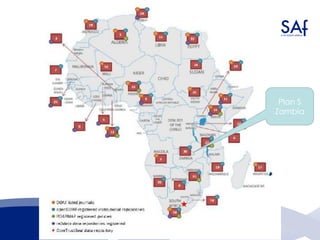
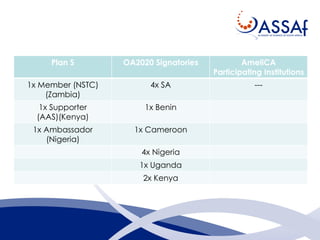
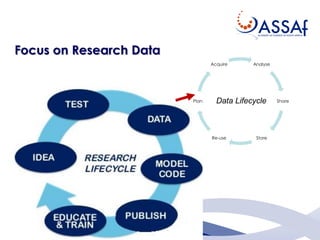
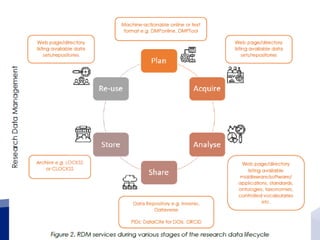
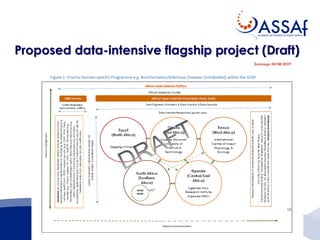
The document summarizes a presentation about the African Open Science Platform (AOSP) and open science in Africa more broadly. It discusses how AOSP aims to address challenges around health data sharing during the 2014-2015 Ebola outbreak in West Africa. It also outlines AOSP's pilot project from 2016-2019 and future plans to build open science capacity and infrastructure in Africa, including through cloud computing, data analysis tools, and research data management services. The overall goal is to support open and collaborative science that addresses key challenges on the continent.