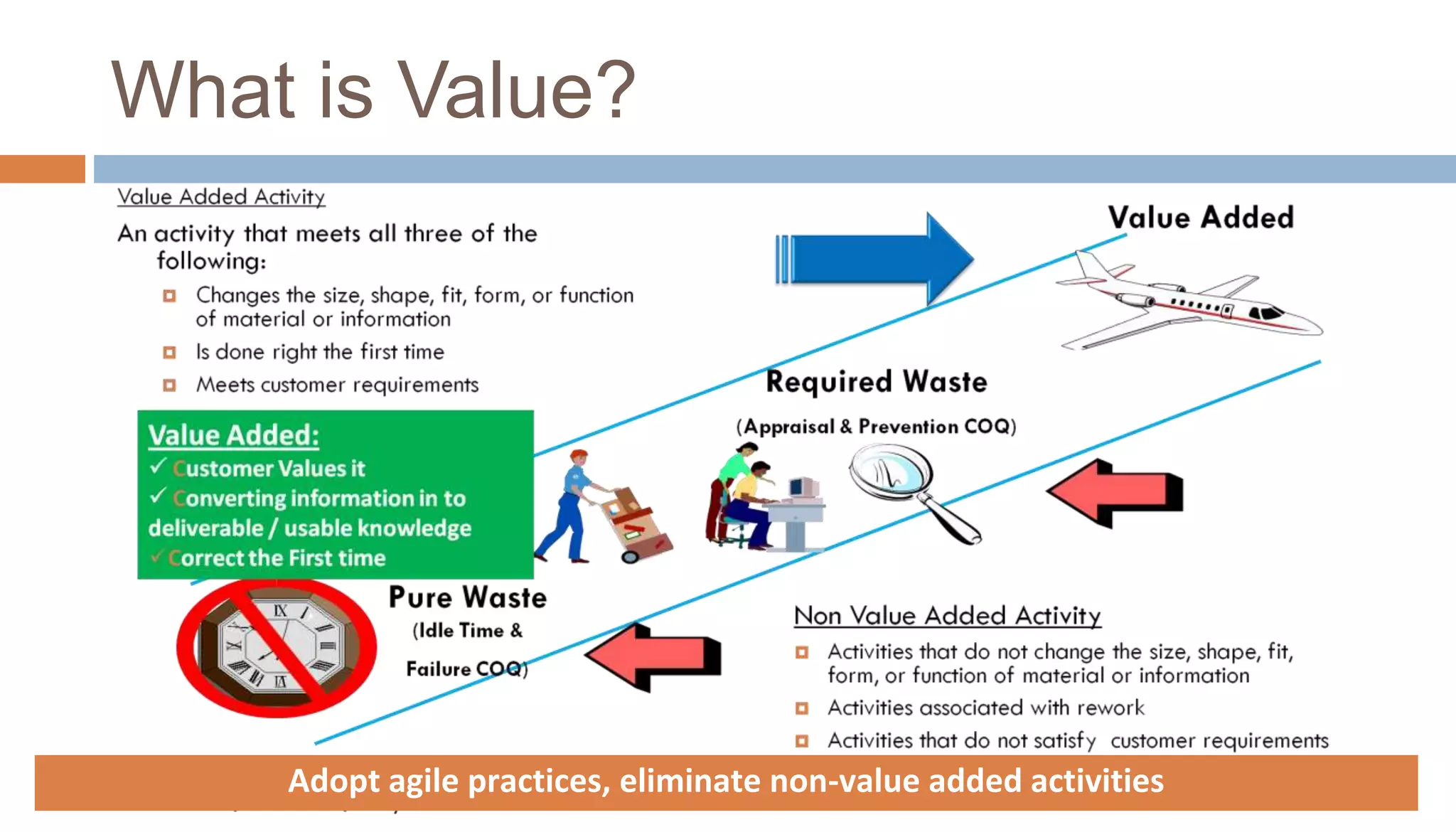
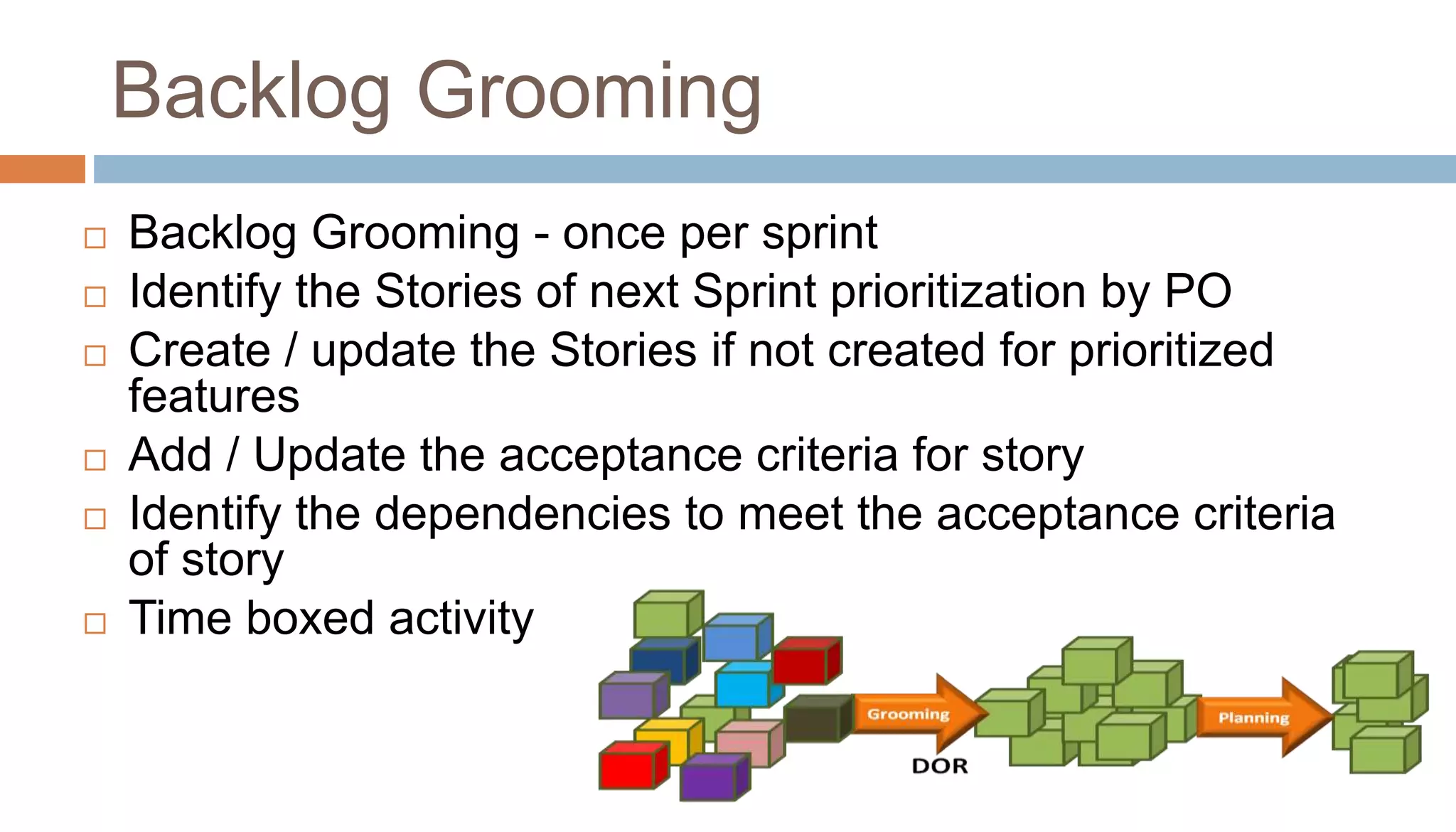
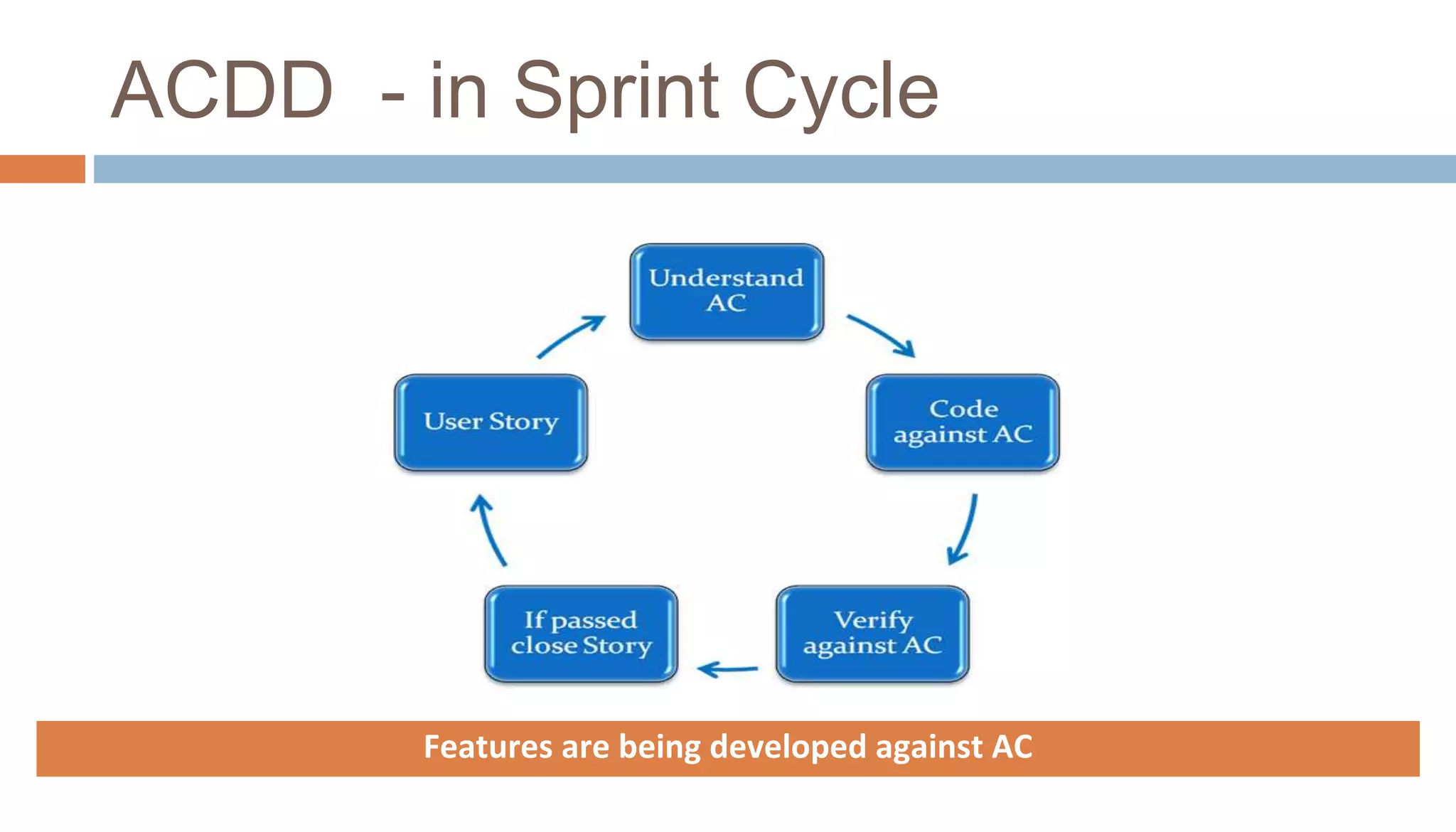
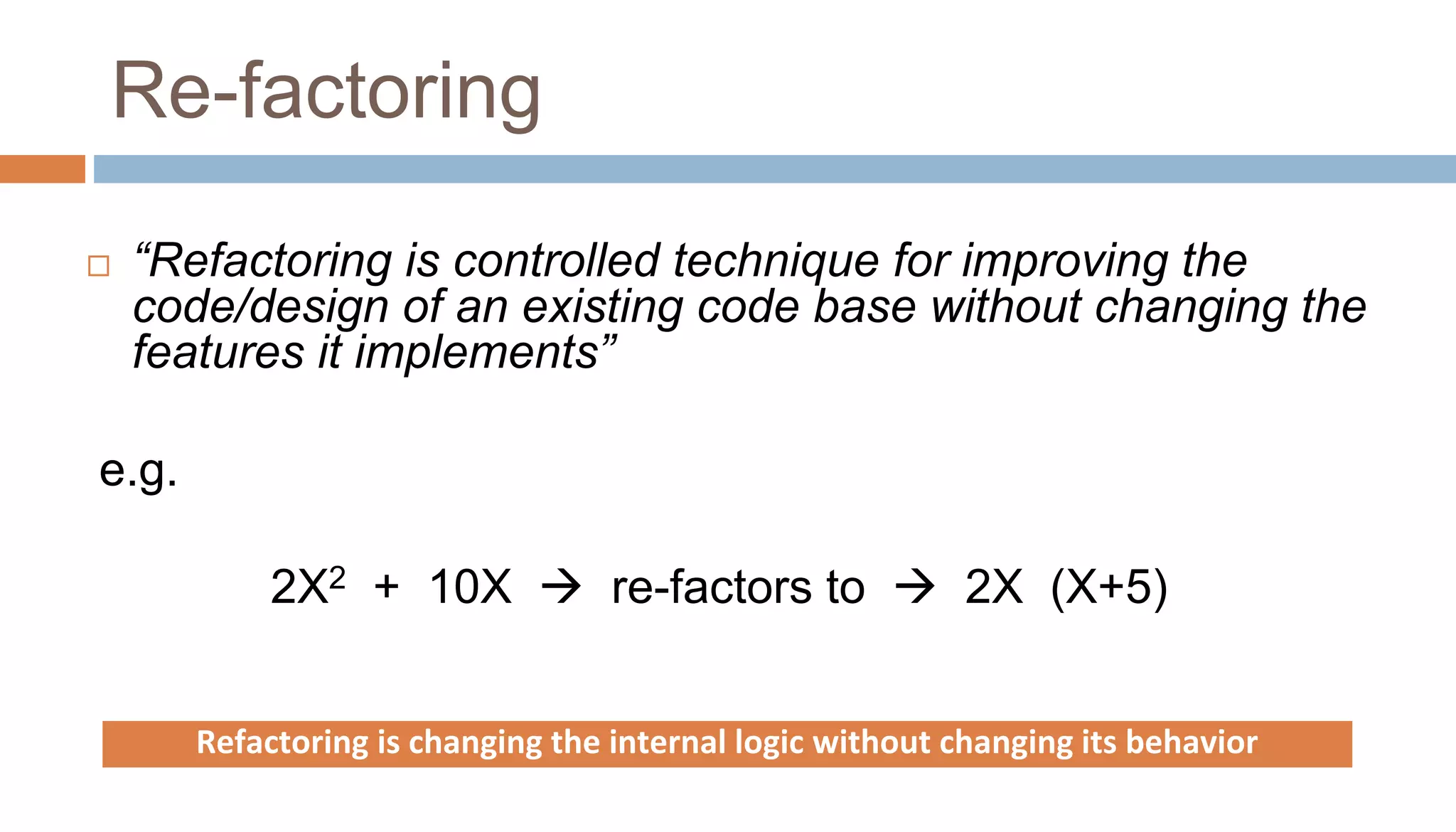
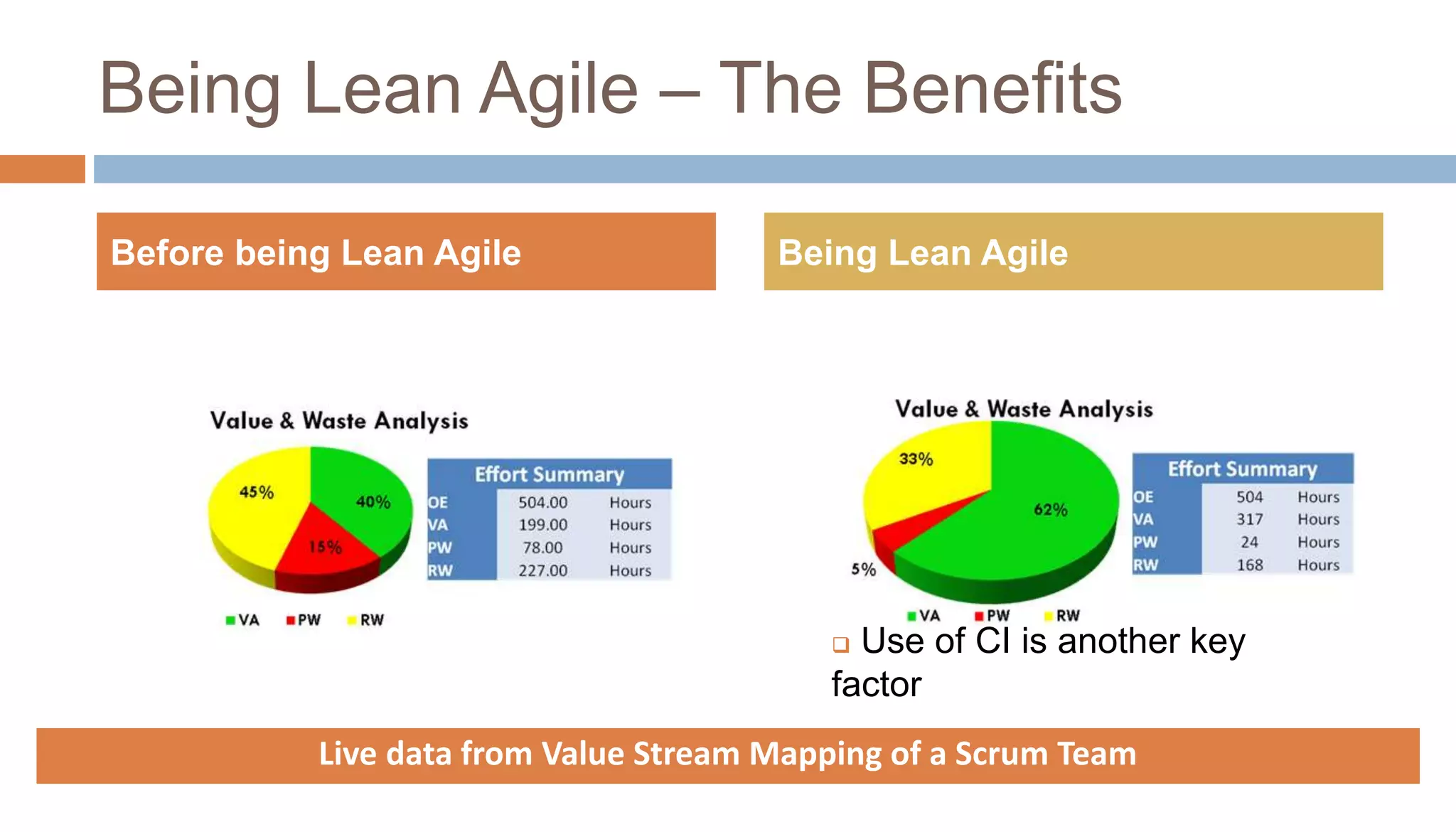
The document discusses the integration of lean principles with agile practices to maximize customer value by eliminating non-value-added activities. Key agile practices such as backlog grooming, acceptance criteria-driven development (ACDD), refactoring, and limiting work in progress (WIP) are highlighted for their roles in enhancing value flow and reducing wastes. Overall, the emphasis is on continuous improvement and empowering employees to achieve a lean agile environment.