The document contains 8 questions related to data structures and algorithms in C programming. Question 1 asks to write a program to search a number from a list using linear and binary search. Question 2 asks to write a program to search a number recursively using binary search. Question 3 asks to write a program to find the factorial of a number recursively and non-recursively and compare performance. The remaining questions ask to write programs for sorting, matrix multiplication using Strassen's algorithm, minimum spanning tree using Kruskal's algorithm, and other algorithms.
![Q1. Write a program to search a number from a given list using linear and binary
search.
#include<stdio.h>
#inlcude<conio.h>
void main()
{
int arr[10];
int i,j;
int n
int snumber;
int count=0;
printf("Enter the number of element in array");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("nEnter the element in array");
for(i=0;i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
printf("nenter the search element");
scanf("%d",&snumber);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(arr[i]==snumber)
{
count=1;
printf("value is found");
break;
}
}
if(count==0)
printf("value is not found");
getch();
}
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/75/Ada-file-1-2048.jpg)

![Q2. Write a program to search a number from a given list using binary search
recursively.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
binary(int,int,int);
int b[25];
void main()
{
int high,low=0,i,j,value,pos,n;
clrscr();
printf("Enter n number of item");
scanf("%d",&n);
high=n;
printf("Enter the value in sorted formn");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
}
printf("Enter the value which you have to find");
scanf("%d",&value);
pos=binary(low,high,value);
//printf("n in location %d th",pos);
getch();
}
int binary(int low,int high,int value)
{
if(low==high)
{
if( b[(low+high)/2]==value)
{
printf("value is found");
return (low+high)/2;
}
else
{
printf("Value is not found");
return;
}
}
if( b[(low+high)/2]>value)
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-3-320.jpg)
![binary(low,(low+high)/2,value);
else if( b[(low+high)/2]<value)
binary(((low+high)/2)+1,high,value);
else
{
printf("value is found");
return(low+high)/2;
}
}
Output
Enter n number of item
5
Enter the value in sorted form
1 2 3 4 5
Enter the value which you have to find3
value is found
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-4-320.jpg)


![Q4. Sort the following list in increasing order of number
9,94,45,47,28,98,65,42,8,4,88,6 using selection sort.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int sort[15];
int i,j;
int n;
int temp;
clrscr();
printf("enter the number of element in array");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("nenter the value in array");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&sort[i]);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(sort[i]>sort[j])
{
temp=sort[i];
sort[i]=sort[j];
sort[j]=temp;
}
}
}
printf("nSorted array:");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("n%d",sort[i]);
getch();
}
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-7-320.jpg)

![Q5. Write a program to sort a list using merge sort by applying divide and conquer
method .
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int a[100];
void merge_sort(int a[],int left,int right);
void merge(int a[],int lb,int le,int rb,int re);
void main()
{
int i,num;
clrscr();
printf("enter the numn");
scanf("%d",&num);
printf("Enter the arrayn");
for(i=0;i<num;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
merge_sort(a,0,num-1);
printf("nSorted list is:n");
for(i=0;i<num;i++)
printf("%dn",a[i]);
getch();
}
void merge_sort(int a[],int left,int right)
{
int mid;
if(right>left)
{
mid=(right+left)/2;
merge_sort(a,left,mid);
merge_sort(a,mid+1,right);
merge(a,left,mid,mid+1,right);
}
}
void merge(int a[],int lb,int le,int rb,int re)
{
int na,nb,nc,k,c[30];
na=lb;
nb=rb;
nc=lb;
while((na<=le)&&(nb<=re))
{
if(a[na]<a[nb])
c[nc++]=a[na++];
else
c[nc++]=a[nb++];
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-9-320.jpg)
![}
if(na>le)
{
while(nb<=re)
c[nc++]=a[nb++];
}
else
{
while(na<=le)
c[nc++]=a[na++];
}
for(k=lb;k<=re;k++)
a[k]=c[k];
}
Output
enter the num
5
Enter the array
5
4
1
2
3
Sorted list is:
1
2
3
4
5
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-10-320.jpg)
![Q6. Write a program to sort a list using quick sort by applying divide and conquer
method .
#include "stdio.h"
int split ( int*, int, int ) ;
void quicksort ( int *, int, int ) ;
void main( )
{
int arr[10];
int i ;
int n;
printf("enter the number of element in array");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter the value of array");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
quicksort ( arr, 0, n ) ;
printf ( "nArray after sorting:n") ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; i++ )
printf ( "%dt", arr[i] ) ;
getch();
}
void quicksort ( int a[ ], int lower, int upper )
{
int i ;
if ( upper > lower )
{
i = split ( a, lower, upper ) ;
quicksort ( a, lower, i - 1 ) ;
quicksort ( a, i + 1, upper ) ;
}
}
int split ( int a[ ], int lower, int upper )
{
int i, p, q, t ;
p = lower + 1 ;
q = upper ;
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-11-320.jpg)
![i = a[lower] ;
while ( q >= p )
{
while ( a[p] < i )
p++ ;
while ( a[q] > i )
q-- ;
if ( q > p )
{
t = a[p] ;
a[p] = a[q] ;
a[q] = t ;
}
}
t = a[lower] ;
a[lower] = a[q] ;
a[q] = t ;
return q ;
}
OUTPUT
enter the number of element in array 5
Enter the value of array 1 4 3 5 2
Array after sorting:
1 2 3 4 5
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-12-320.jpg)
![Q7. Write a program to perform product of two matrix of order nxn using
strassen’s multiplication method.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void main()
{
int a[4][4],b[4][4],c[4][4],d[7],e[7],f[7],g[7],i,j,choice;
do
{
printf("n1. 4*4 matrix.");
printf("n2. 2*2 matrix.");
printf("n3. Exit.");
printf("nEnter your choice : ");
scanf("%d",&choice);
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
{
printf("nEnter value for matrix A : ");
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
printf("nEnter value for matrix B : ");
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
scanf("%d",&b[i][j]);
d[0]=(a[0][0]+a[1][1])*(b[0][0]+b[1][1]);
d[1]=(a[1][0]+a[1][1])*b[0][0];
d[2]=a[0][0]*(b[0][1]-b[1][1]);
d[3]=a[1][1]*(b[1][0]-b[0][0]);
d[4]=(a[0][0]+a[0][1])*b[1][1];
d[5]=(a[1][0]-a[0][0])*(b[0][0]+b[0][1]);
d[6]=(a[0][1]-a[1][1])*(b[1][0]-b[1][1]);
e[0]=(a[0][2]+a[1][3])*(b[0][2]+b[1][3]);
e[1]=(a[1][2]+a[1][3])*b[0][2];
e[2]=a[0][2]*(b[0][3]-b[1][3]);
e[3]=a[1][3]*(b[1][2]-b[0][2]);
e[4]=(a[0][2]+a[0][3])*b[1][3];
e[5]=(a[1][2]-a[0][2])*(b[0][2]+b[0][3]);
e[6]=(a[0][3]-a[1][3])*(b[1][2]-b[1][3]);
f[0]=(a[2][0]+a[3][1])*(b[2][0]+b[3][1]);
f[1]=(a[3][0]+a[3][1])*b[2][0];
f[2]=a[2][0]*(b[2][1]-b[3][1]);
f[3]=a[3][1]*(b[3][0]-b[2][0]);
f[4]=(a[2][0]+a[2][1])*b[3][1];
f[5]=(a[3][0]-a[2][0])*(b[2][0]+b[2][1]);
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-13-320.jpg)
![f[6]=(a[2][1]-a[3][1])*(b[3][0]-b[3][1]);
g[0]=(a[2][2]+a[3][3])*(b[2][2]+b[3][3]);
g[1]=(a[3][2]+a[3][3])*b[2][2];
g[2]=a[2][2]*(b[2][3]-b[3][3]);
g[3]=a[3][3]*(b[3][2]-b[2][2]);
g[4]=(a[2][2]+a[2][3])*b[3][3];
g[5]=(a[3][2]-a[2][2])*(b[2][2]+b[2][3]);
g[6]=(a[2][3]-a[3][3])*(b[3][2]-b[3][3]);
c[0][0]=d[0]+d[3]-d[4]+d[6];
c[0][1]=d[2]+d[4];
c[1][0]=d[1]+d[3];
c[1][1]=d[0]+d[2]-d[1]+d[5];
c[0][2]=e[0]+e[3]-e[4]+e[6];
c[0][3]=e[2]+e[4];
c[1][2]=e[1]+e[3];
c[1][3]=e[0]+e[2]-e[1]+e[5];
c[2][0]=f[0]+f[3]-f[4]+f[6];
c[2][1]=f[2]+f[4];
c[3][0]=f[1]+f[3];
c[3][1]=f[0]+f[2]-f[1]+f[5];
c[2][2]=g[0]+g[3]-g[4]+g[6];
c[2][3]=g[2]+g[4];
c[3][2]=g[1]+g[3];
c[3][3]=g[0]+g[2]-g[1]+g[5];
printf("nMatrix multiplication is : n");
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
printf("%d",c[i][j]);
}
printf("n");
}
break;
}
case 2:
{
printf("nEnter value for matrix A : ");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
printf("nEnter value for matrix B : ");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
scanf("%d",&b[i][j]);
d[0]=(a[0][0]+a[1][1])*(b[0][0]+b[1][1]);
d[1]=(a[1][0]+a[1][1])*b[0][0];
d[2]=a[0][0]*(b[0][1]-b[1][1]);
d[3]=a[1][1]*(b[1][0]-b[0][0]);
d[4]=(a[0][0]+a[0][1])*b[1][1];
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-14-320.jpg)
![d[5]=(a[1][0]-a[0][0])*(b[0][0]+b[0][1]);
d[6]=(a[0][1]-a[1][1])*(b[1][0]-b[1][1]);
c[0][0]=d[0]+d[3]-d[4]+d[6];
c[0][1]=d[2]+d[4];
c[1][0]=d[1]+d[3];
c[1][1]=d[0]+d[2]-d[1]+d[5];
printf("nMatrix multiplication is : n");
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
printf("%d",c[i][j]);
}
printf("n");
}
break;
}
case 3:
{
exit(0);
}
default:
{
printf("nInvalid chocie.");
printf("nSelect value from 1-4...");
}
}
}while(choice!=3);
getch();
}
OUTPUT
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-15-320.jpg)
![Q8. Write a program to find minimum spanning tree using Kruskal’s method.
#include<stdio.h>
#define INF 1000
char vertex[10];
int wght[10][10];
int span_wght[10][10];
int source;
struct Sort
{
int v1,v2;
int weight;
}que[20];
int n,ed,f,r;
int cycle(int s,int d)
{
int j,k;
if(source==d)
return 1;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(span_wght[d][j]!=INF && s!=j)
{
if(cycle(d,j))
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void build_tree()
{
int i,j,w,k,count=0;
for(count=0;count<n;f++)
{
i=que[f].v1;
j=que[f].v2;
w=que[f].weight;
span_wght[i][j]=span_wght[j][i]=w;
source=i;
k=cycle(i,j);
if(k)
span_wght[i][j]=span_wght[j][i]=INF;
else
count++;
}
}
void swap(int *i,int *j)
{
int t;
t=*i;
*i=*j;
*j=t;
}
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-16-320.jpg)
![void main()
{
int i,j,k=0,temp;
int sum=0;
clrscr();
printf("ntEnter the No. of Nodes : ");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("ntEnter %d value : ",i+1);
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c",&vertex[i]);
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
wght[i][j]=INF;
span_wght[i][j]=INF;
}
}
printf("nnGetting Weightn");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
printf("nEnter 0 if path Doesn't exist between %c to %c : ",vertex[i],vertex[j]);
scanf("%d",&ed);
if(ed>=1)
{
wght[i][j]=wght[j][i]=ed;
que[r].v1=i;
que[r].v2=j;
que[r].weight=wght[i][j];
if(r)
{
for(k=0;k<r;k++)
if(que[k].weight>que[r].weight)
{
swap(&que[k].weight,&que[r].weight);
swap(&que[k].v1,&que[r].v1);
swap(&que[k].v2,&que[r].v2);
}
}
r++;
}
}
build_tree();
printf("nttLIST OF EDGESnn");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)
if(span_wght[i][j]!=INF)
{
printf("ntt%c ------ %c = %d ",vertex[i],vertex[j],span_wght[i][j]);
sum+=span_wght[i][j];
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-17-320.jpg)
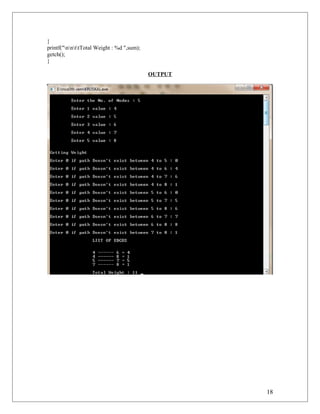
![Q9. Write a program to find minimum spanning tree using Prim’s method .
Code.
#include <stdio.h>
int n;
int weight[100][100];
char inTree[100];
int d[100];
int whoTo[100];
void updateDistances(int target) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if ((weight[target][i] != 0) && (d[i] > weight[target][i])) {
d[i] = weight[target][i];
whoTo[i] = target;
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
FILE *f = fopen("dist.txt", "r");
fscanf(f, "%d", &n);
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j)
fscanf(f, "%d", &weight[i][j]);
fclose(f);
/* Initialise d with infinity */
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
d[i] = 100000;
/* Mark all nodes as NOT beeing in the minimum spanning tree */
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
inTree[i] = 0;
/* Add the first node to the tree */
printf("Adding node %cn", 0 + 'A');
inTree[0] = 1;
updateDistances(0);
int total = 0;
int treeSize;
for (treeSize = 1; treeSize < n; ++treeSize) {
/* Find the node with the smallest distance to the tree */
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-19-320.jpg)
![int min = -1;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (!inTree[i])
if ((min == -1) || (d[min] > d[i]))
min = i;
/* And add it */
printf("Adding edge %c-%cn", whoTo[min] + 'A', min + 'A');
inTree[min] = 1;
total += d[min];
updateDistances(min);
}
printf("Total distance: %dn", total);
getch();
return 0;
}
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-20-320.jpg)

![Q10. Write a program to find single shortest path using dijekstra algorithm.
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int shortest(int ,int);
int cost[10][10],dist[20],i,j,n,k,m,S[20],v,totcost,path[20],p;
main()
{
int c;
cout <<"enter no of vertices";
cin >> n;
cout <<"enter no of edges";
cin >>m;
cout <<"nenternEDGE Costn";
for(k=1;k<=m;k++)
{
cin >> i >> j >>c;
cost[i][j]=c;
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(cost[i][j]==0)
cost[i][j]=31999;
cout <<"enter initial vertex";
cin >>v;
cout << v<<"n";
shortest(v,n);
}
int shortest(int v,int n)
{
int min;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
S[i]=0;
dist[i]=cost[v][i];
}
path[++p]=v;
S[v]=1;
dist[v]=0;
for(i=2;i<=n-1;i++)
{
k=-1;
min=31999;
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-22-320.jpg)
![for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(dist[j]<min && S[j]!=1)
{
min=dist[j];
k=j;
}
}
if(cost[v][k]<=dist[k])
p=1;
path[++p]=k;
for(j=1;j<=p;j++)
cout<<path[j];
cout <<"n";
//cout <<k;
S[k]=1;
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(cost[k][j]!=31999 && dist[j]>=dist[k]+cost[k][j] && S[j]!=1)
dist[j]=dist[k]+cost[k][j];
}
}
OUTPUT
Enter no of vertices6
enter no of edges11
enter
EDGE Cost
1 2 50
1 3 45
1 4 10
2 3 10
2 4 15
3 5 30
4 1 10
4 5 15
5 2 20
5 3 35
6 5 3
enter initial vertex 1
1
14
145
1452
13
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-23-320.jpg)
![Q11. Write a program to knapsack problem.
# include<stdio.h>
# include<conio.h>
void knapsack(int , float[], float[], float);
void main()
{
float weight[20], profit[20], capacity;
int n, i ,j;
float ratio[20], temp;
clrscr();
printf ("n Enter the no of objects:- ");
scanf ("%d", &n);
printf ("n Enter the profits and weight of each object:- ");
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%f %f", &profit[i],&weight[i]);
}
printf ("n Enter the capacity of knapsack:- ");
scanf ("%f", &capacity);
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
ratio[i]=profit[i]/weight[i];
}
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j< n; j++)
{
if(ratio[i]<ratio[j])
{
temp= ratio[j];
ratio[j]= ratio[i];
ratio[i]= temp;
temp= weight[j];
weight[j]= weight[i];
weight[i]= temp;
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-24-320.jpg)
![temp= profit[j];
profit[j]= profit[i];
profit[i]= temp;
}
}
}
knapsack(n, weight, profit, capacity);
getch();
}
void knapsack(int n, float weight[], float profit[], float capacity)
{
float x[20], tp=0 ;
int i, j, u;
u=capacity;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
x[i]=0.0;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(weight[i]>u)
break;
else
{
x[i]=1.0;
tp= tp+profit[i];
u=u-weight[i];
}
}
if(i<n)
x[i]=u/weight[i];
tp= tp + (x[i]*profit[i]);
printf("n The result vector is:- ");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("%ft",x[i]);
printf("n Maximum profit is:- %f", tp);
}
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-25-320.jpg)

![Q12. Write a program to find the optimal sequence of performing the jobs to get
maximum profit.
void JS(int d[],int j[],int n,int p[])
{
int profit=0,i,q,m;
int k=1,r;
j[1]=1;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
r=k;
while((d[j[r]]>d[i]) && (d[j[r]]!=r))
r=r-1;
if(d[j[r]]<=d[i] && d[i]>r)
{
for(q=(k);q>=(r+1);q--)
{
if(q==-1)
break;
j[q+1]=j[q];
}
j[r+1]=i;
k=k+1;
}
}
for(m=1;m<=k;m++)
{
profit+=p[m];
}
printf("n MAXIMUM PROFIT: %d",profit);
}
void main()
{
int q,n,p[10],d[10],i,j[10];
clrscr();
printf("n enter no of processes : ");
scanf("%d",&n);
d[0]=j[0]=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
printf("n enter profit of process %d:",i);
scanf("%d",&p[i]);
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
printf("n enter deadline ");
scanf("%d",&d[i]);
j[i]=0;
}
for(i=n-1;i>0;i--)
for(q=1;q<=i;q++)
if(p[q]<p[q+1])
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-27-320.jpg)
![{
int t;
t=p[q];
p[q]=p[q+1];
p[q+1]=t;
}
printf("nProfits : ");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf(" %d",p[i]);
JS(d,j,n,p);
getch();
}
OUTPUT
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-28-320.jpg)
![Q13. Write a program to place the queen on a square chessboard using
Backtracking approach.
# include <stdio.h>
# include <stdlib.h>
# include <time.h>
int N; //For N * N ChessBoard
int flag;
void printArray(int a[]); /* Just to Print the Final Solution */
void getPositions(int a[],int n1,int n2); /* The Recursive Function */
int main()
{int *a;
int ctr=0;
printf("nTHE N QUEENS PROBLEM ");
printf("nNumber Of Rows(N) For NxN Chessboard.");
scanf("%d",&N);
a=(int *)(malloc(sizeof(int)*N));
printf("nAll possible Solutions .. n");
printf("nIn Each of the solutions the Coordinates of the N-Queens are given
(Row,Col) .");
printf("nNote that the Rows and Colums are numbered between 1 - N :n");
for(ctr=0;ctr<N;ctr++)
getPositions(a,0,ctr);
getchar();
getchar();
}
void printArray(int a[])
{
int i,choice;
static int counter=0;
counter++;
printf("nSOLUTION # %d :",counter);
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
printf("(%d,%d) ",i+1,a[i]+1);
if(counter%10==0) { printf("nEnter 0 to exit , 1 to continue .");
scanf("%d",&choice);
if(choice==0) exit(0);
};
}
void getPositions(int a1[],int colno,int val)
{ int ctr1,ctr2;
a1[colno]=val;
if(colno==N-1)
{ printArray(a1) ; return;
};
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-29-320.jpg)
![for(ctr1=0;ctr1<N;)
{ /* This Loop Finds Suitable Column Numbers , in the NEXT ROW */
for(ctr2=0;ctr2<=colno;ctr2++)
if(a1[ctr2]==ctr1 || (colno+1-ctr2)*(colno+1-ctr2)==(ctr1-a1[ctr2])*(ctr1-a1[ctr2]))
goto miss1;
getPositions(a1,colno+1,ctr1);
miss1:
ctr1++;
}
}
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-30-320.jpg)
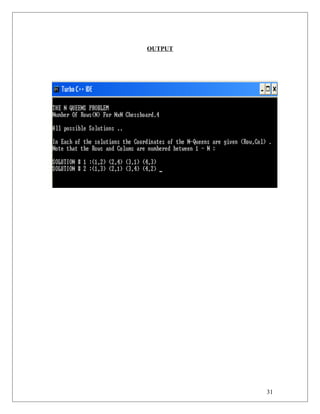
![Q14. Write the program to solve Graph Coloring problem using Backtracking
approach.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void colournext(int k,int colour[],int n,int m,int edge[20][20])
{
int flag=0,j;
do
{
flag=0;
colour[k]=(colour[k]+1)%(m+1);
if(colour[k]==0)
return;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if((edge[k][j]==1) && (colour[k]==colour[j]))
flag=1;
}
}while(flag==1);
}
void main()
{
int i,t,j,h,n,m,k,maxclique=0;
int edge[20][20];
int colour[20];
printf("n Enter the no. of vertices in the graph : ");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
colour[i]=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
edge[i][j]=0;
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
t=0;
printf("n Enter number of adjacent nodes from node %d : ",i);
scanf("%d",&t);
if(t>maxclique)
maxclique=t;
printf("n Enter those adjacent nodes : ");
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-32-320.jpg)
![for(j=0;j<t;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&h);
edge[i][h]=1;
}
}
m=maxclique;
k=0;
do
{
colournext(k,colour,n,m,edge);
if(colour[k]==0)
{k--;colour[k]=colour[k+1]%(m+1);}
else
k++;
}
while( k<n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("tnode : %d tcolor no. : %d",i,colour[i]);
printf("n");
}
}
OUTPUT
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-33-320.jpg)
![Q15. Write a program of disjoint set union.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int nlist,a[10],b[10],i,j,k,l,m;
printf("Enter total no of elements including all the listn");
scanf("%d",&j);
for(i=0;i<j;i++)
{
printf("Enter elementn");
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
printf("nEnter element's parentn");
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
}
printf("Elements are:n");
for(i=0;i<j;i++)
{
printf("%dt",a[i]);
}
printf("nparents are:n");
for(i=0;i<j;i++)
{
printf("%dt",b[i]);
}
printf("nPlease enter the set's element you want to joinn");
scanf("%d %d",&k,&l);
for(i=0;i<j;i++)
{
if((a[i]==l) && (b[i]==-1))
{
b[i]=k;
}
else if((a[i]==l) && (b[i]!=-1))
{
m=b[i];
for(i=0;i<j;i++)
{
if((a[i]==m) && (b[i]==-1))
{
b[i]=k;
}
}
}
}
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-34-320.jpg)
![printf("nnElements are:n");
for(i=0;i<j;i++)
{
printf("%dt",a[i]);
}
printf("nparents are:n");
for(i=0;i<j;i++)
{
printf("%dt",b[i]);
}
getch();
return 0;
}
OUTPUT
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adafile-140507040852-phpapp01/85/Ada-file-35-320.jpg)