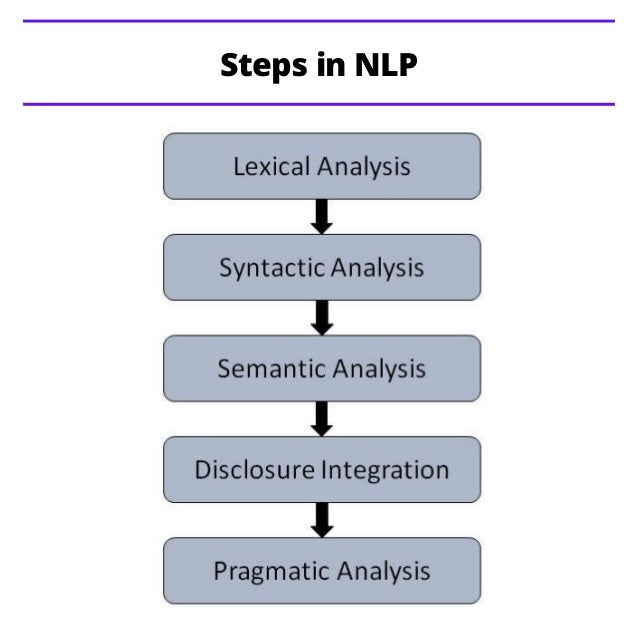
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables communication between humans and intelligent systems using natural languages. It consists of two main components: Natural Language Understanding (NLU), which interprets input, and Natural Language Generation (NLG), which produces meaningful language outputs. NLP faces challenges such as ambiguity at various levels and involves several linguistic studies, including phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, pragmatics, and discourse.