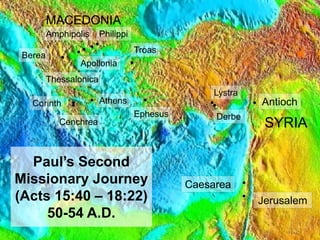
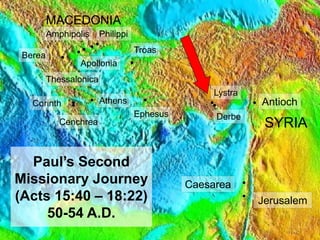
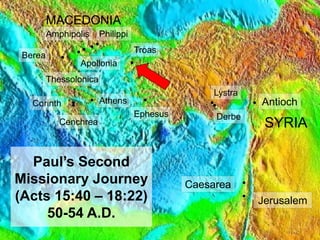
1) Paul and Silas travel to Lystra where they meet Timothy. Paul has Timothy circumcised so he can help preach to Jews.
2) In Troas, Paul has a vision of a man from Macedonia asking for help. They go to Philippi in Macedonia.
3) In Philippi, Paul preaches to Lydia who becomes the first Christian convert in Macedonia after her household is baptized.
4) Paul casts a demon out of a slave girl, angering her masters. He and Silas are arrested, beaten, and imprisoned.