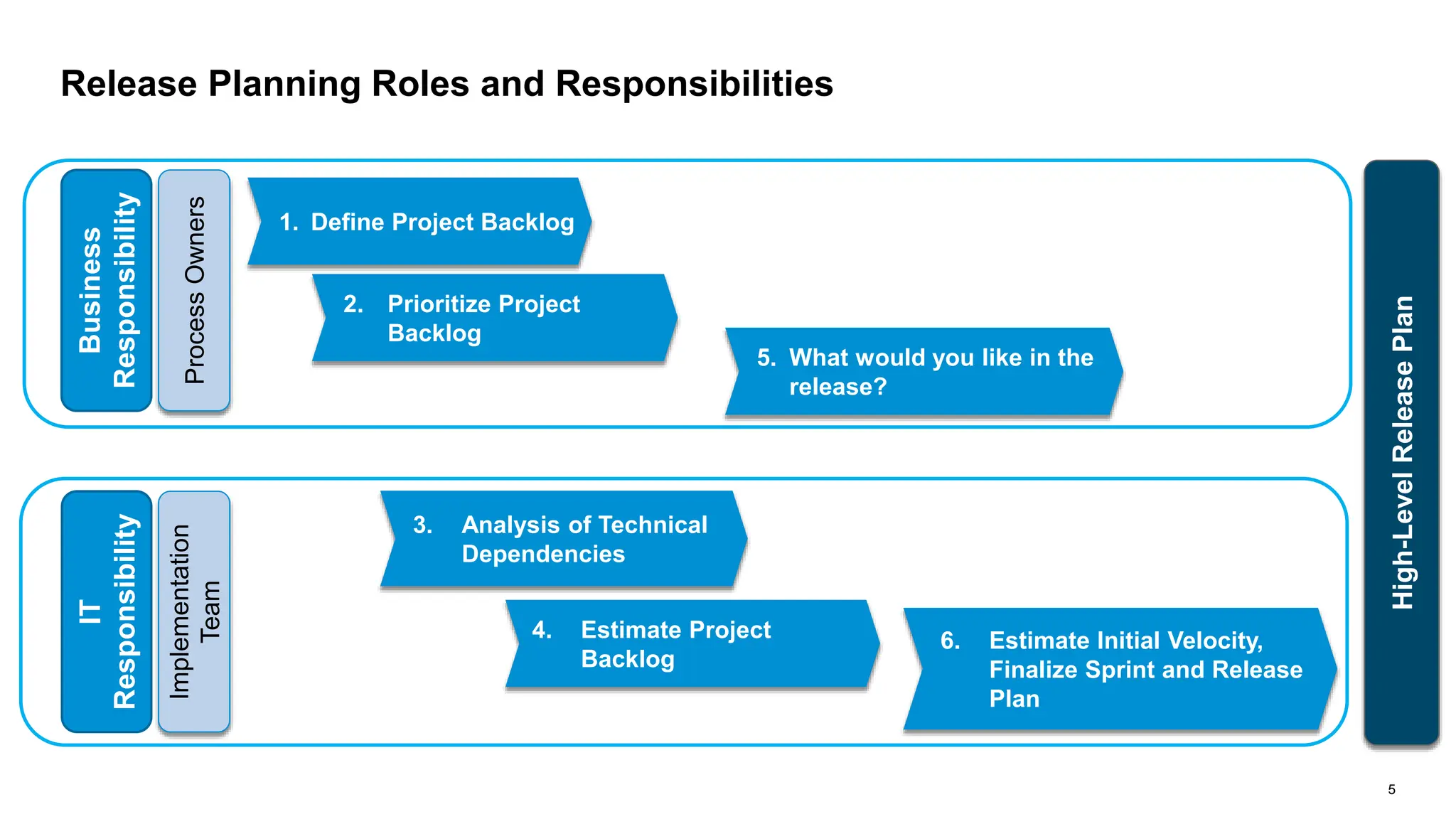
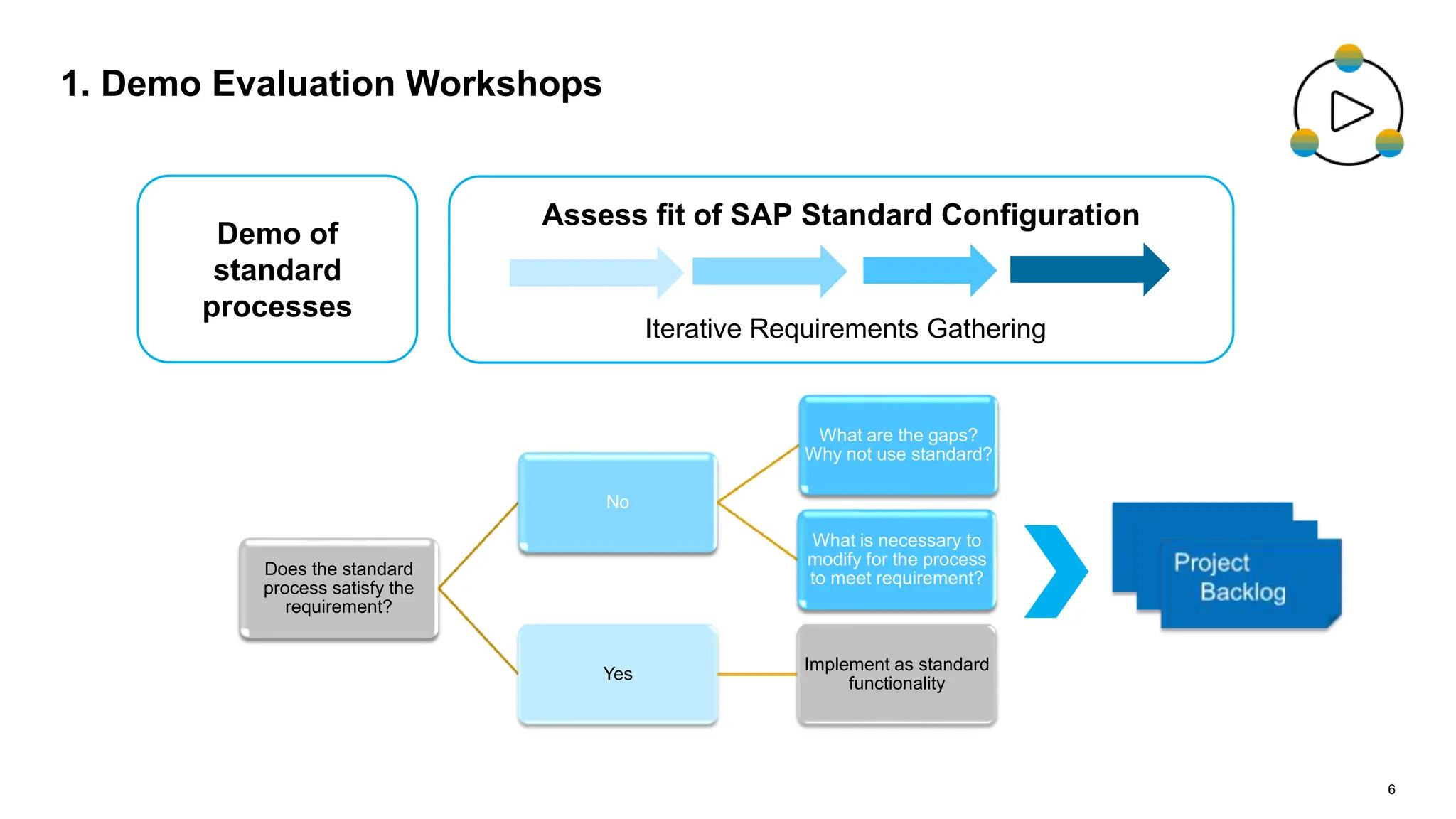
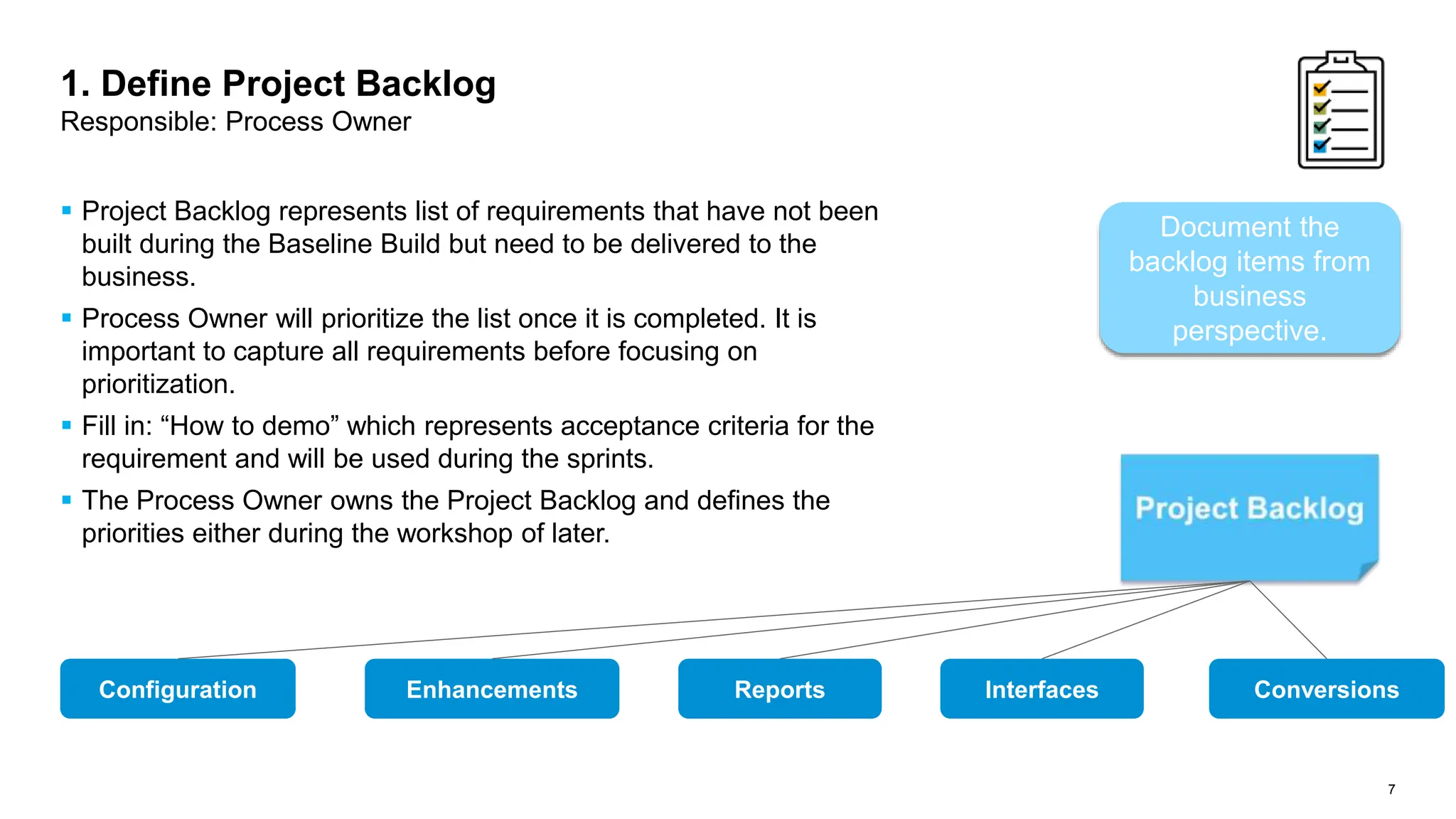
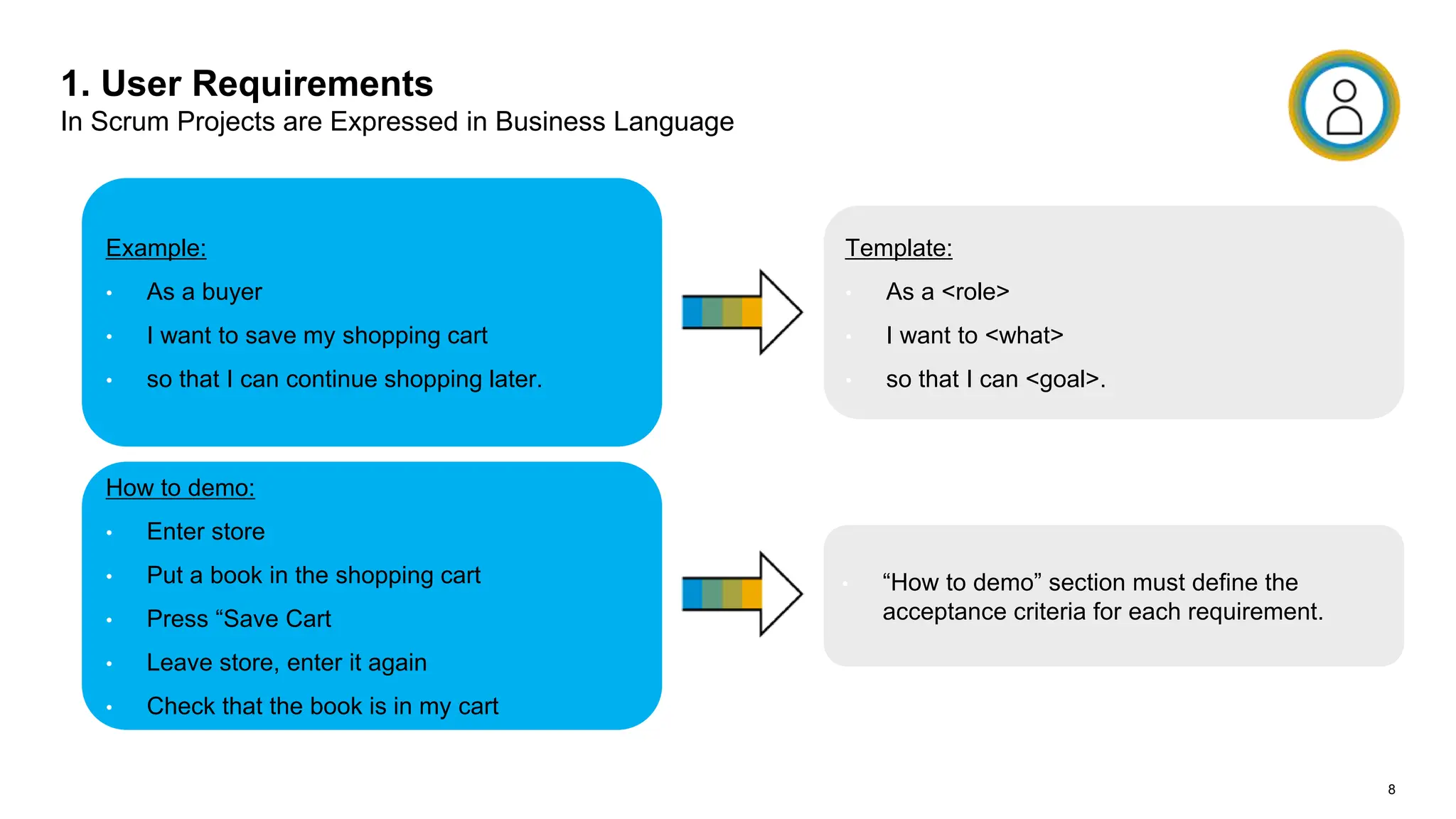
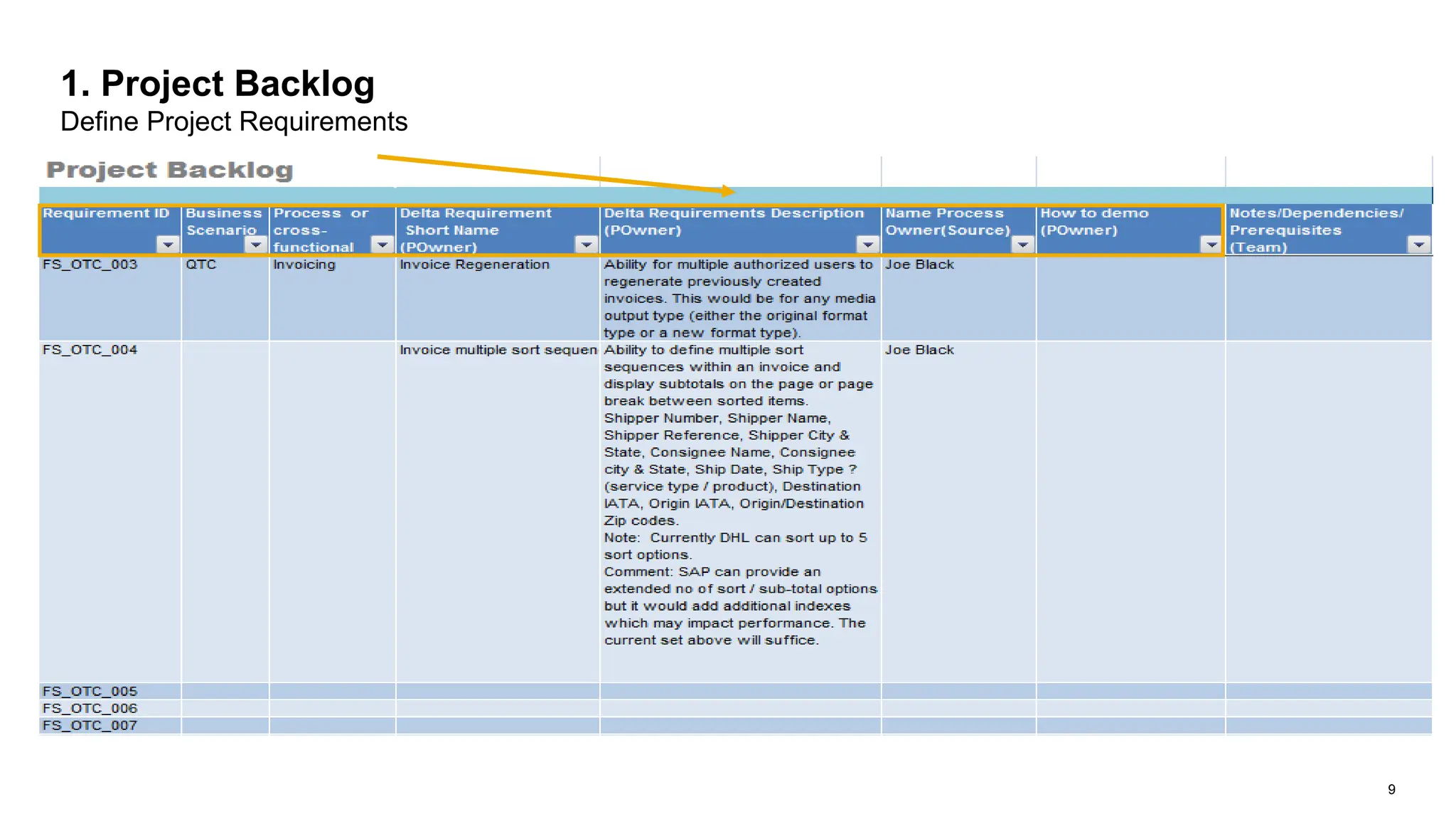
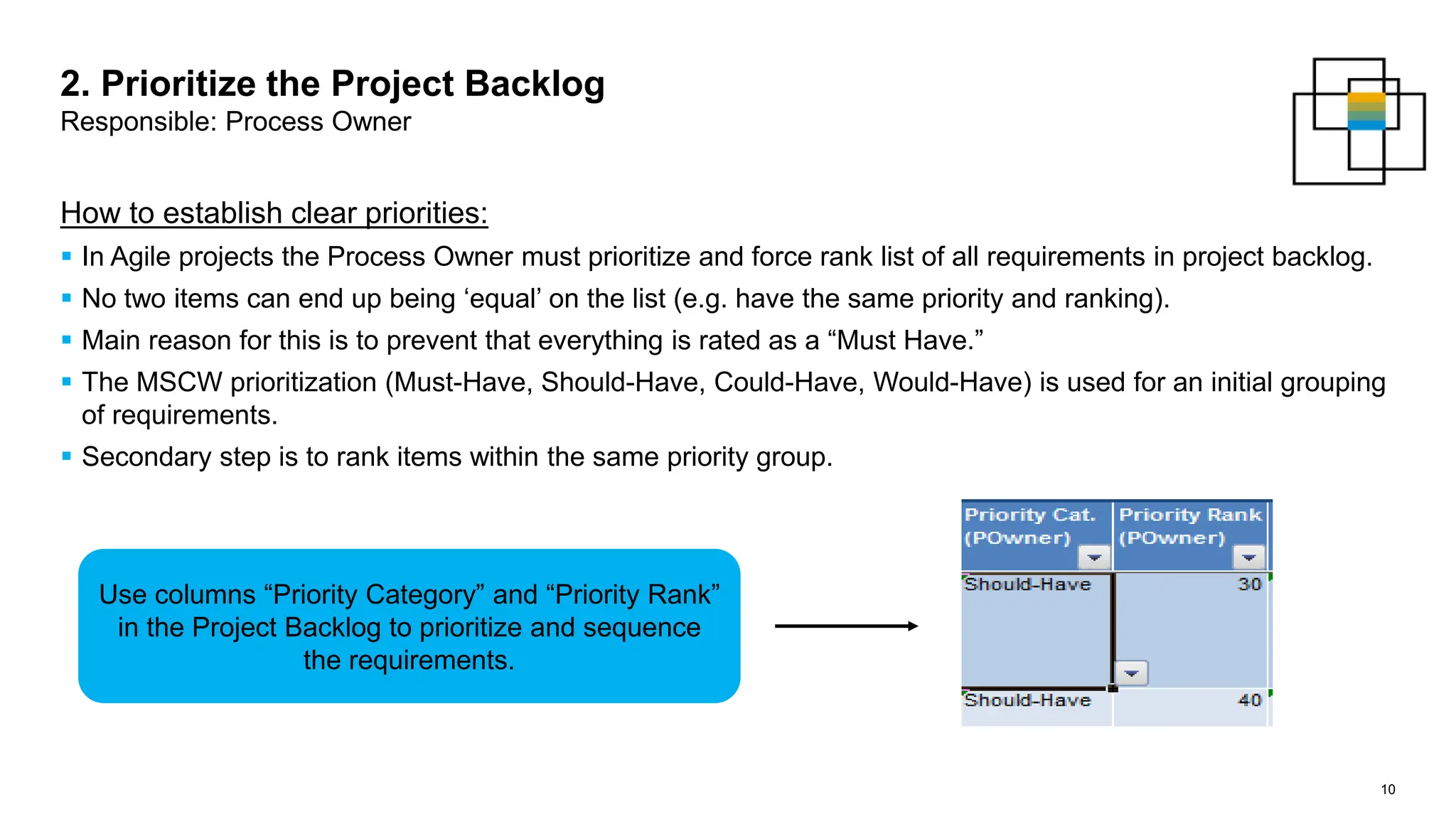
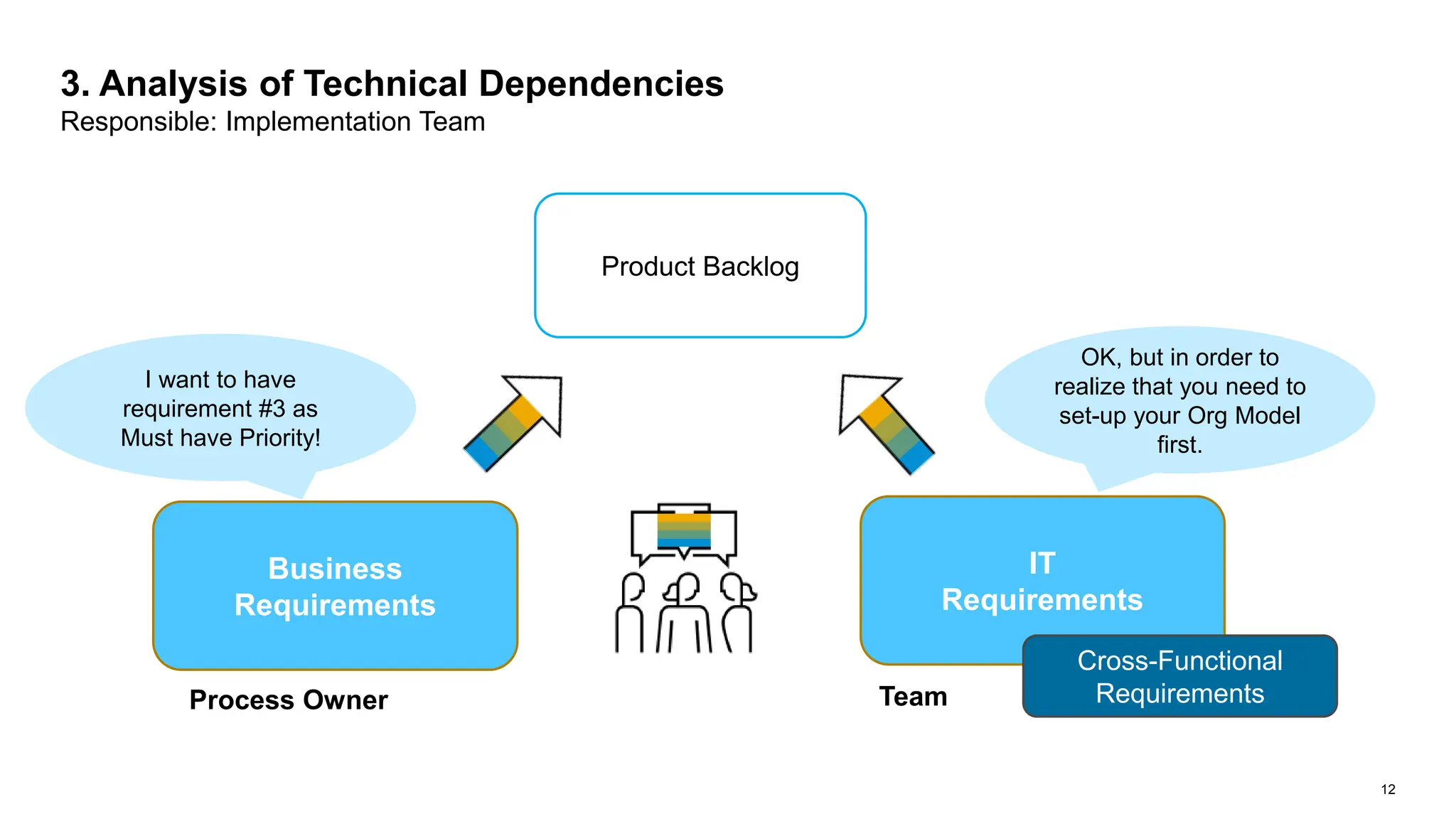
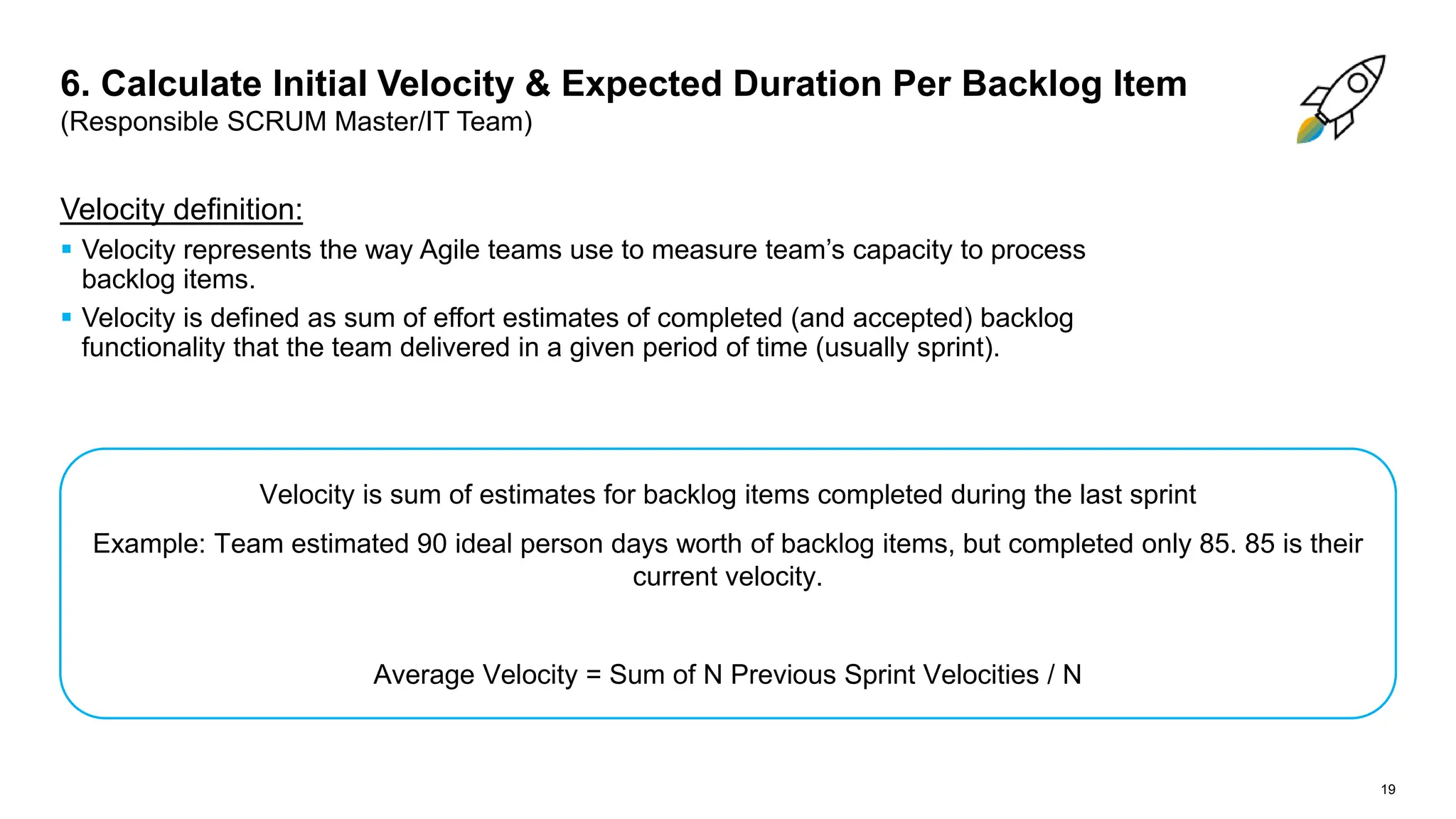
The document outlines steps for planning a release using an agile implementation methodology, focusing on backlog prioritization, estimation techniques, and roles in the release planning process. It details how to define project backlogs, prioritize requirements, estimate team velocity, and establish a high-level release plan. Additionally, it discusses estimation methods, including planning poker, and emphasizes the importance of defining completion criteria for sprints and releases.


![3
Agile Release Planning
Prepare Realize
Explore Deploy Run
Realize Release 2
Data Management
RUN SAP
Organizational Change Management
Baseline Build
Working
Software
Release 1
Sprint
Sprint
Sprint
Business
Priority
Time
Iterations / Demos
Evaluate
Define
&
Analyze
Scope
Demo
SAP
Standard
Setting
the
scene
Must
Should
Could
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
09
08
07
06
05
04
03
02
01
Would
Demo
Support
Evaluation &
Release Planning
Tests
Final
Prep.
Prep. Sprint
Sprint
Release 2
Sign-Off
Process WS
& Sol.Archit.
4
5
1
8
2
7
3
4
2
2
4
3
3
6
4
5
Checkpoint
Checkpoint
Checkpoint
Accelerators
Enablement
Organization
readiness
Project Backlog
Priority [d]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ag17-240517224204-6a52f01f/75/Agile-implementation-Methodology-strategy-3-2048.jpg)