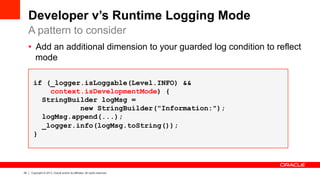
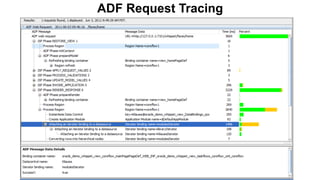
The document outlines best practices for logging in Oracle ADF, emphasizing the importance of effective instrumentation for debugging and support. It discusses the benefits of the ADF logger over traditional logging methods, detailing when and where to log, and the need for proper log message design aimed at different user roles. The document also covers logging rules, examples of key logging points, and tools for analyzing logs to enhance application performance and supportability.











![13 Copyright © 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Using the Logger
• However, logging needs a degree of design
• Consider
– Placement
– Message Level (use Config, Info, Warning, Error)
– Detail / content
– Message consumers [User Admin | Support | Developer]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/300-v1-140707225950-phpapp02/85/Oracle-ADF-Architecture-TV-Development-Logging-13-320.jpg)