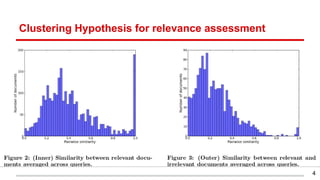
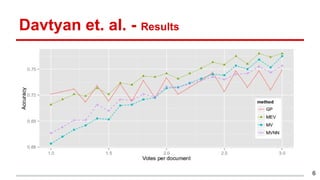
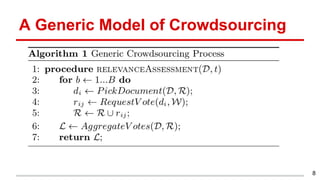
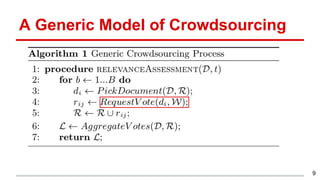
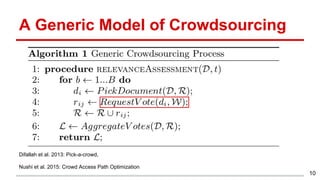
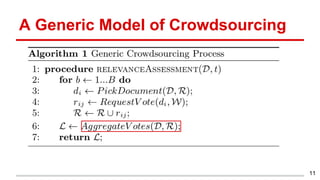
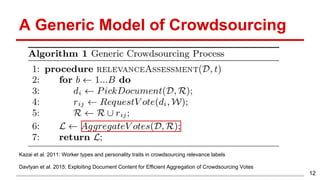
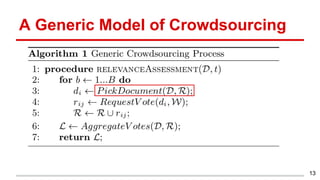
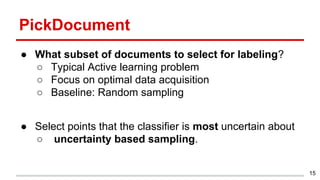
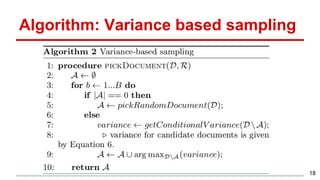
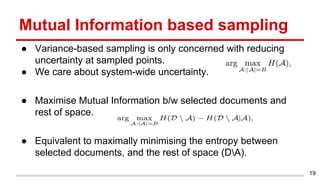
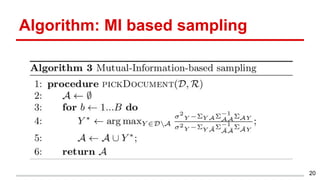
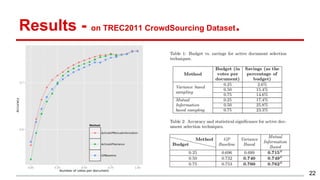
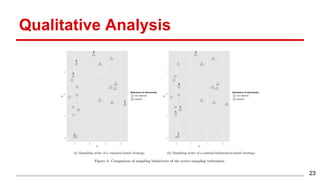
This document discusses methods for active content-based task selection in crowdsourcing, focusing on optimizing relevance assessments under budget constraints using information-theoretic approaches. It presents algorithms for variance-based and mutual information-based sampling to improve the efficiency and quality of relevance votes, demonstrating significant budget savings. Experiments conducted on the TREC crowdsourcing dataset illustrate the proposed methods' effectiveness and efficiency, leading to potential applications in other fields.