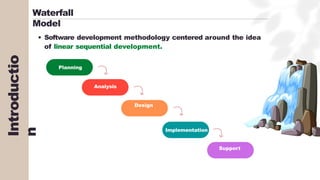
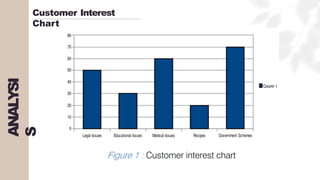
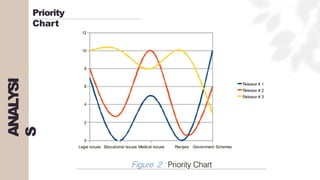
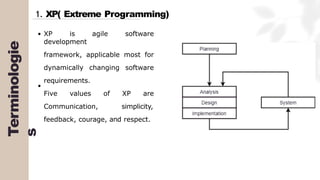
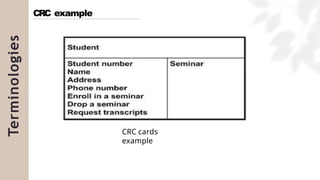
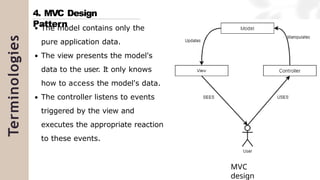
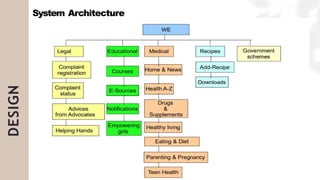
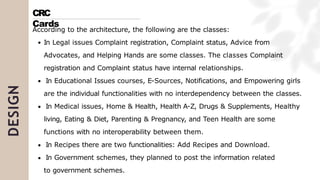
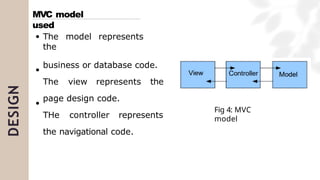
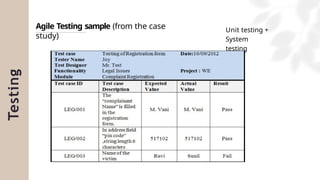
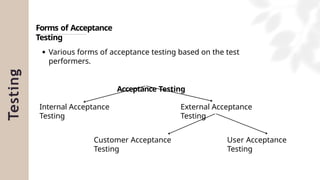
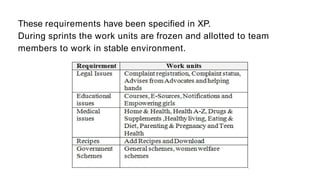
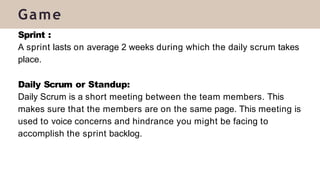
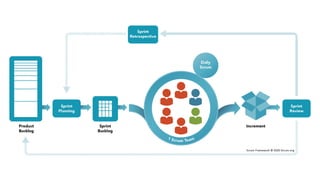
The document presents a case study on agile software development methodologies, specifically focusing on creating a web application aimed at supporting women in Andhra Pradesh. It discusses the advantages of agile methods, such as flexibility and client involvement, compared to the traditional waterfall model, and details various methodologies including Scrum and Extreme Programming (XP). The application development process includes phases for analysis, design, testing, and feedback mechanisms to ensure effective collaboration and responsiveness to user needs.