The document defines and provides brief descriptions of common digital technologies and online platforms:
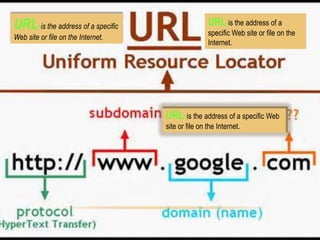
Email allows digital messages to be exchanged between users. Wikis enable collaborative editing of content. Social bookmarking allows users to bookmark and share web documents. HTML is the language used to create web pages. Podcasts are downloadable audio or video files. VoIP converts analog signals to digital for phone calls over the internet. Online chat provides real-time text messaging. The World Wide Web consists of hyperlinked documents on the internet. Streaming delivers multimedia continuously as it is received. Blogs are websites with periodic posts displayed in reverse chronological order. URLs specify the location of websites and files. Web feeds provide frequently updated content for users to subscribe to.