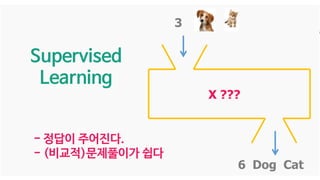
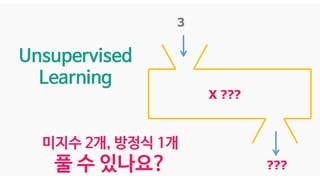
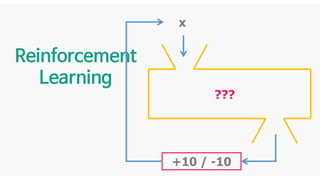
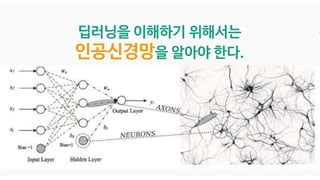
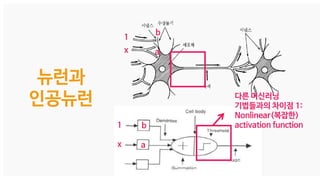
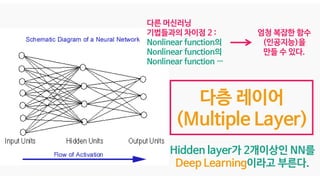
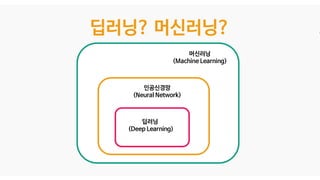
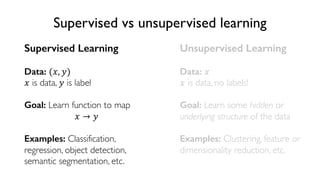
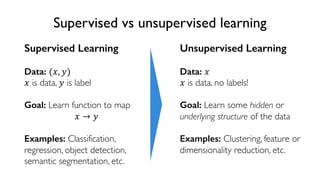
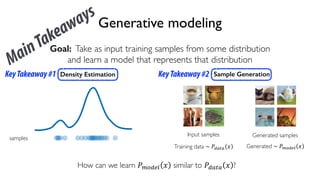
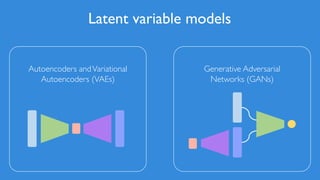
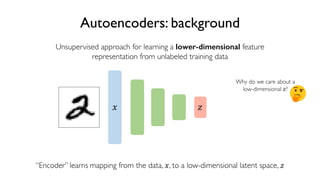
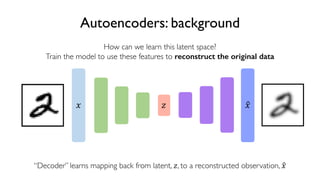
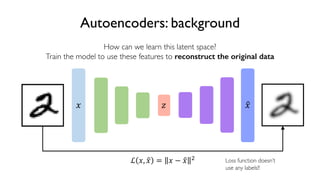
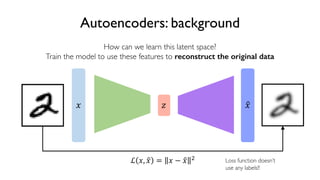
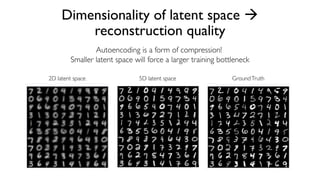
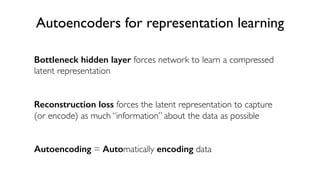
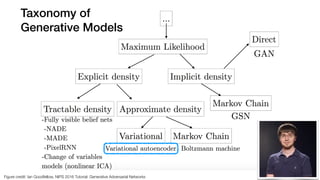
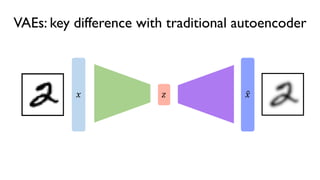
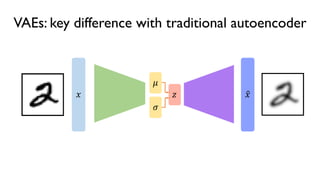
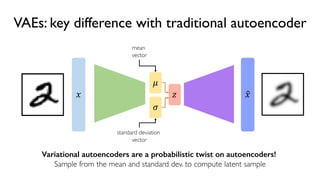
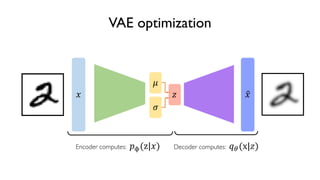
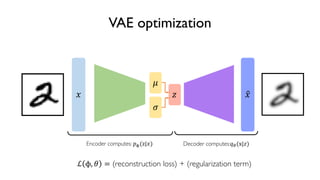
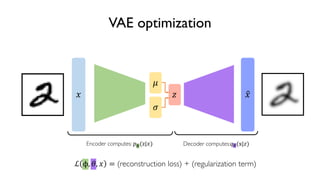
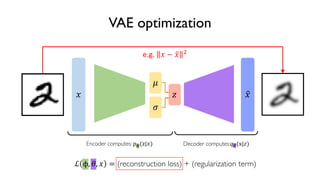
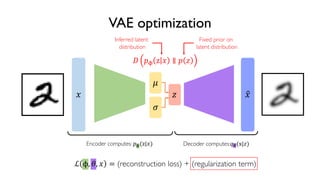
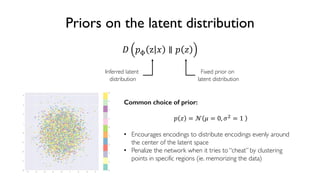
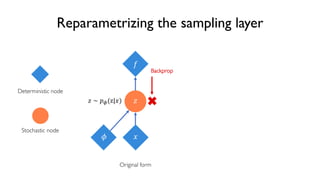
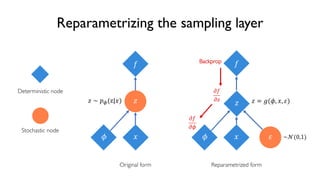
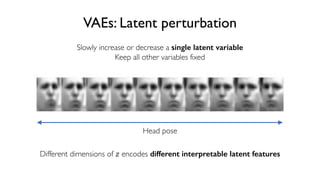
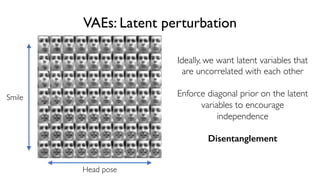
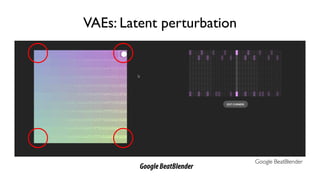
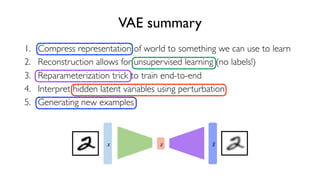
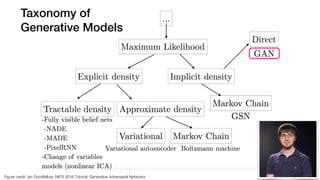
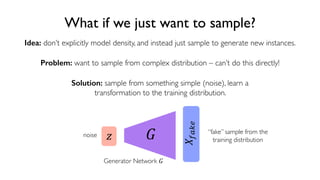
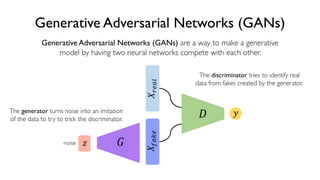
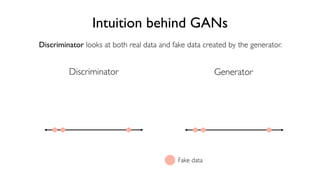
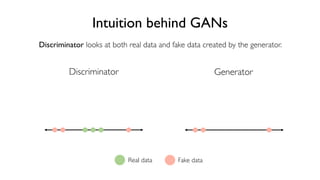
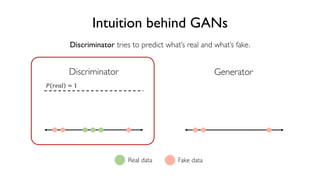
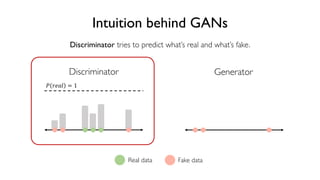
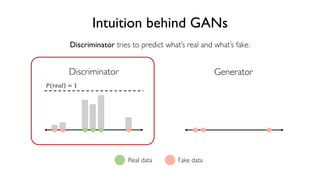
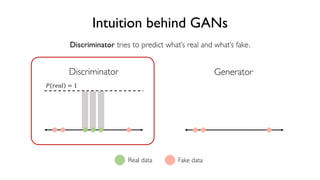
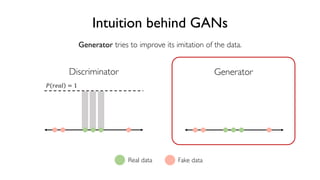
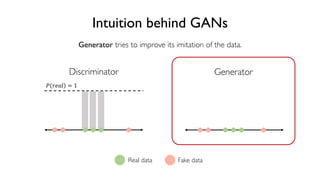
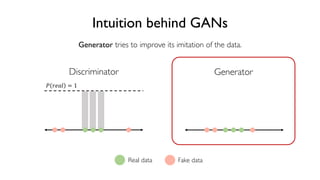
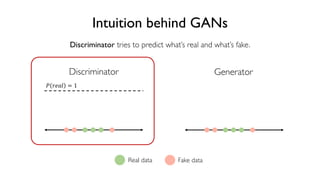
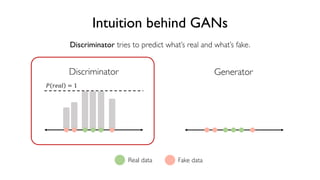
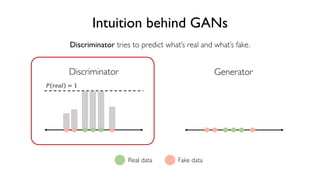
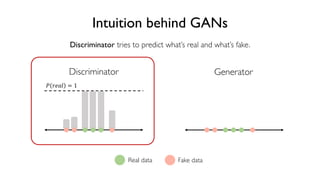
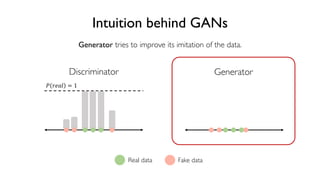
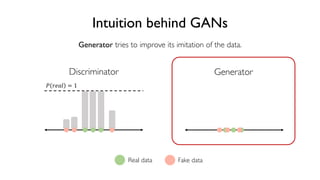
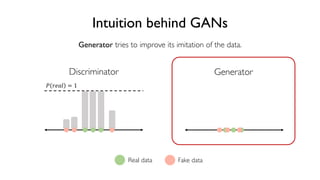
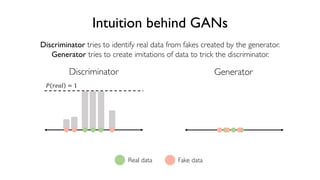
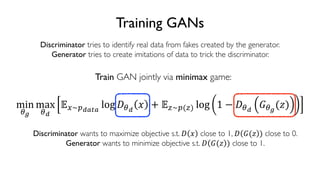
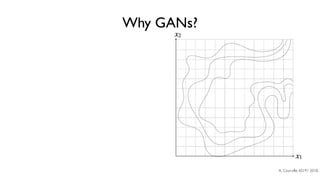
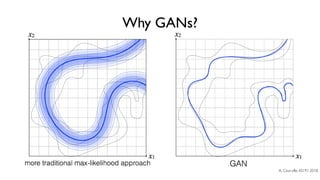
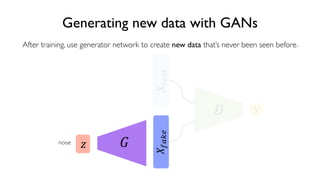
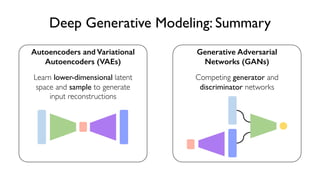
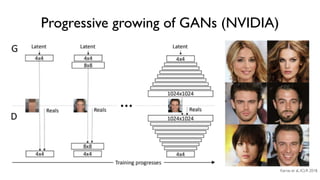
The document discusses deep generative models in artificial intelligence, focusing on techniques such as autoencoders, variational autoencoders (VAEs), and generative adversarial networks (GANs). It explains the concepts of supervised and unsupervised learning, generative modeling, and the purpose of latent variables in creating representations of data. Key insights include understanding how these models learn from data to generate new samples and improve their performance in various applications.







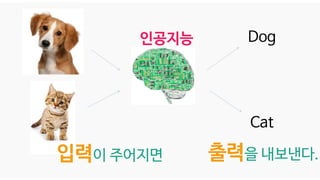

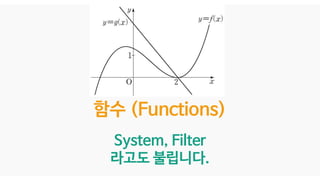


![X[n]
F[n] F[n-1]
Y[n]
n : data index
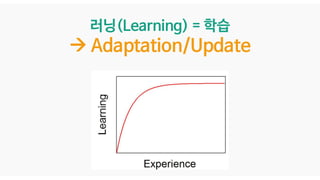
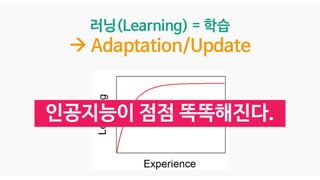
Data가 늘어날수록
점점 인공지능 알고리즘이
학습(Learning)한다.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-deepgenerativemodels-190528011731/85/AI-16-320.jpg)