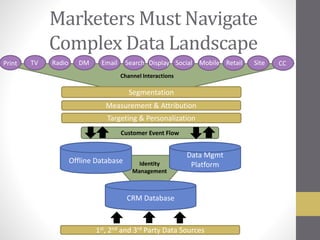
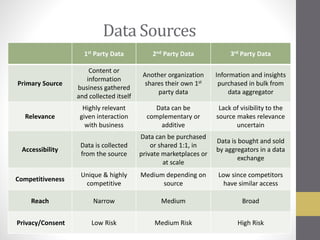
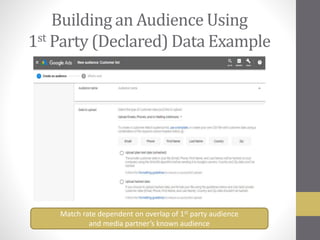
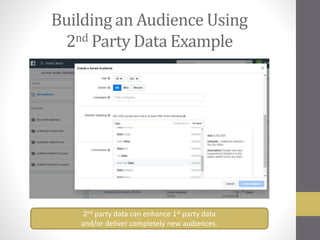
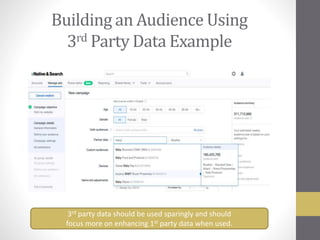
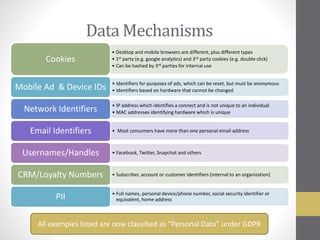
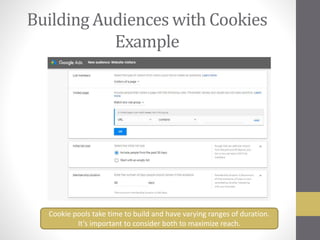
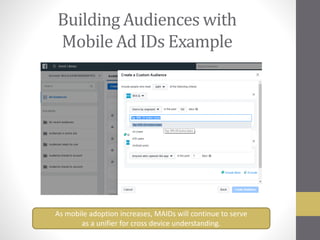
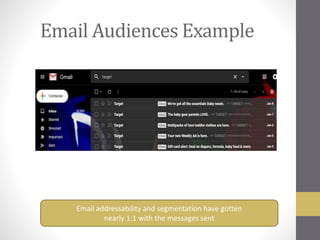
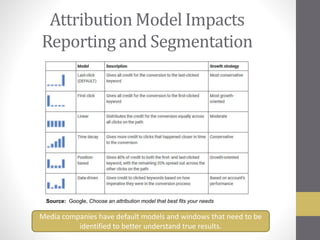
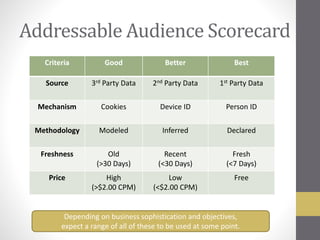
This document provides an overview of addressable audiences and people-based marketing. It discusses key considerations for building audiences using various data sources like 1st, 2nd, and 3rd party data. It also covers data mechanisms like cookies and mobile IDs. The document outlines different data matching and attribution methods and provides examples. It concludes with a scorecard for evaluating addressable audience criteria.