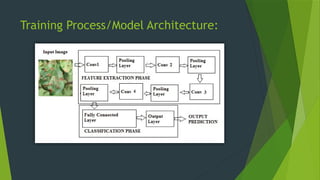
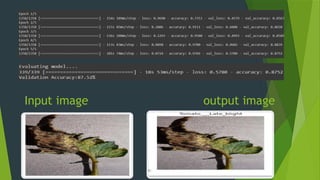
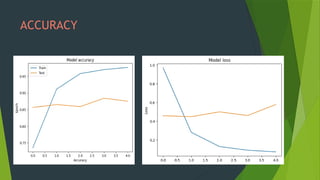
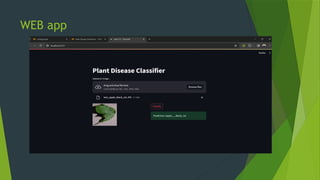
The project focuses on using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for the automatic classification of plant diseases, addressing a significant threat to agricultural productivity in India. It involves the use of a large dataset of 87,000 images representing 38 different diseases from various crops, aiming to improve early detection and monitoring through advanced machine learning techniques. Additionally, the trained model will be integrated into a Streamlit web application for user-friendly access to disease classification results.