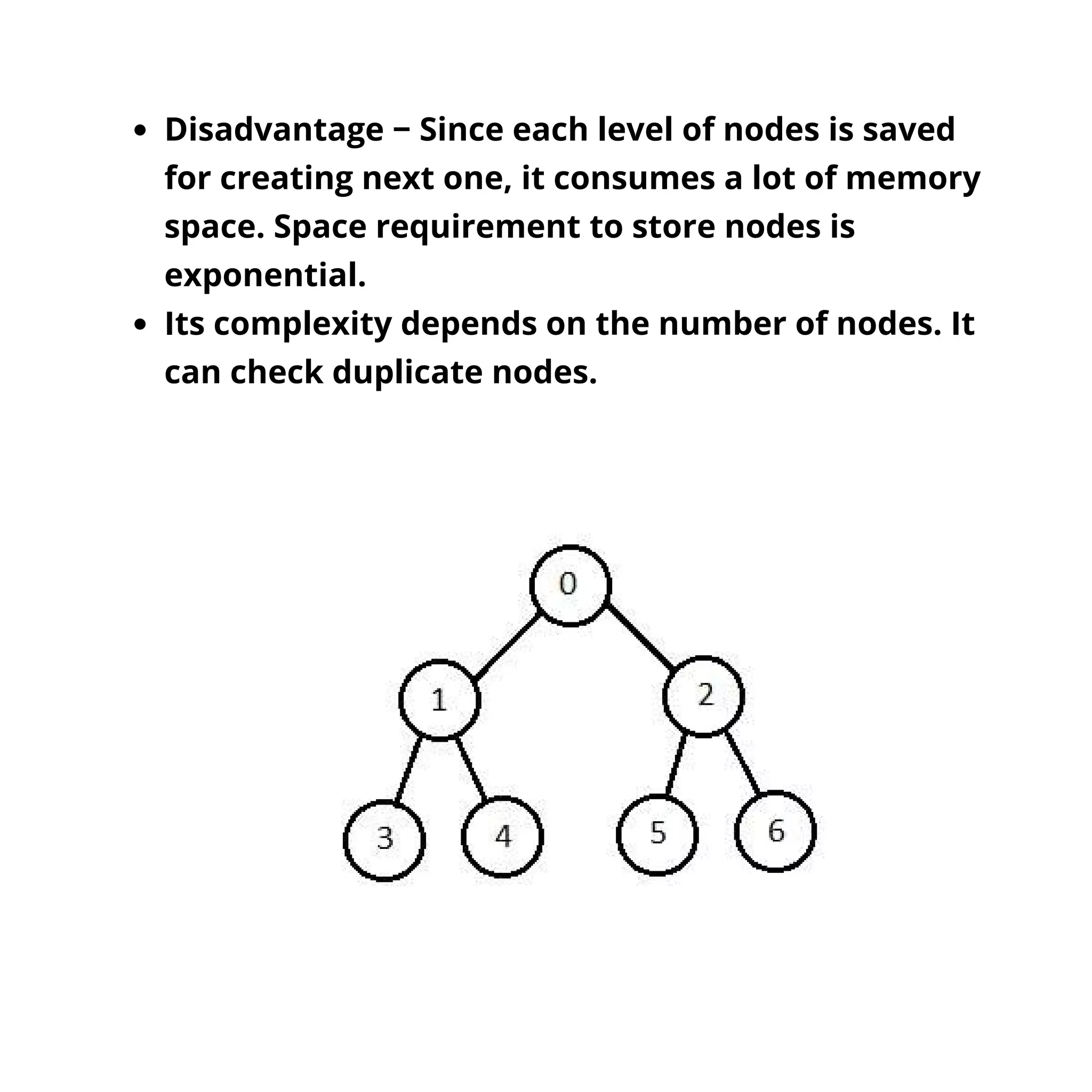
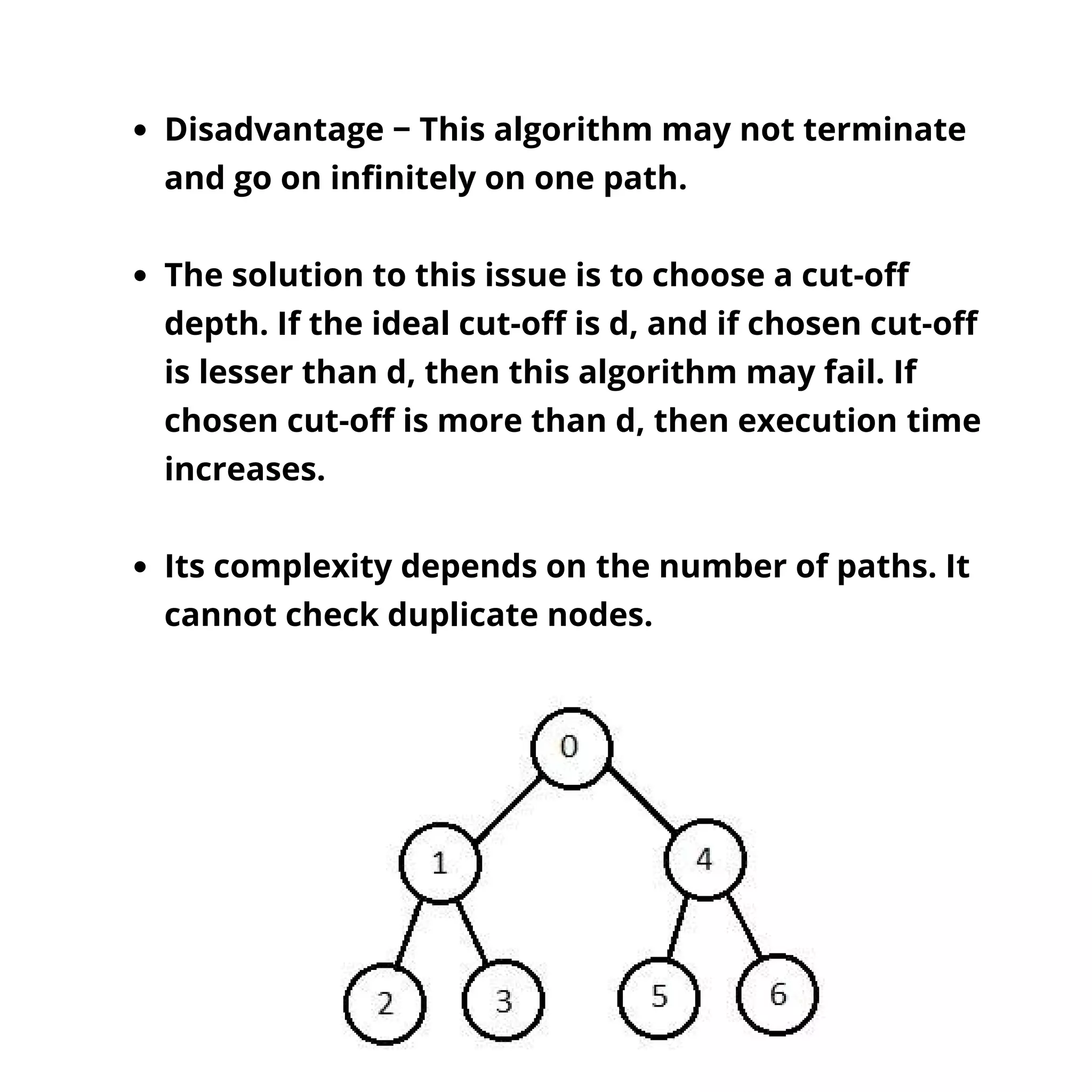
The document discusses popular search algorithms in artificial intelligence, particularly focusing on single-agent pathfinding challenges like tile puzzles and the traveling salesman problem. It explains concepts such as problem space, search terminology, and different search strategies like breadth-first and depth-first search, detailing their advantages, disadvantages, and complexity. The document highlights the importance of these algorithms in solving problems efficiently without requiring domain-specific knowledge.