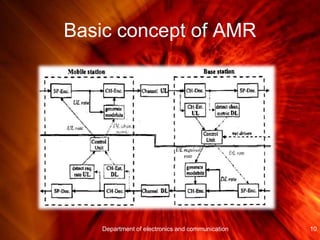
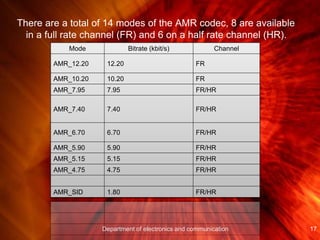
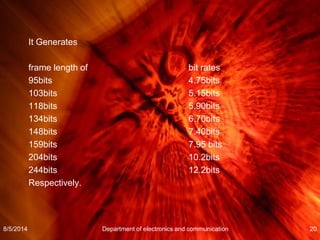
- Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) speech coding allows variable bit rates depending on channel conditions between 4.75 kbit/s and 12.2 kbit/s over full-rate channels and between 4.75 kbit/s and 7.95 kbit/s over half-rate channels. It uses source coding, channel coding, and rate adaptation based on channel estimation to optimize quality and efficiency.
- AMR utilizes algebraic code excited linear prediction speech coding, unequal error protection, recursive systematic convolutional channel coding, and discontinuous transmission with voice activity detection and comfort noise generation. This allows it to save bandwidth during silence and adapt to changing channel conditions.