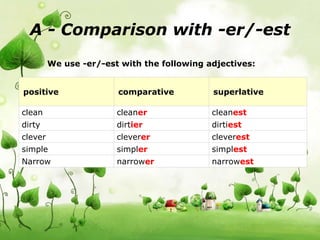
This document defines and describes different types of adjectives. It discusses qualitative/descriptive adjectives that describe qualities like size, color, shape, etc. It also covers quantitative adjectives that indicate number, demonstrative adjectives that point out nouns, possessive adjectives that show ownership, and more. The document provides examples of different types of adjectives and explains how to compare adjectives using -er/est, more/most, or irregular forms.