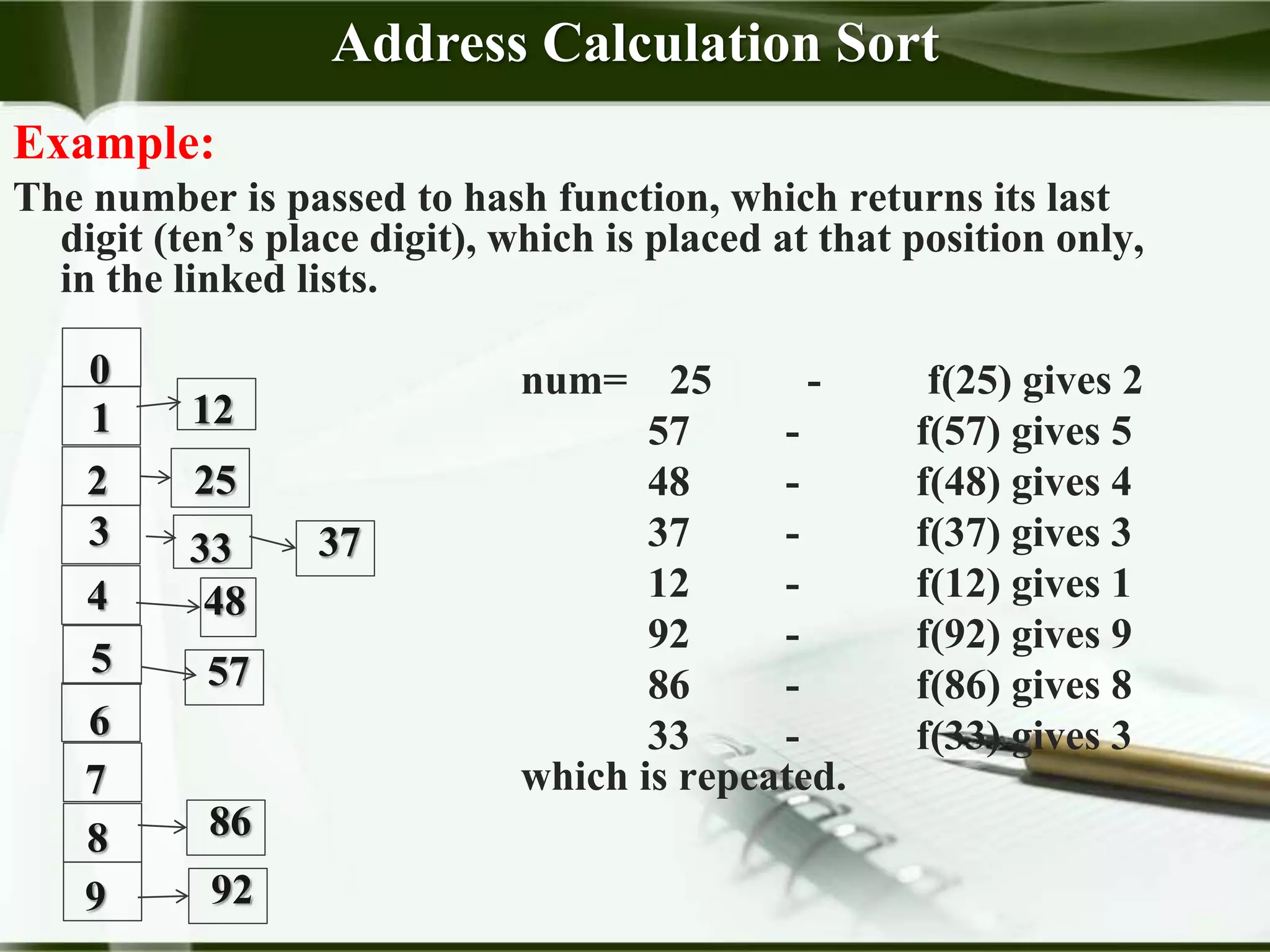
This document describes address calculation sorting, also known as hashing. It works by applying a hash function to each element in the list to determine which "subfile" or linked list that element belongs in. Elements are inserted into the correct position in their subfile using another sorting method like insertion sort. Once all elements are placed, the subfiles are concatenated to produce the final sorted list. The example demonstrates hashing each number to its last digit and placing it in the corresponding subfile. When the subfiles are concatenated, the list is sorted from lowest to highest. Address calculation sorting can be very fast if elements are uniformly distributed across subfiles, but less efficient if most elements hash to just one or two subfiles.